Mobile robot positioning method based on visual guidance laser repositioning
A technology of mobile robot and positioning method, which is applied in the directions of instruments, electromagnetic wave re-radiation and utilization of re-radiation, etc. It can solve the problems of difficult error recovery, difficult initialization, easy loss of positioning, etc., and achieves stable and reliable positioning, rich positioning information, and positioning stable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. This embodiment is carried out on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation and specific operation process are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
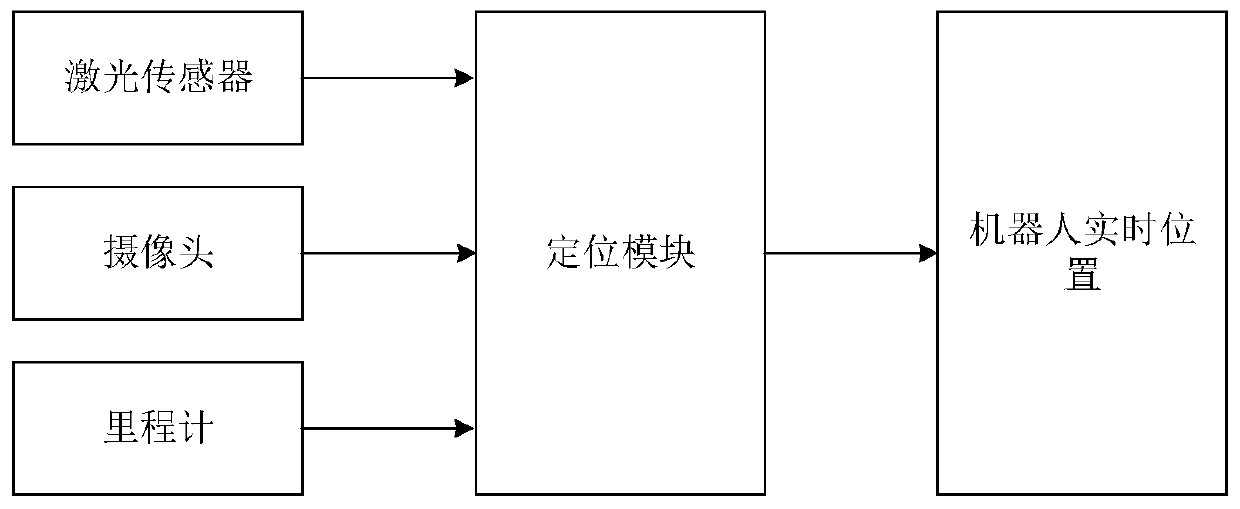
[0050] like figure 1 As shown, the positioning system adopted by the robot in this embodiment includes a laser sensor, a camera, and an odometer, and a positioning module respectively connected to the laser sensor, the camera, and the odometer. The mobile robot positioning method based on vision-guided laser relocation is implemented in the positioning module to output the position of the robot in real time.
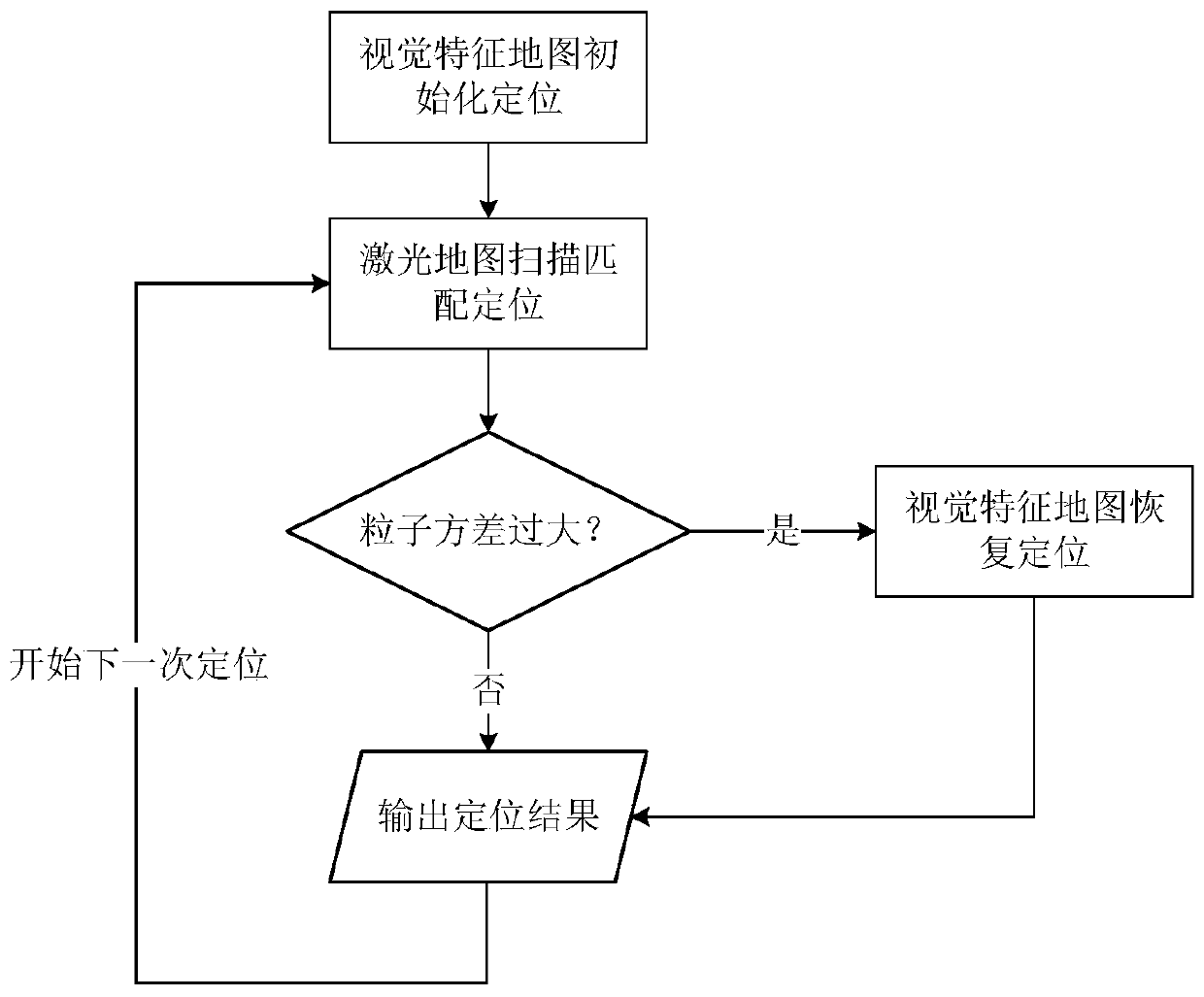
[0051] like Figure 5As shown, the robot is equipped with a camera, lidar and wheel odometry. Define the world coordinate system as the coordinate system used when building l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com