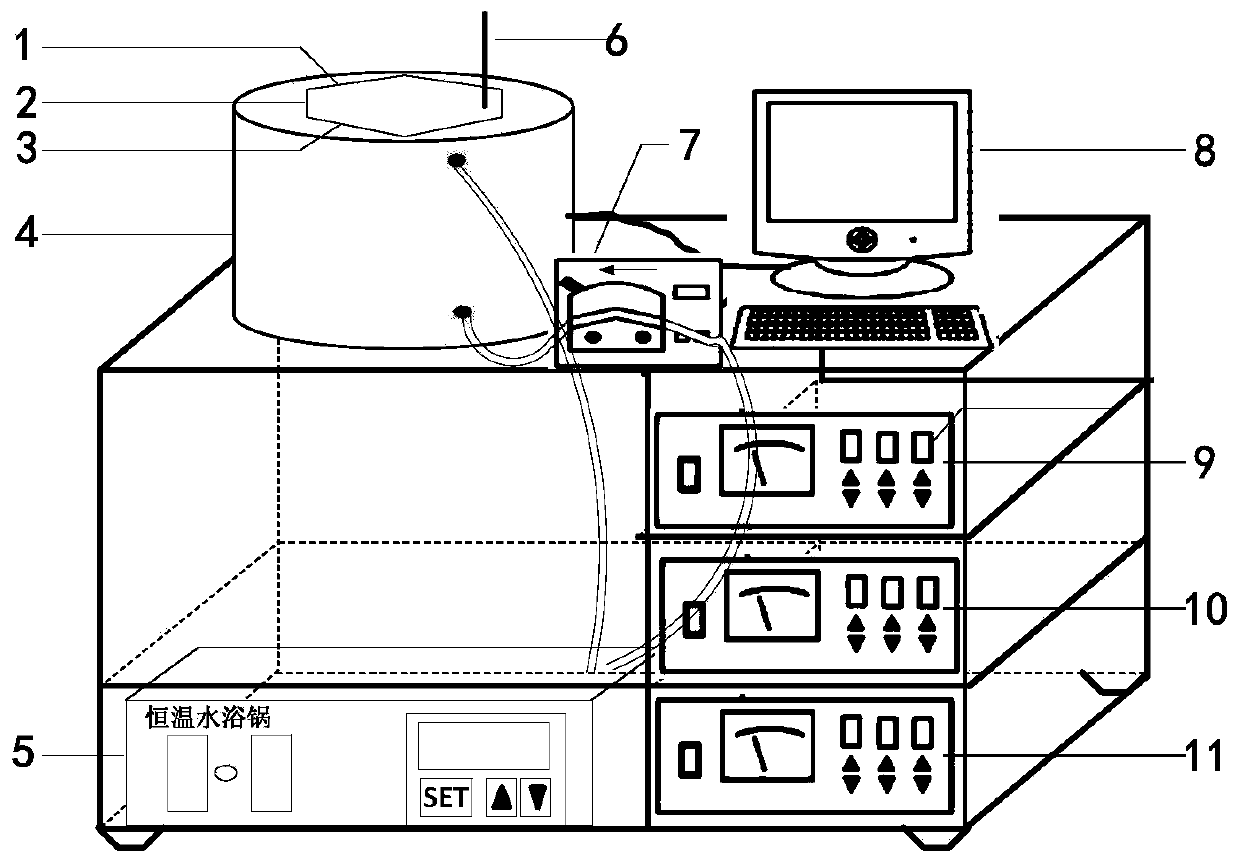
Ultrasonic wave synergetic biological enzyme preparation method for nelumbo nucifera gaertn resistant starch
A technology of resistant starch and ultrasound is applied in the field of deep processing of lotus root to achieve the effect of increasing added value and good food processing characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: The effect of the amount of pullulanase added on the preparation of lotus root resistant starch by pullulan enzyme method
[0036] (1) Accurately weigh 2 g of lotus root starch into a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask to obtain a starch suspension (4%, m / m), and place it in an autoclave for high temperature treatment at 121° C. for 20 min.
[0037] (2) Place it in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C, adjust the pH value with 0.05mol / L HCl solution, add pullulanase, and perform debranching treatment for 20 hours under the condition of a water bath at 50°C, with an addition amount of 9 npun / g (starch) .
[0038] (3) Cool to room temperature, then pour the sample into a petri dish, age at 4°C for 24 hours, freeze-dry for 48 hours, grind, package, and store in a desiccator. According to the national standard NY-T 2638-2014, the content of resistant starch in lotus root was determined to be 11.21%.
[0039] It shows that the amount of pullulanase added is 9 npun / g (...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: The effect of the amount of pullulanase added on the preparation of lotus root resistant starch by pullulan enzyme method
[0041] (1) Accurately weigh 2 g of lotus root starch into a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask to obtain a starch suspension (4%, m / m), and place it in an autoclave for high temperature treatment at 121° C. for 20 min.
[0042] (2) Place it in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C, adjust the pH value with 0.05mol / L HCl solution, add pullulanase, and perform debranching treatment for 20 hours under the condition of a water bath at 50°C, with an addition amount of 9 npun / g (starch) and 45npun / g (starch).
[0043] (3) Cool to room temperature, then pour the sample into a petri dish, age at 4°C for 24 hours, freeze-dry for 48 hours, grind, package, and store in a desiccator. According to the national standard NY-T 2638-2014, the content of resistant starch in lotus root was determined to be 17.01%.
[0044] When the amount of pullulanase was 45n...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Effect of Enzymolysis Time on Preparation of Lotus Root Resistant Starch by Pullulan Enzyme Method
[0046] (1) Accurately weigh 2 g of lotus root starch into a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask to obtain a starch suspension (4%, m / m), and place it in an autoclave for high temperature treatment at 121° C. for 20 min.
[0047] (2) Place it in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C, adjust the pH value with 0.05mol / L HCl solution, add 27 npun / g (starch) of pullulanase, perform debranching treatment under the condition of 50°C water bath, enzymolysis Time 6h.
[0048] (3) Cool to room temperature, then pour the sample into a petri dish, age at 4°C for 24 hours, freeze-dry for 48 hours, grind, package, and store in a desiccator. According to the national standard NY-T 2638-2014, the content of resistant starch in lotus root was determined to be 11.51%. Compared with lotus root starch, there is basically no significant difference.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com