Biochar-bioelectrochemistry coupled soil remediation system and method
A bioelectrochemical and soil remediation technology, applied in the field of soil in-situ remediation, can solve the problems of hindering the degradation of pollutants and large internal resistance, and achieve the effects of shortening the degradation cycle, low equipment cost, and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
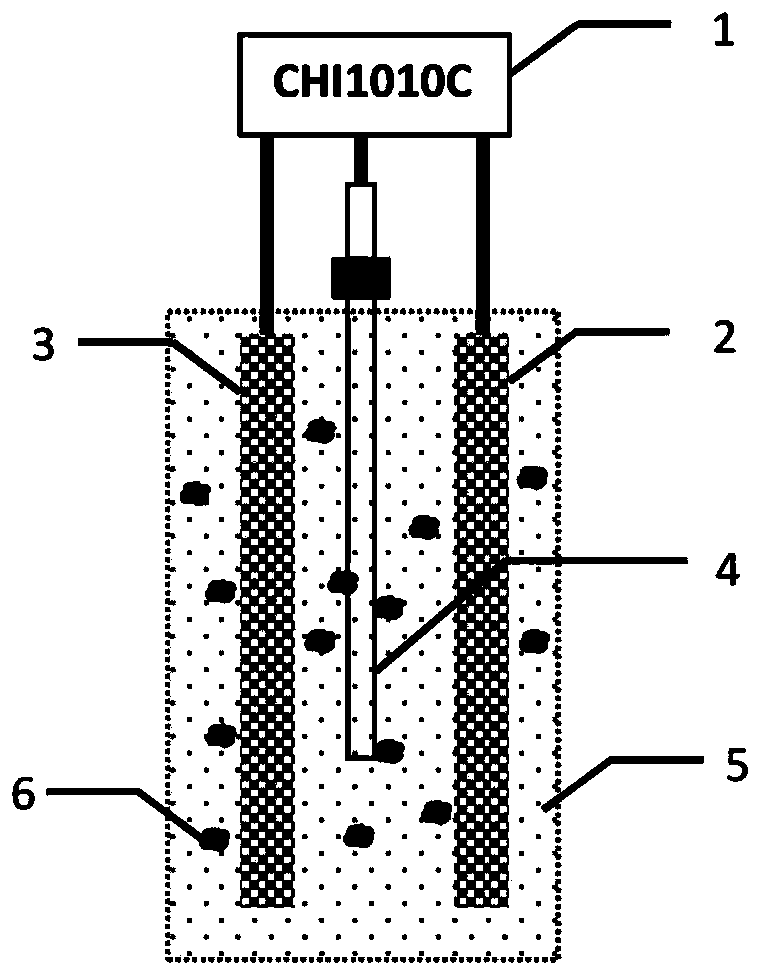
[0040] A biochar-coupled bioelectrochemical soil remediation system includes a bioelectrochemical reactor and biochar 6 for mixing with the soil to be remediated. The bioelectrochemical reactor includes a reaction vessel for holding the soil to be repaired 5, an electrode for inserting the soil to be repaired 5, and an electrochemical workstation 1; the electrodes include a working electrode 2, an auxiliary electrode 3 and a reference electrode 4, and the working electrode 2. The auxiliary electrode 3 and the reference electrode 4 are electrically connected to the electrochemical workstation 1 .
[0041] Specifically, the structure of the soil restoration system of the present embodiment, and the soil restoration method are as follows:
[0042] 1) Design of bioelectrochemical reactor:
[0043] Use a square simulated reactor: use a rectangular polypropylene container of 30×5×5cm (length×width×height), fill it with PCP-contaminated soil with a total volume of 200mL, and distrib...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Compared with Example 1, the difference is that the pyrolysis temperature of biochar in this example is 600°C, and the obtained biochar is named BC600; 4) In the proportion of contaminated soil and biochar and operating parameters, 0%, 1 %, 6% (mass fraction) of BC600 were mixed with the soil respectively, and the above treatments were abbreviated as SBES, SBES-BC600 (1%), and SBES-BC600 (6%). Cultivate at room temperature (25-28°C);
[0053] Other raw materials and steps are identical with embodiment 1.
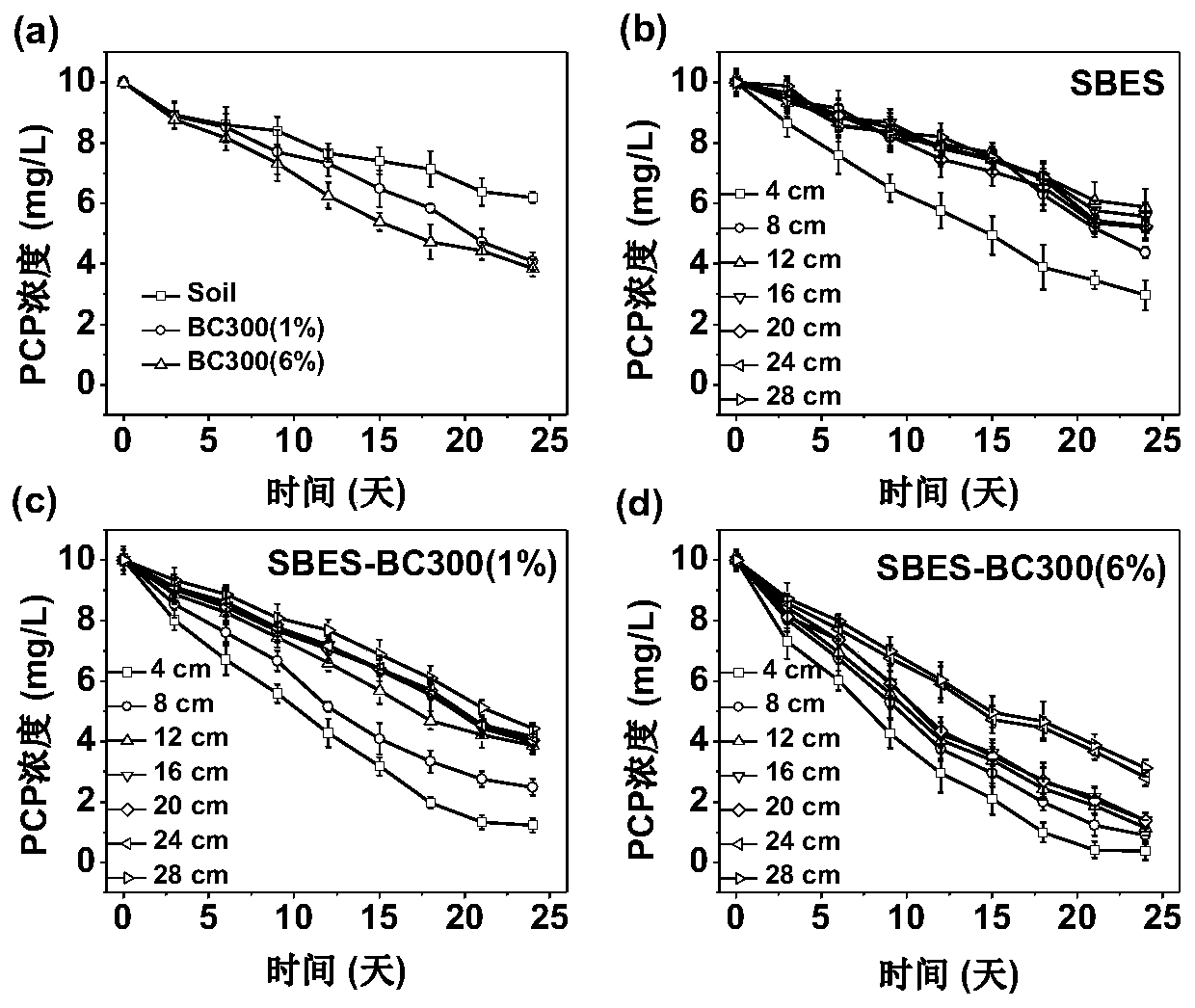
[0054] Experimental results such as Figure 4 as shown, Figure 4 (b) is the degradation situation of different positions (4-28cm) away from the cathode in the SBES treatment; Figure 4 (c) SBES-BC600 (1%) degrades from different positions (4 to 28 cm) away from the cathode in the treatment; Figure 4 (d) is the degradation of different positions (4-28cm) from the cathode during the treatment of SBES-BC600 (6%).
Embodiment 3
[0056] Compared with Example 1, the difference is that the pyrolysis temperature of biochar in this example is 900°C, and the obtained biochar is named BC900; 4) In the ratio of contaminated soil to biochar and operating parameters, 0%, 1 %, 6% (mass fraction) of BC900 were mixed with the soil respectively, and the above treatments were abbreviated as SBES, SBES-BC900 (1%), SBES-BC900 (6%), and each treatment was set in three parallels, and placed in the dark Cultivate at room temperature (25-28°C);
[0057] Other raw materials and steps are identical with embodiment 1.
[0058] Experimental results such as Figure 5 as shown, Figure 5 (b) is the degradation situation of different positions (4-28cm) away from the cathode in the SBES treatment; Figure 5 (c) SBES-BC900 (1%) degrades from different positions (4 to 28 cm) away from the cathode in the treatment; Figure 5 (d) is the degradation of SBES-BC900 (6%) at different positions (4-28cm) away from the cathode during th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com