Key negotiation method, device and equipment
A technology of key negotiation and encryption algorithm, applied in the field of key negotiation, which can solve the problems of poor security, long negotiation time between communication parties, and complex key calculation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
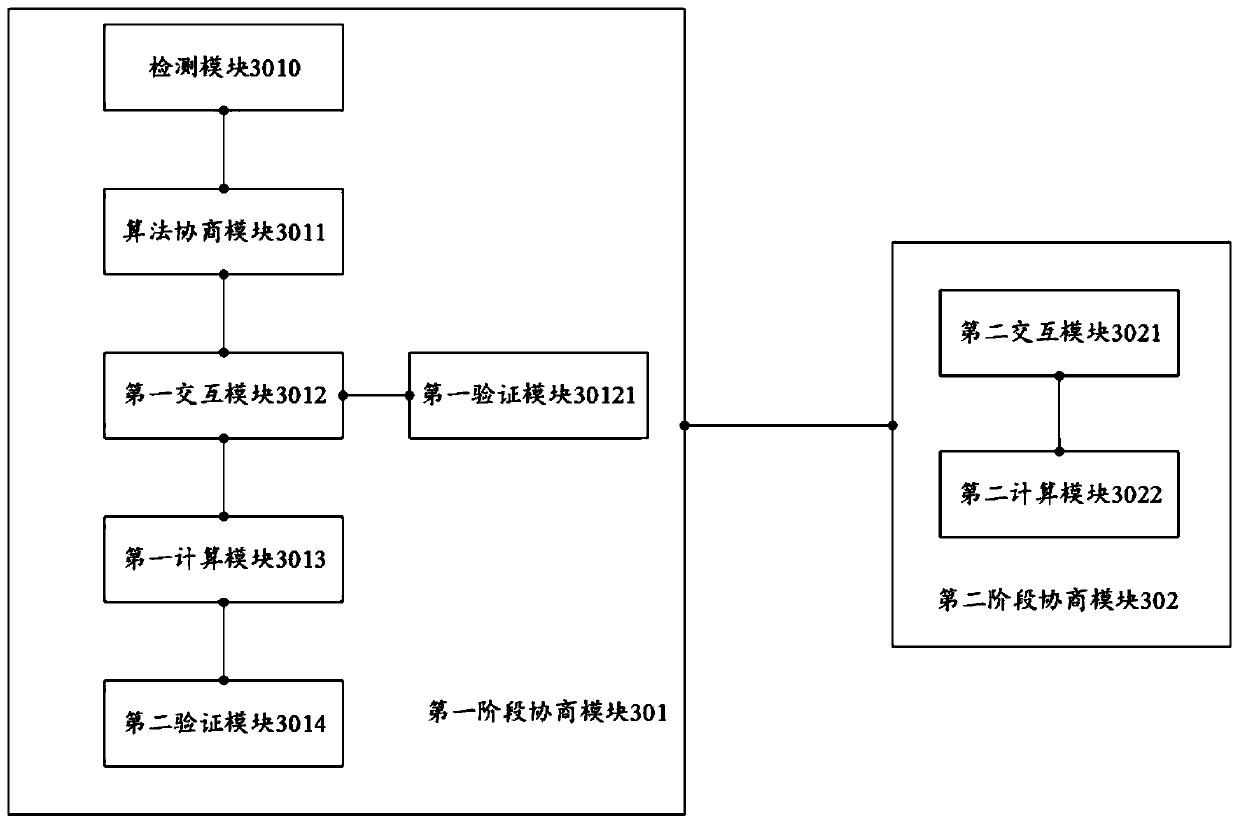
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
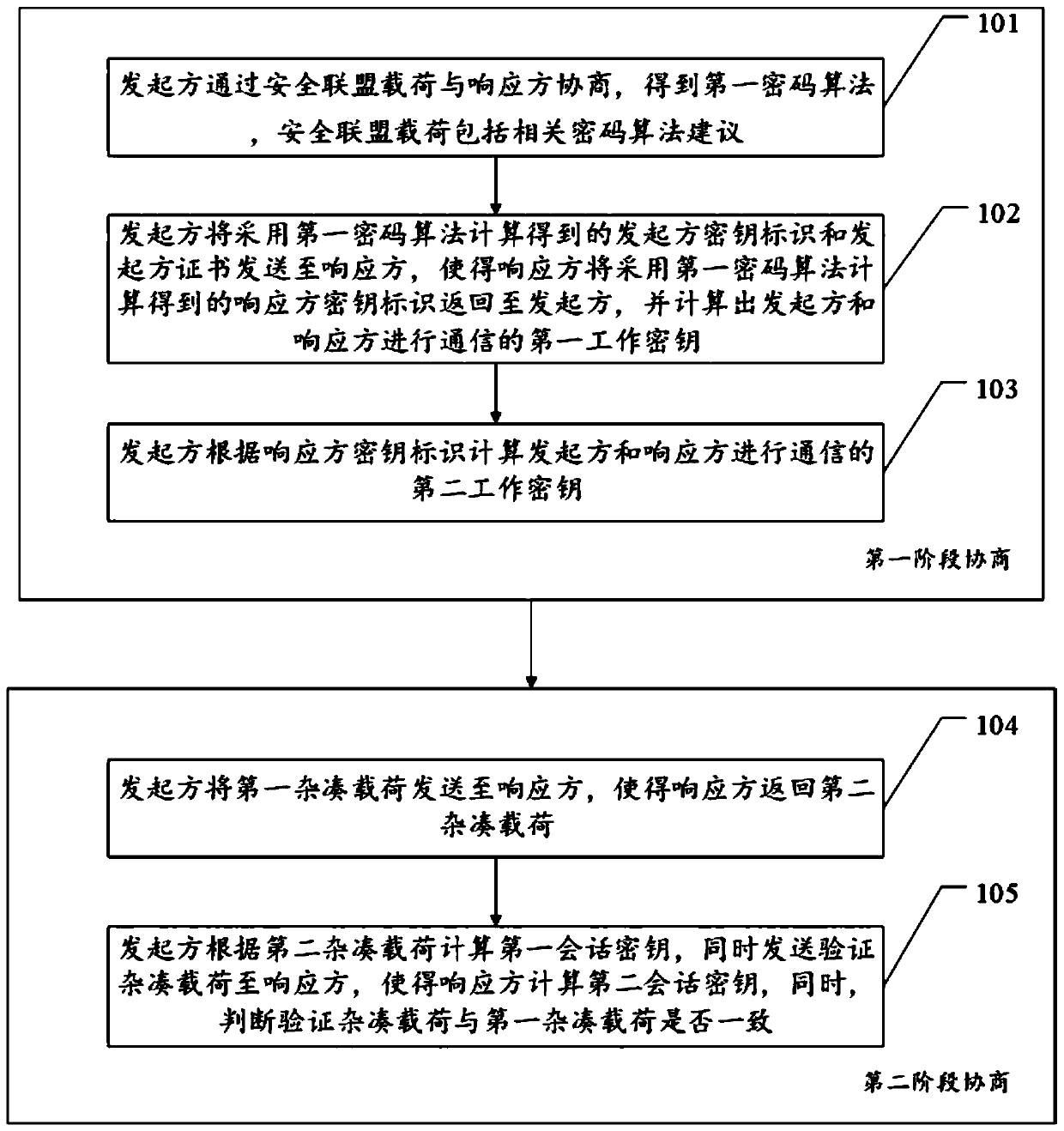
[0047] For ease of understanding, see figure 1 , Embodiment 1 of a key agreement method provided by this application includes: first-stage negotiation and second-stage negotiation.
[0048] Phase 1 negotiations include:
[0049] Step 101, the initiator negotiates with the responder through the security association payload to obtain the first cryptographic algorithm, and the security association payload includes relevant cryptographic algorithm suggestions.
[0050] It should be noted that the cryptographic algorithm may include at least one of the following: asymmetric cryptographic algorithm SM2, symmetric cryptographic algorithm SM1, cryptographic hash algorithm SM3, and a randomly generated temporary password; the initiator encapsulates the proposal of the cryptographic algorithm into a security association payload and sends it To the responding party, the responding party will reply a response security association payload, which includes accepting the cryptographic algori...
Embodiment 2
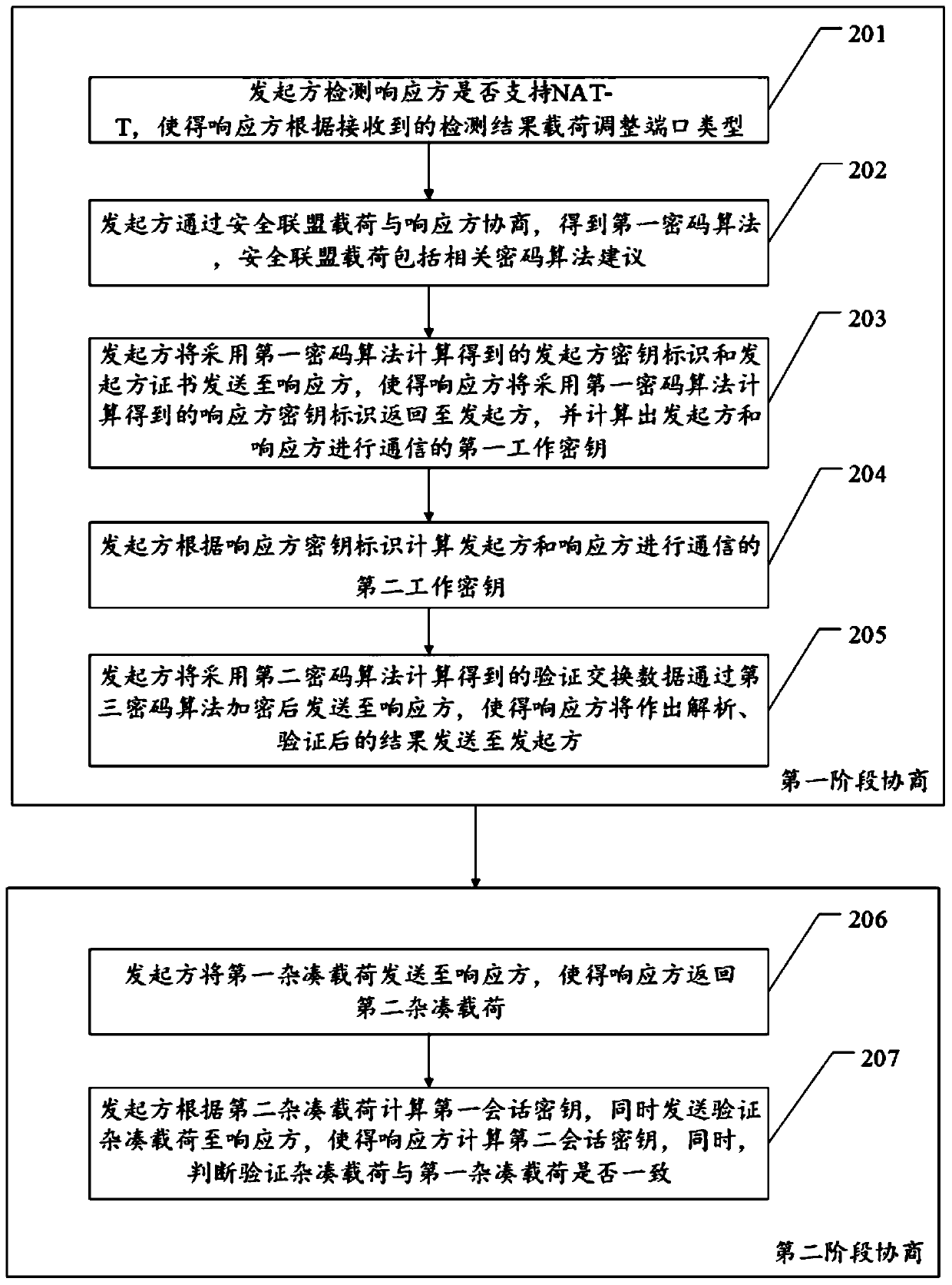
[0063] For ease of understanding, see figure 2 , the embodiment of this application provides a second embodiment of a key agreement method, including: a first-stage negotiation and a second-stage negotiation.
[0064] Phase 1 negotiations include:
[0065] Step 201, the initiator detects whether the responder supports NAT-T, so that the responder adjusts the port type according to the received detection result.
[0066] It should be noted that the detection of whether the other party supports NAT-T can be realized by exchanging the vendor ID payload. If it supports NAT-T, the NAT_D payload must be sent in the first stage of key negotiation. The responder receives this packet and decrypts it and passes the authentication. Finally, the original state of processing port 500 should be changed to port 4500. The subsequent negotiation process will be carried out using port 4500. Afterwards, all packets received by port 500 that are not newly negotiated will be discarded; the remai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com