Methods for remediating contaminated soil and groundwater
A technology for polluted soil and groundwater, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc. The effect of natural degradation, shortened repair time, and low operating cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
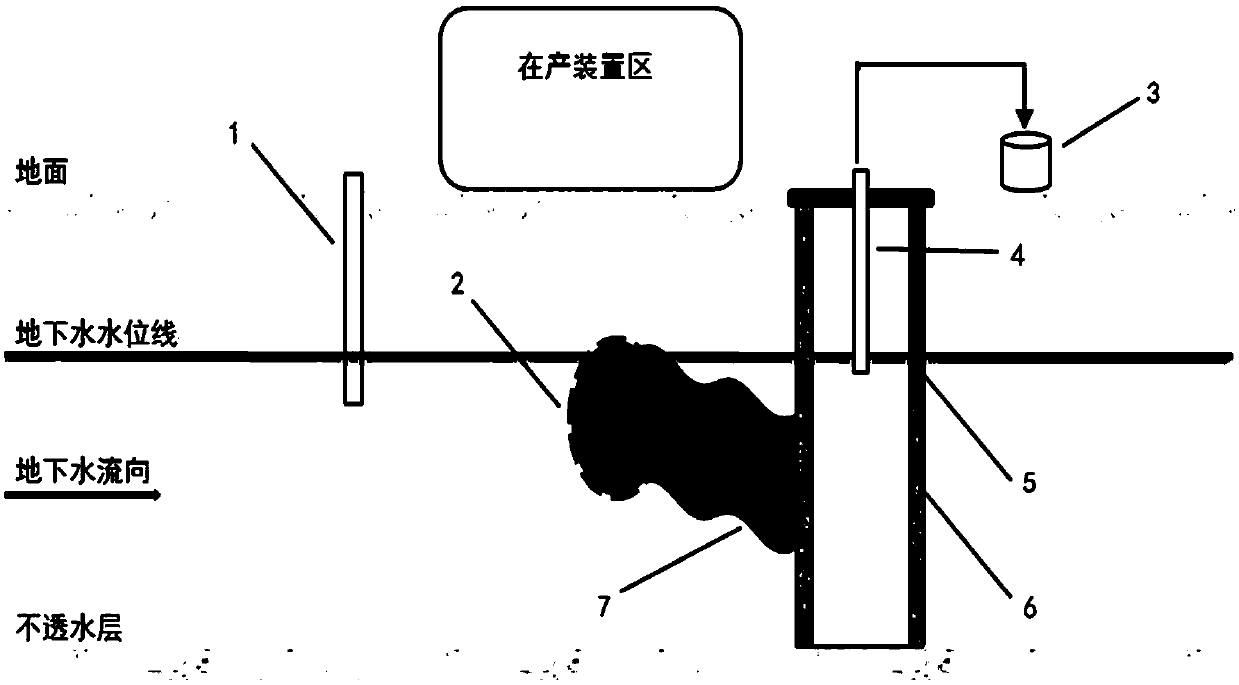
[0020] In the present invention, the injection well is built upstream of the groundwater in the polluted area, and is used to inject the biosurfactant slurry into the groundwater, so that the biosurfactant migrates into the polluted area along with the groundwater. When constructing the injection well, the depth of the well should be dug below the groundwater level. The present invention has no special limitation on the specific construction method and specification of the injection well, which can be selected with reference to the prior art. According to one embodiment, the diameter of the injection well is 5-10 cm.
[0021] In the present invention, the pollutants in the polluted area comprise volatile and / semi-volatile organic compounds. Specific examples of the pollutants include, but are not limited to, one or more of diesel, gasoline, benzene, toluene, di-n-octyl phthalate, and benzo(a)pyrene.
[0022] Preferably, the biosurfactant is selected from at least one of rham...
Embodiment 1
[0041] Diesel leakage from a buried pipeline at a gas station caused pollution. Before this method was implemented, the total petroleum hydrocarbon (C10-C40) content in the soil in the polluted area was 17439 mg / kg, which exceeded the screening value for the second-class land use in GB36600-2018 4500mg / kg, the benzene content of groundwater is 402μg / L, exceeding the conventional index limit of 120μg / L for Class IV water in GB / T14848-2017. The total petroleum hydrocarbon (C10-C40) content in the soil at the collection ditch was 5591 mg / kg, and the benzene content in the groundwater was 57.1 μg / L.
[0042] Build an injection well upstream of the groundwater in the polluted area. The diameter of the injection well is 5cm. Build a collection ditch downstream of the groundwater in the polluted area. The width of the formed collection ditch is 1m, and the length is longer than the scope of the pre-repaired pollution plume. The depth is dug to the impermeable layer , one side of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The ground pipeline buried in a sewage pool leaked, causing the sewage containing dioctyl phthalate to seep into the ground. Before implementing this method, in the polluted area, the content of dioctyl phthalate in the soil was 5617mg / kg. Exceeding the screening value of 2812mg / kg for Class II land use specified in GB36600-2018, the content of dioctyl phthalate in groundwater is 554μg / L, exceeding the unconventional index limit of 300μg / L for Class IV water in GB / T14848-2017 L. The content of di-n-octyl phthalate in the soil at the collection ditch was 4124 mg / kg, and the content of di-n-octyl phthalate in the groundwater was 472 μg / L.
[0047] Build an injection well upstream of the groundwater in the polluted area. The diameter of the injection well is 10cm. Build a collection ditch downstream of the groundwater in the polluted area. The width of the formed collection ditch is 1.2m, the length is longer than the scope of the pre-repaired pollution plume, and the dept...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com