Method for qualitatively judging water filling condition of karst cave in front of tunnel based on diffracted transverse waves
A technology of shear wave and diffraction, which is applied in the field of qualitatively judging the water filling situation of the cave in front of the tunnel based on the diffraction shear wave, which can solve the problems that the diffraction shear wave cannot be extracted, the water filling situation of the cave cannot be detected, and the safe excavation work of the tunnel is affected.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
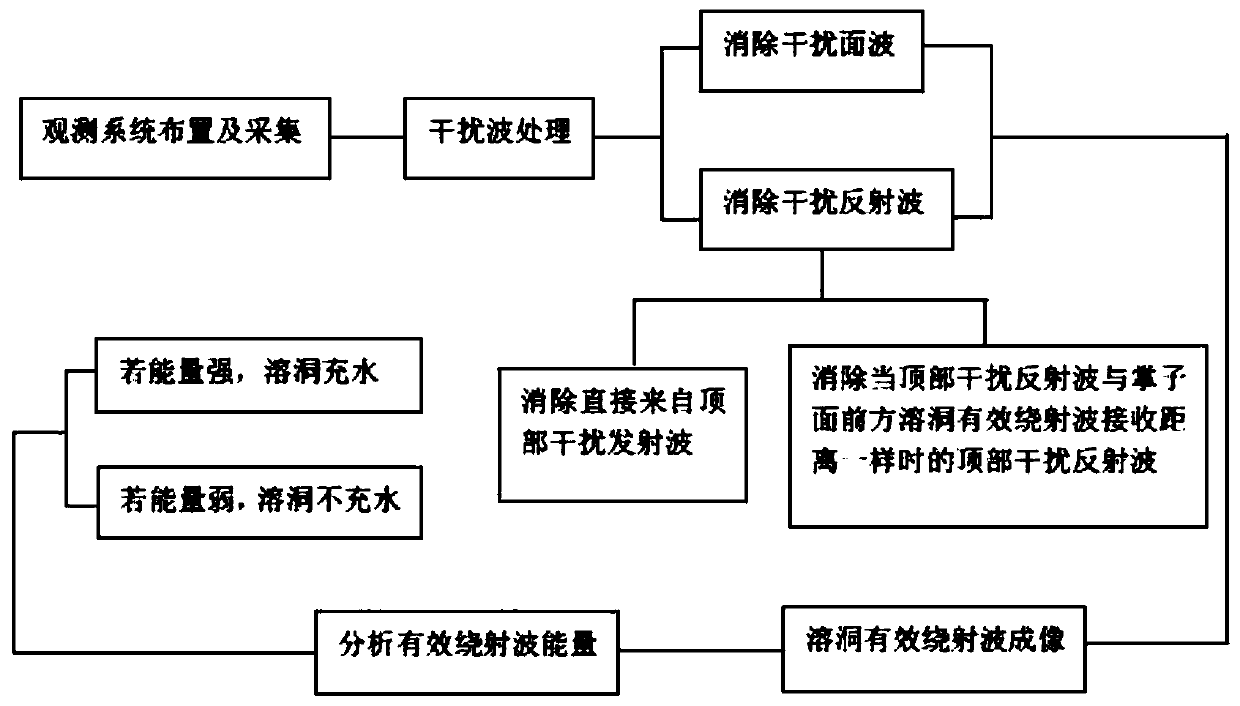
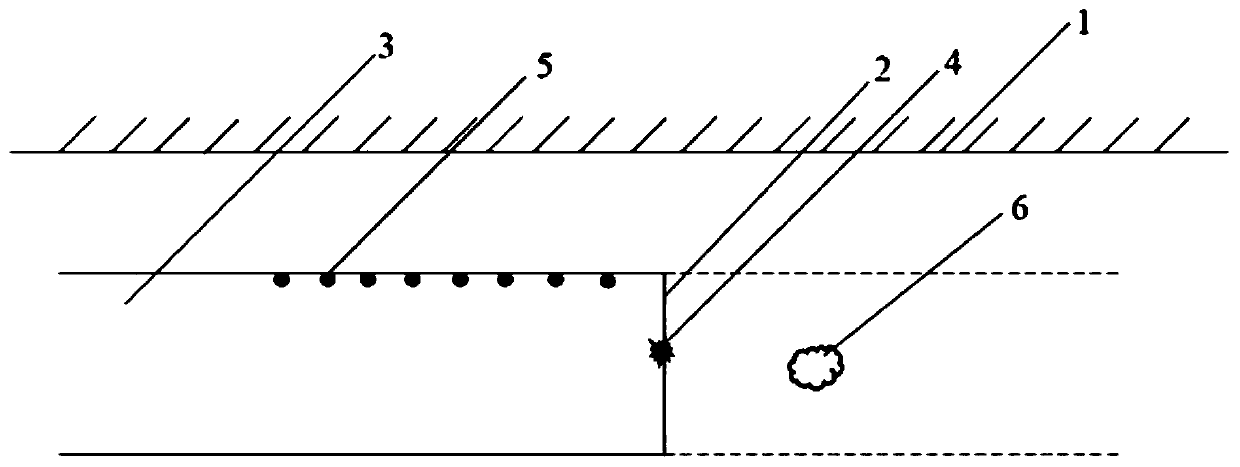
[0028] As shown in the figure, the concrete steps of the present invention are:
[0029] Step 1: Arrange an excitation point 4 on the face 2 of the subway tunnel 3 to excite seismic shear waves; set eight three-component geophones 5 on one side of the tunnel behind the excitation point 4;
[0030] Step 2: Excite seismic shear waves in front of the tunnel face 2 at the excitation point 4, and then each three-component geophone 5 receives the feedback seismic data in real time and transmits them to the seismic recorder;
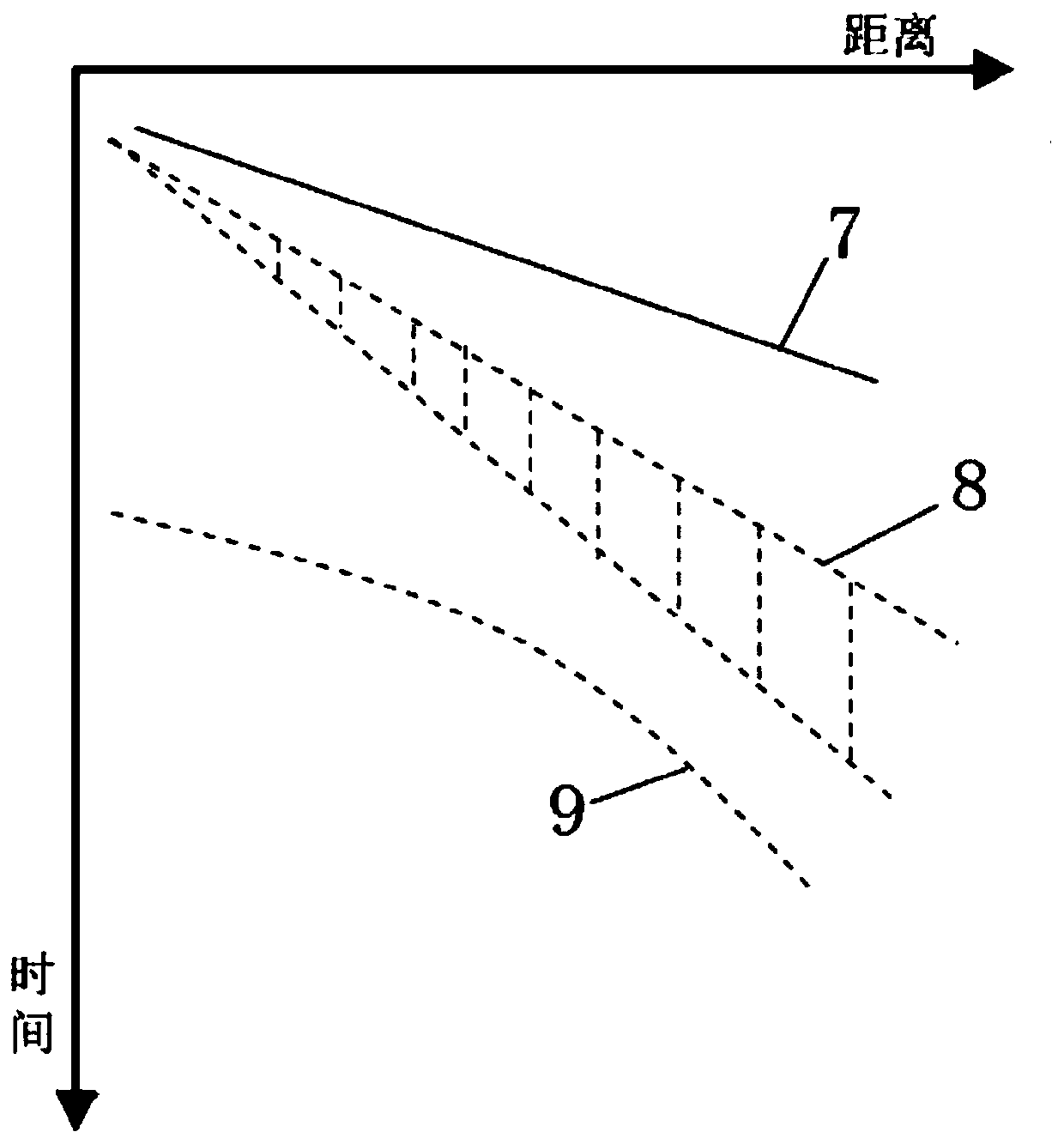
[0031] Step 3: Perform interference wave elimination processing on the seismic data received by the seismic recorder. The interference waves to be eliminated include:
[0032] A, interference surface wave 8, its source is that after exciting the seismic source, each three-component geophone 5 can receive the surface wave from the tunnel face 2 rear, and transmit it to the seismograph;
[0033] B. Interfering reflected waves 9 on the surface of the tunnel top, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com