A CRISPR/Cas9 system and its application for knocking out the DMRT1 gene at double gRNA sites in peltaceae
A yellow catfish and gene technology, applied in the fields of biotechnology and genetic breeding, can solve the problems of high cost, difficult identification, and high uncertainty of DNA self-repair, and achieve the effect of reducing identification cost and high knockout efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Step (1) Target site design:
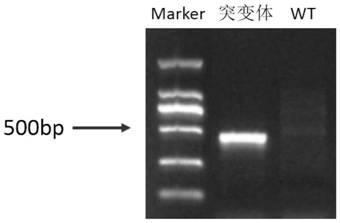
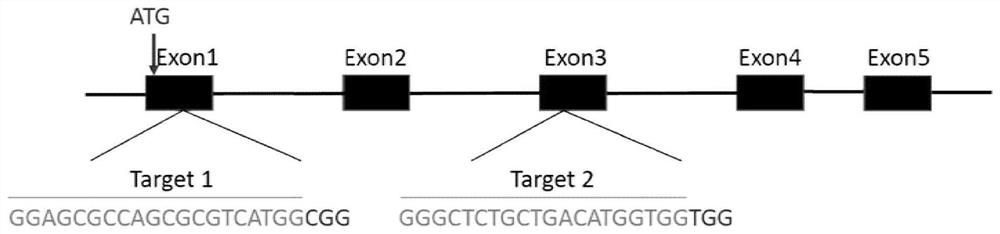
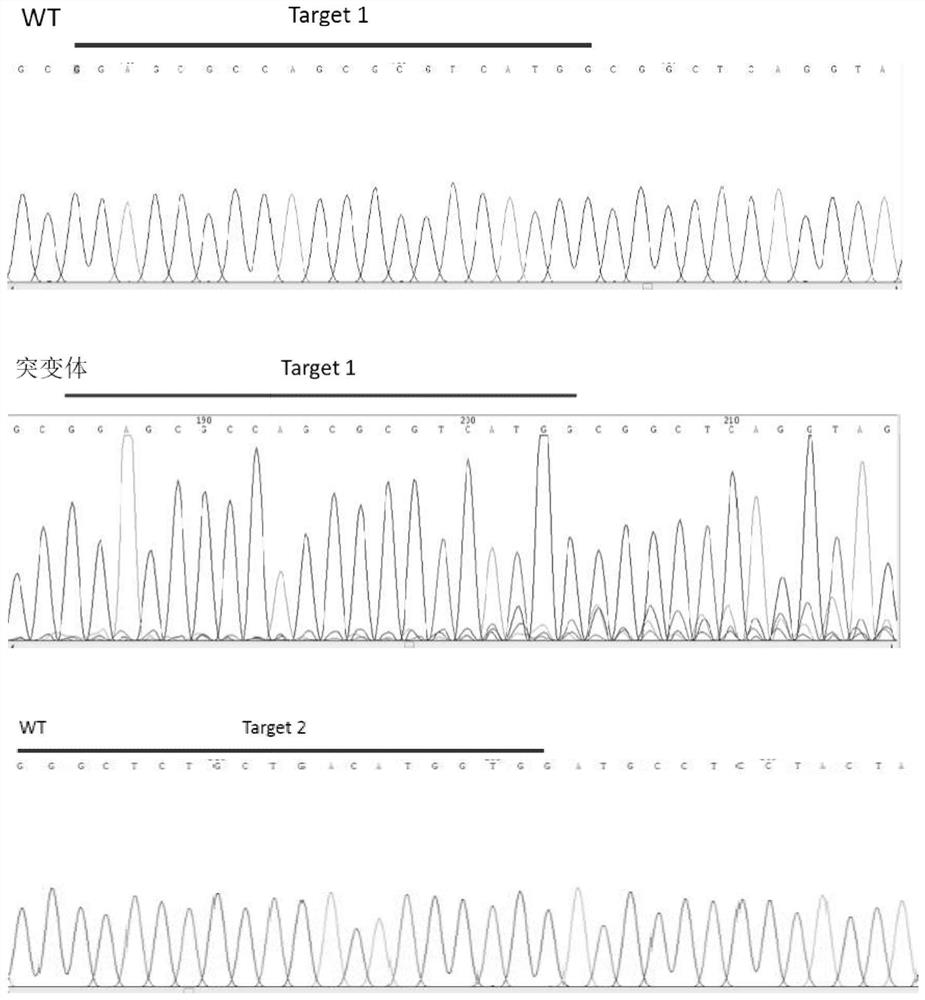
[0037] Query the genomic DNA sequence and mRNA sequence of the dmrt1 gene of the yellow catfish on NCBI. The full length of the dmrt1 gene of the yellow catfish is 18952bp, including 5 exons and 4 introns. Design a target site for the first exon and the third exon respectively, the sequence of the target site is shown in Table 1, and the structure diagram of the target site is shown in figure 1 shown. The target sequence was compared by Blast on the NCBI website to verify the specificity of the target site.
[0038] Target site selection principles:
[0039] A. The target site contains 20 bases, of which the 5' end should be GG. This is because the gRNA used in the present invention is transcribed in vitro using a T7 promoter, and the T7 promoter requires the first two digits of the transcription start site to be GG , and the third place is preferably G or A.
[0040] B. The 3 bases immediately adjacent to the 3' end of the target site...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com