A kind of printing and dyeing wastewater treatment agent and treatment method
A technology for printing and dyeing wastewater and treatment methods, which is applied in the textile industry wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, adsorption water/sewage treatment, etc. It has been greatly improved, and it cannot meet the problems of economic and environmental protection, and achieves excellent flocculation effect, improved adsorption and removal effect, and excellent flocculation effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Preparation of printing and dyeing wastewater treatment agent:
[0050] 1) Preparation of modified nano starch adsorbent:
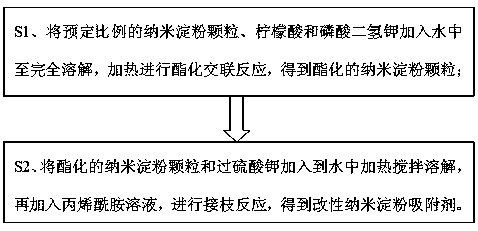
[0051] S1. Add nano-starch granules, citric acid and potassium dihydrogen phosphate according to the ratio of 80% by mass: 11%: 9% to a container filled with deionized water until they are completely dissolved, and put them in an oven at 140°C Carry out the esterification cross-linking reaction under the conditions for 4 hours; use deionized water to wash to neutrality, then filter the solid through a suction filtration instrument, and dry it to obtain esterified nano-starch particles;
[0052] S2. Add the esterified nano-starch granules and potassium persulfate into a container filled with deionized water, heat to 80° C. and stir for 0.5 h to prepare a mixed solution, wherein the concentration of potassium persulfate is 0.006 mol / L; Then add 1 mol / L acrylamide solution, stir at 80°C for 4 hours to carry out acrylamide grafting reaction, then cool...
Embodiment 2-5
[0064] The difference from Example 1 lies in that the adjustment settings of the pH value are different, as shown in Table 1, and other steps are the same as in Example 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0065] Table 1 is the adjustment setting of pH value and its adsorption performance parameter measured value in embodiment 1-5 and comparative example 1
[0066]
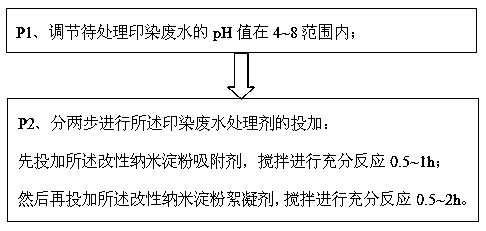
[0067] Please refer to Table 1. As the pH value of printing and dyeing wastewater increases, the adsorption effect of the modified nano-starch adsorbent on methylene blue gradually increases. Methylene blue is a cationic dye with positive charge. In the present invention, the carboxylic acid group (-COOH) on the adsorbent grafted and cross-linked by citric acid has a deprotonation process after the pH increases, and -COOH removes H to form -COO - , which in turn has an excellent adsorption effect on the positively charged methylene blue on the surface. When the pH value gradually increased, the deprotonation of...
Embodiment 6-7
[0076] The difference with Example 1 is: the difference in the preparation process parameters of the modified nano-starch adsorbent, as shown in Table 3, other steps are the same as in Example 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0077] Table 3 is the setting of modified nano starch adsorbent preparation process parameters in embodiment 1 and embodiment 6-7
[0078] Example Nano starch: citric acid: Potassium dihydrogen phosphate Acrylamide potassium persulfate Example 1 80%:11%:9% 1mol / L 0.006mol / L Example 6 85%:8%:7% 2mol / L 0.008mol / L Example 7 75%:14%:11% 0.5mol / L 0.003mol / L
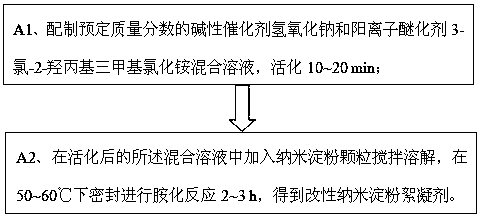
[0079]In the process of preparing the modified nano-starch adsorbent, the mass ratio of nano-starch, citric acid and potassium dihydrogen phosphate, as well as changes in temperature and time will all affect the esterification and cross-linking reaction of nano-starch particles by citric acid. It will have a certain impact, and then affect the number of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com