CRISPR/Cas9 system and method for efficiently producing mutant plants without carrying transgenic elements in plants
A transgenic and plant technology, which is applied in the field of efficiently obtaining edited mutants without transgenic elements, and efficiently obtaining mutants that have undergone multiple editing and without transgenic elements, and can solve the problem of not discussing editing efficiency, editing element removal effect, No clear use, no research on the effects of editing on T2 plants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
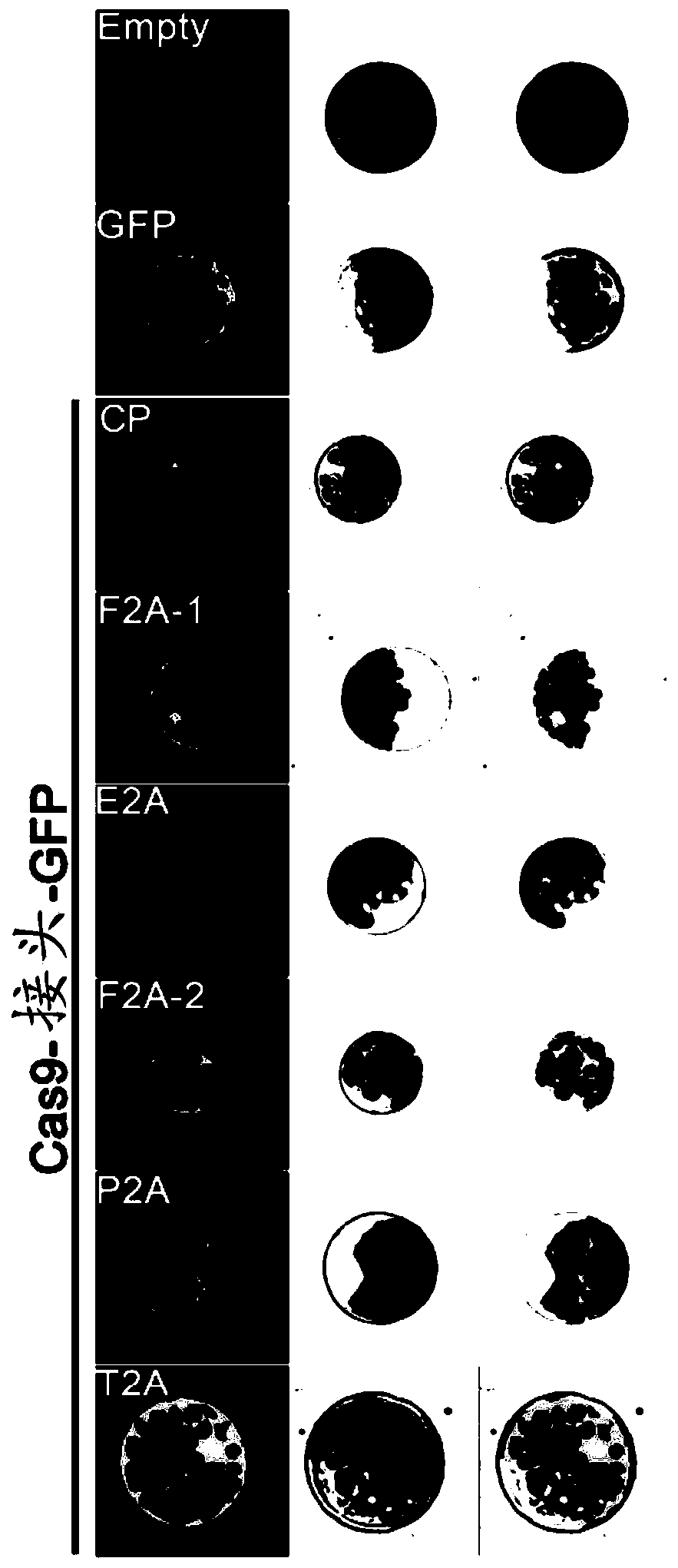
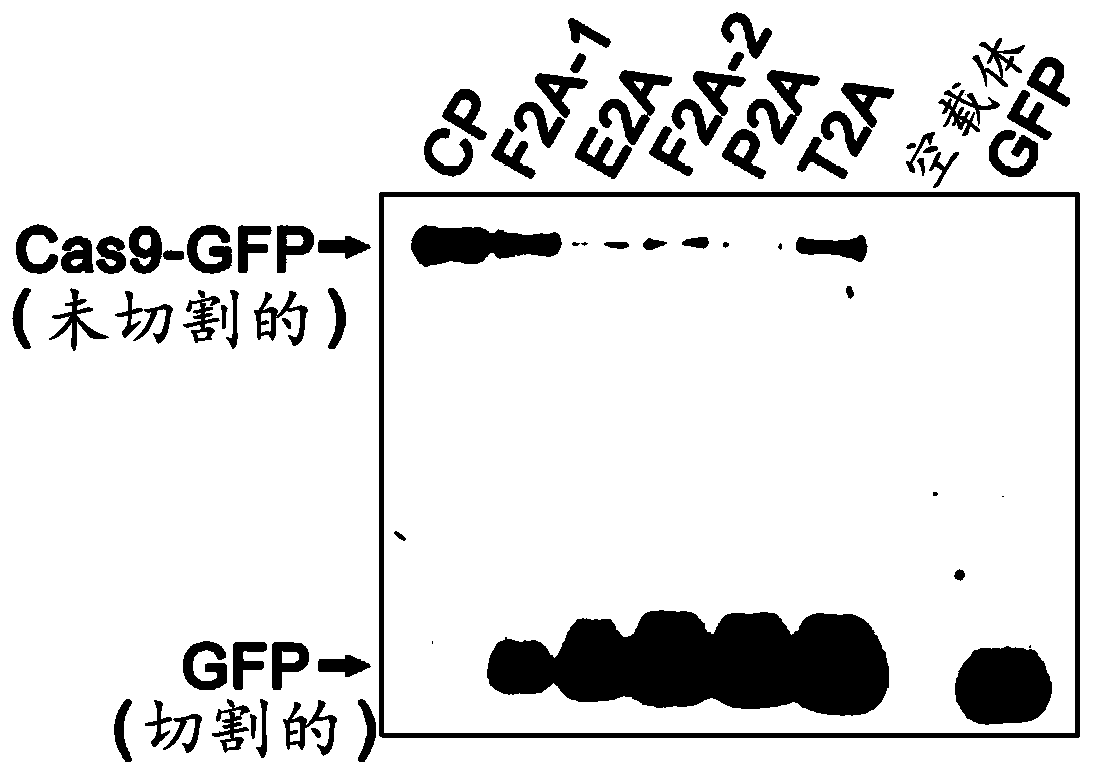
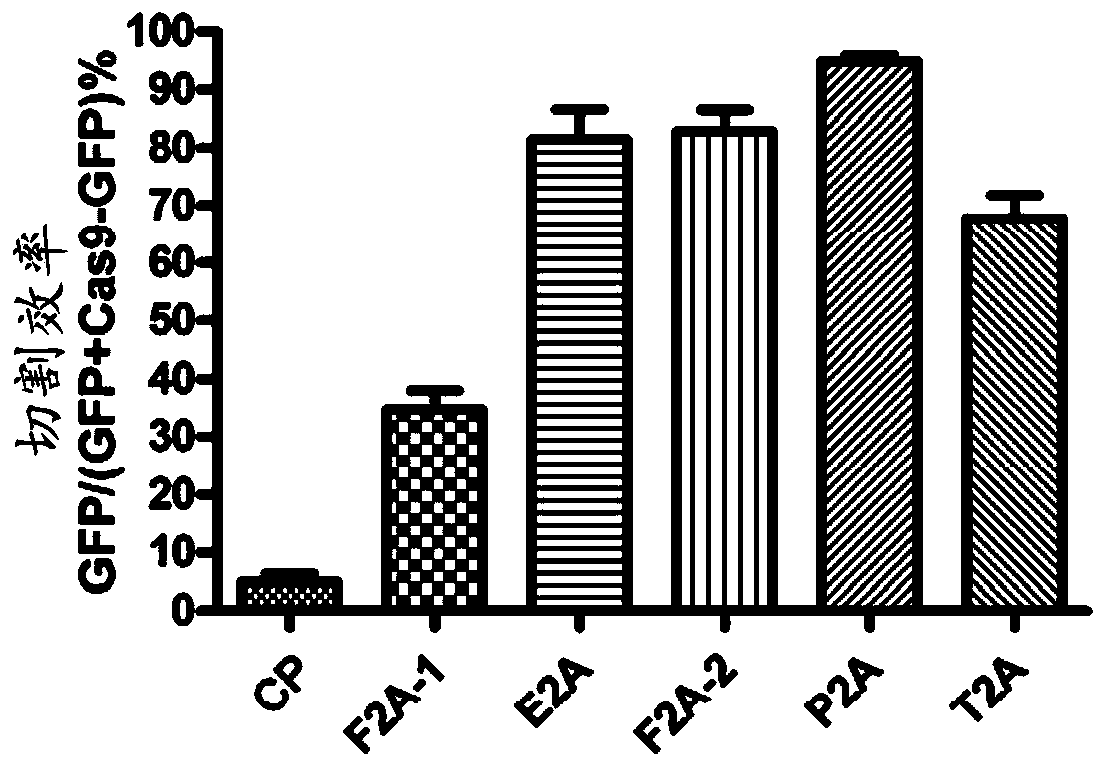
[0065] Example 1. Potency of 2A peptides from different sources
[0066] In order to obtain a CRISPR system capable of visually measuring the abundance of functional Cas9 in plants, the present inventors explored a variety of plant-applicable self-cleaving peptides for linking Cas9 and reporter proteins. Picornavirus-derived 2A peptides were shown to exhibit self-cleavage properties in more than 100 animal cells and tissues (Kim et al., PLoS One 6, e18556, 2011), to test whether 2A peptides could also function in plants To obtain a similar effect, and which 2A peptide has the best effect in plants, five different 2A peptides were tested as follows: Two 2A peptides derived from foot-and-mouth disease virus (F2A-1 and F2A-2, encoding nucleotides) The sequences are respectively SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 4), derived from the 2A peptide (E2A, the coding nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO: 3) of the corona virus, derived from the East Asia virus (Thosea asignavirus) The 2A peptid...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Example 2. Efficacy of different promoters
[0096] The promoter is one of the key factors in the CRISPR system that can affect the editing efficiency. There are some previous studies showing that the Cas9 system regulated by the 35S promoter is inefficient and that the induced somatic mutations cannot be inherited.
[0097] In order to select an efficient promoter to drive Cas9-P2A-GFP and to test whether GFP intensity correlates with gene editing efficiency, the Arabidopsis BRI1 (Brassinosteroid-Insensitive 1) gene was selected as the target gene to study different promoters, including dual CaMV 35S promoter and the Arabidopsis ubiquitin 10 (UBQ10) gene promoter, and tested different vectors, including pJim19 and pCAMBIA1300.
[0098] The BRI1 gene encodes a receptor protein with kinase activity that regulates the signaling cascade of growth and development by binding to brassinosteroid. If the BRI1 gene is edited so that it does not function properly, the edited ...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Example 3. Multiplex Editing Using Isocaudal Enzymes
[0108] In order to explore whether the system of the present invention is suitable for multiplex gene editing, the construct of the present invention was combined with an assembly method based on homocaudal restriction enzymes. Since the experiment in this example was performed before the experiment in Example 2, the 35S promoter was still used.
[0109] To generate expression cassettes for multiple sgRNAs, the pAtU6-26-SK vector (Feng et al., 2013, supra) was modified by deleting the Spe I site downstream of the sgRNA scaffold and adding a Nhe I site between Xho I and Sal I point to modify, get pAtU6-26-M ( Figure 5 ).
[0110] Multiple sgRNAs were inserted into the BbsI site of pAtU6-26-M. Assemble multiple sgRNA expression cassettes using Sal I and a pair of homologous restriction enzymes Spe I / Nhe I, such as Figure 1D shown.
[0111] To generate the final genome editing plasmid, the multiple sgRNA exp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com