Method for detecting and locating weak signals of static radiation source target
A weak signal detection and radiation source technology, applied in the field of target detection, can solve problems such as unavailability, lack of prior knowledge, difficult positioning of a single passive radar, and achieve the effect of improved signal-to-noise ratio and high detection probability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with specific examples:
[0039] The present invention utilizes matlab to verify the above-mentioned detection and positioning algorithm scheme; assume that the master station, slave station and target are all in a two-dimensional plane; the master station and slave station self-positioning errors are not included; all measurement errors are assumed to be Gaussian distribution assumptions The target is stationary or moving at an extremely slow speed.
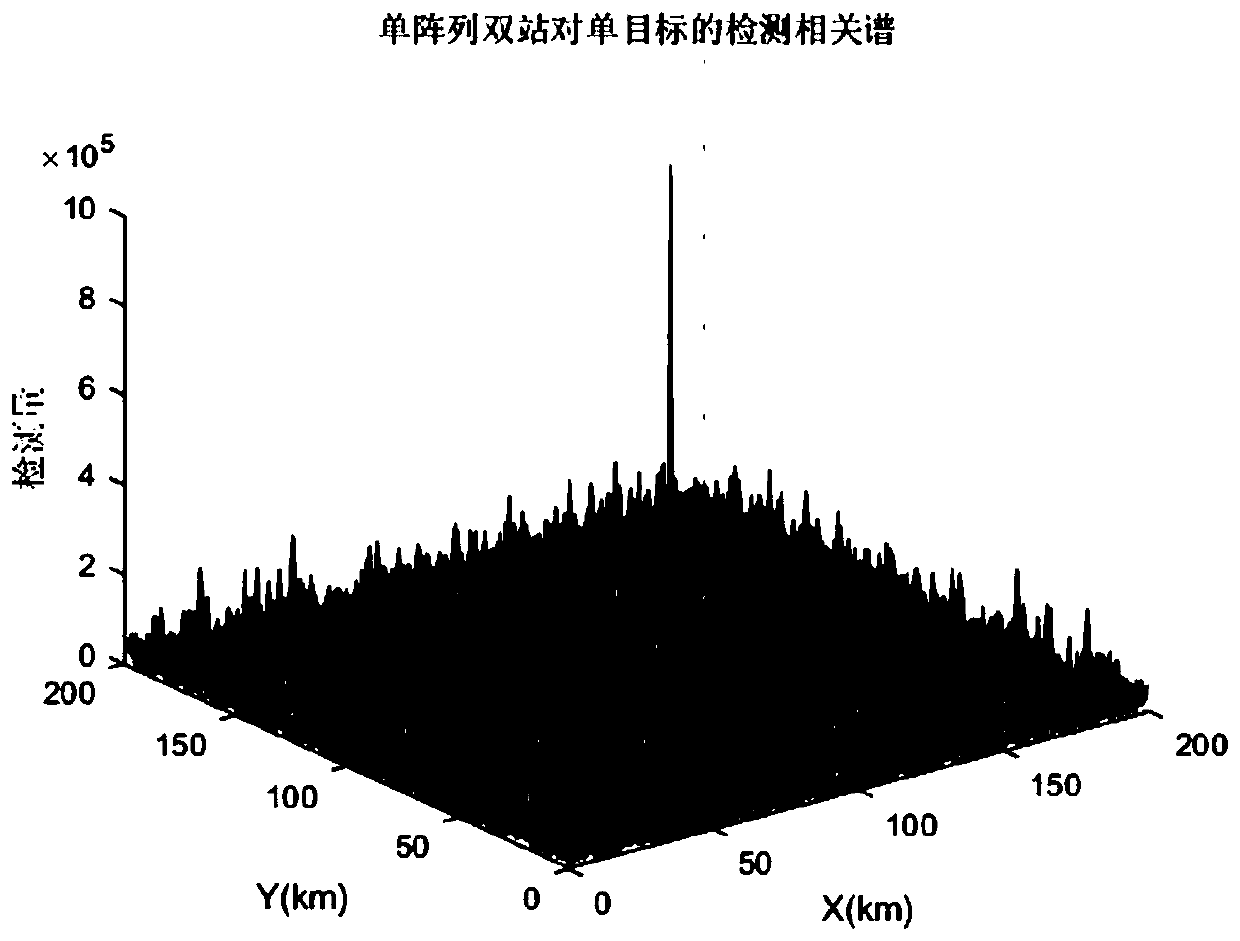
[0040] Suppose there are two emitter reconnaissance stations located at q 1 =[0,0] T and q 2 =[100,0] T , the target is located at u=[150,150] T , the target area is 200km×200km, and the distance between the grid points is 1km; single-array dual-station (without digital beamforming method) and multi-array dual-station (assuming 8 arrays) are used to detect and locate a single target respectively, where image 3 is the correlation spectrum of the target...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com