Linkage molecular markers of maize rough dwarf disease resistance main-effect QTL and application of linkage molecular markers
A technology of molecular markers and crude dwarf disease, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of restricting research results in breeding applications, and the small effect value of a single QTL, so as to achieve detection The method is convenient and fast, improves the anti-rough dwarf traits, and saves production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
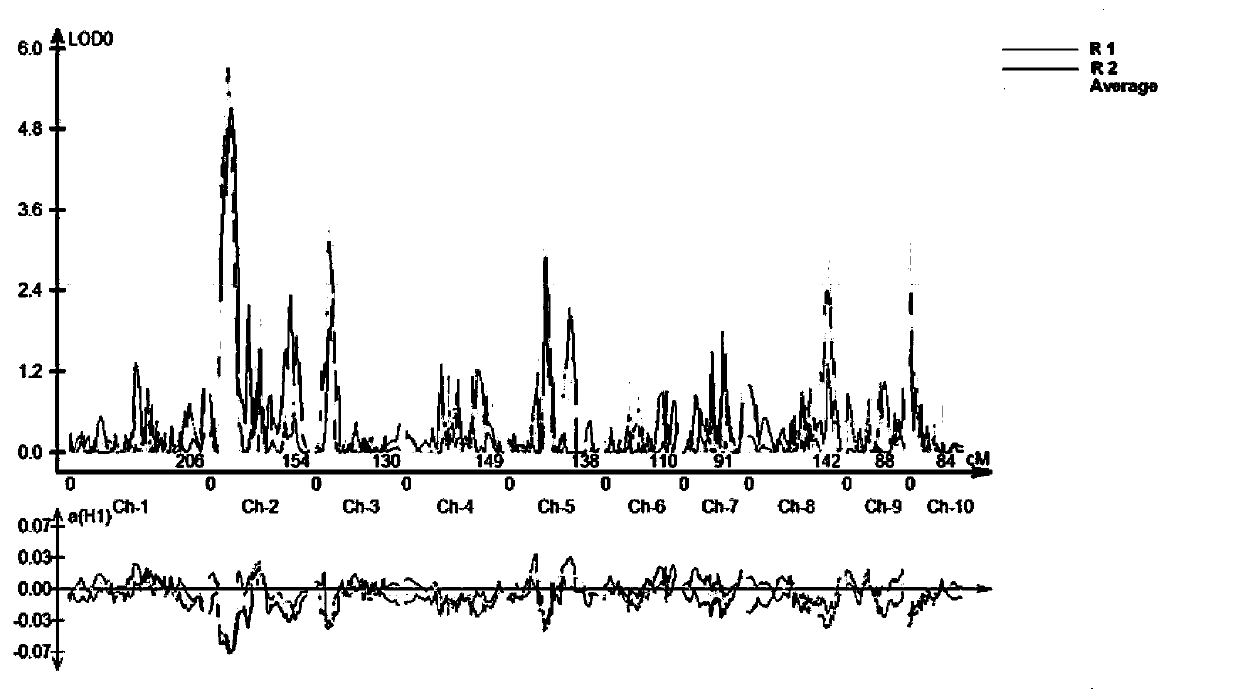
[0040] Example 1: Obtaining the linkage molecular markers of the main QTL for resistance to rough dwarf disease in maize:
[0041] (1) Construction of positioning separation groups:
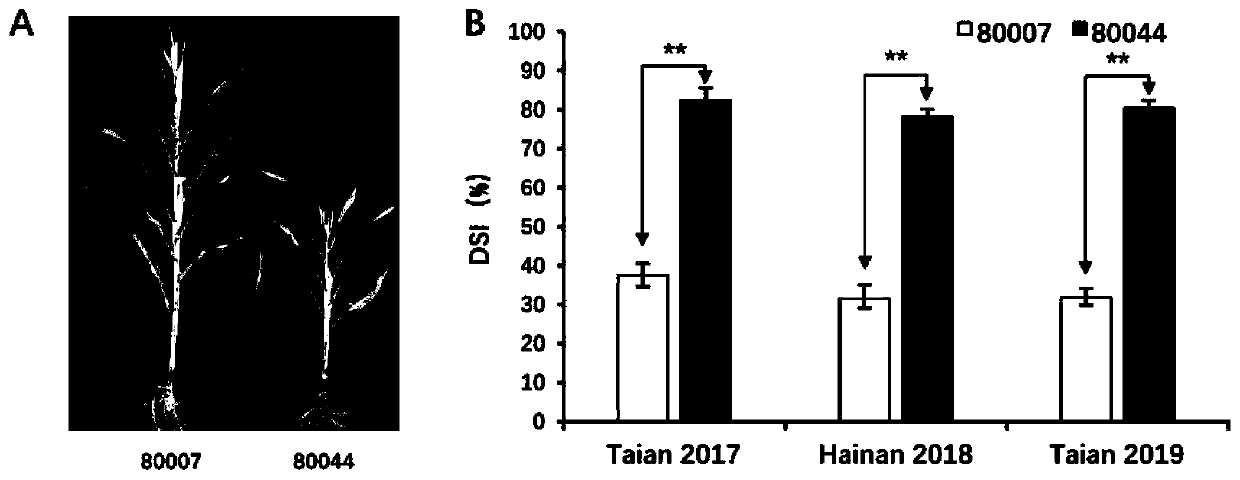
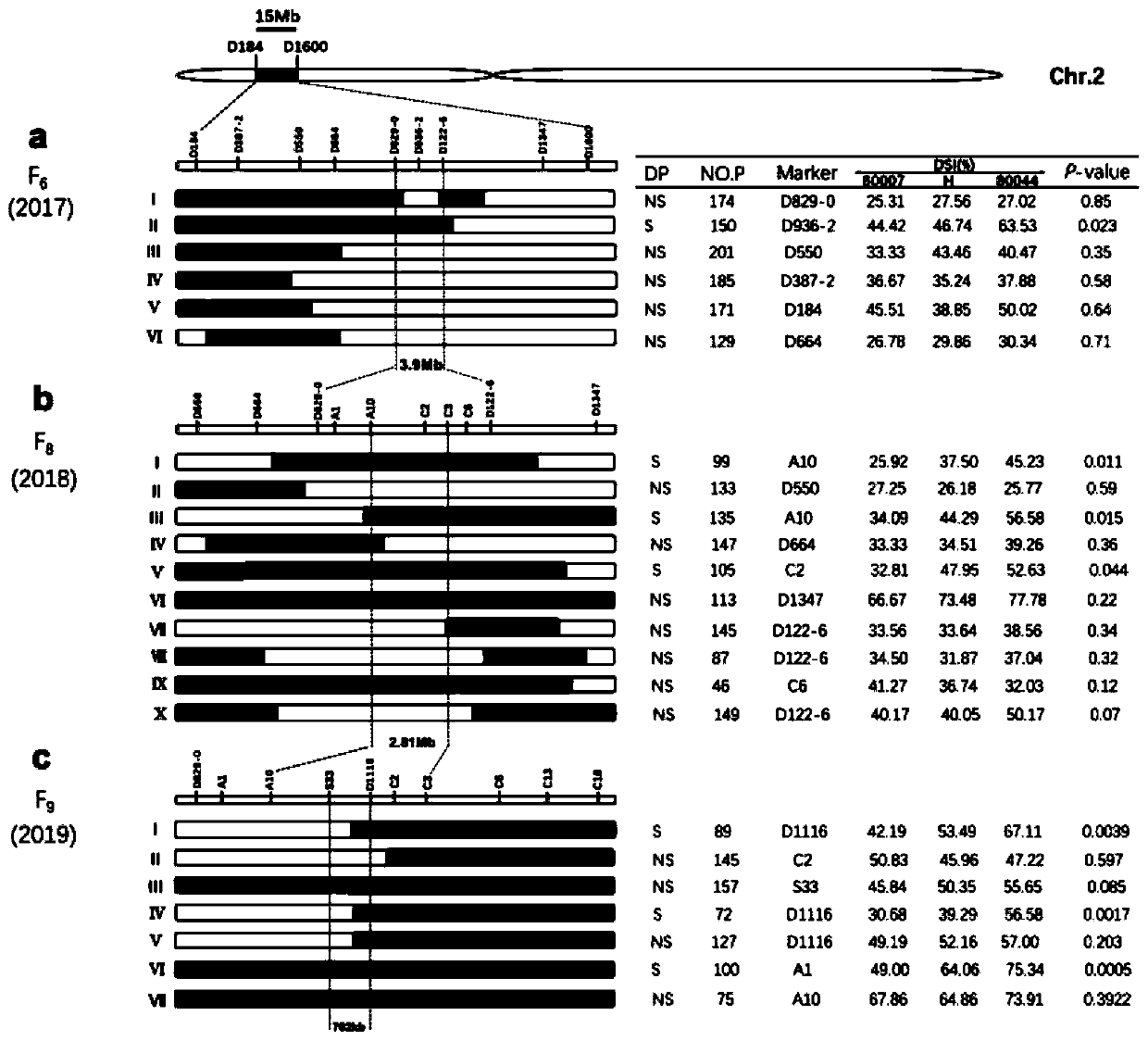
[0042] In the spring of 2013, two experimental sites in Jining City, Shandong Province, planted 199 RIL populations constructed from maize inbred lines 80007 (disease-resistant parent) and 80044 (susceptible parent), and carried out the evaluation of the incidence level of rough dwarf disease under natural inoculation conditions. Phenotype identification. At the same time, 58 RILs were selected to hybridize with 80044 to obtain F 1 , F 1 Continuous selfing for multiple generations as a fine-mapped population.
[0043] (2) DNA extraction:
[0044] Total DNA was extracted from leaves of inbred lines 80007 (disease-resistant parent) and 80044 (susceptible parent) and segregation populations by conventional SDS method (Murray and Thompson 1980).
[0045] (3) Development and synthesis of primers:...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Application of molecular markers S33 and D1116 in assisted selection of maize rough dwarf resistance traits
[0055] Its steps include:
[0056] (1) In the spring of 2019, the finely positioned F 8 The population was identified by artificial inoculation (Ren Chunmei, 2018), a single plant was listed and sampled at the seedling stage, and the total DNA of the leaves was extracted, and the qMrdd2 genotype was judged by molecular markers S33 and D1116;
[0057] Those with homozygous band A detected by molecular markers S33 and D1116, and those with one band A and the other heterozygous band or both were detected as resistant strains ;Use molecular markers S33 and D1116 to detect homozygous band type B, and record it as a susceptible individual plant.
[0058] (2) Both artificial inoculation identification and natural disease identification adopt the same disease investigation method. In the maize maturation stage, the disease severity is divided into 5 grades...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com