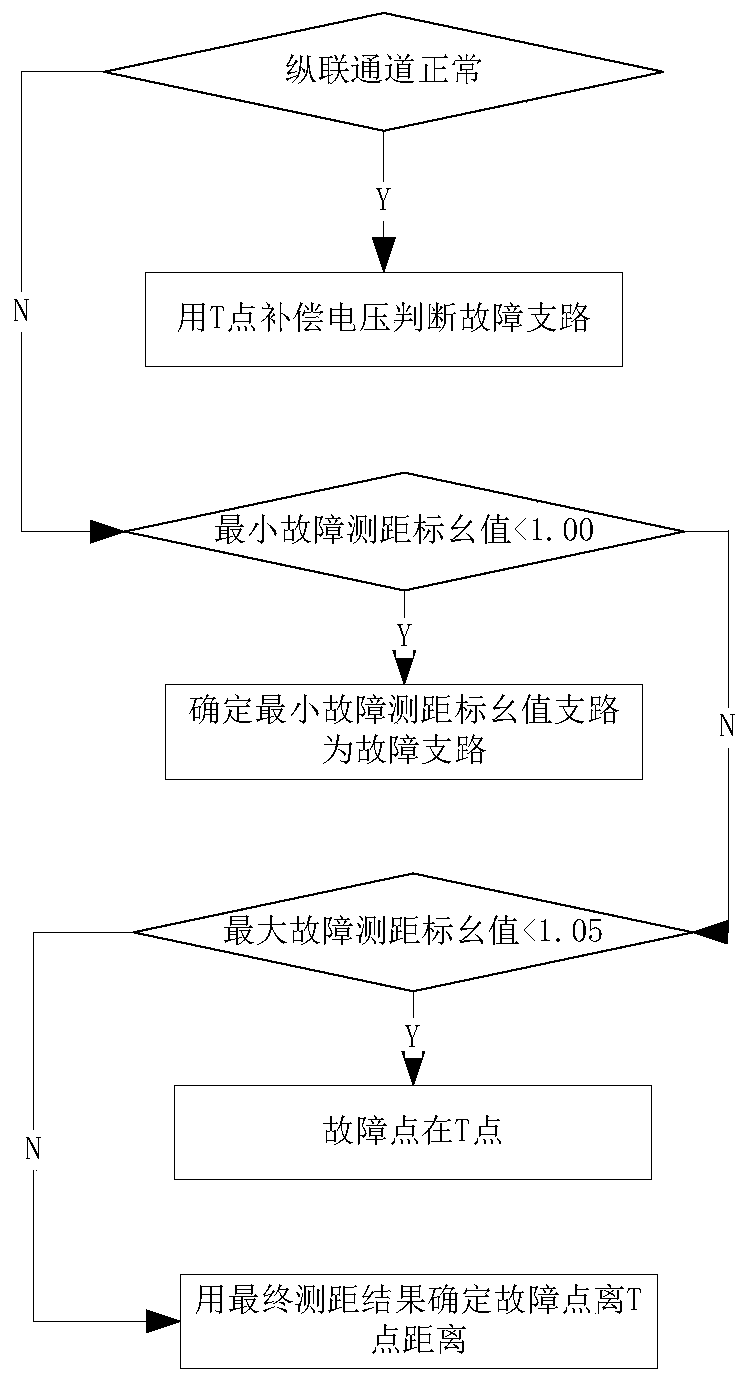
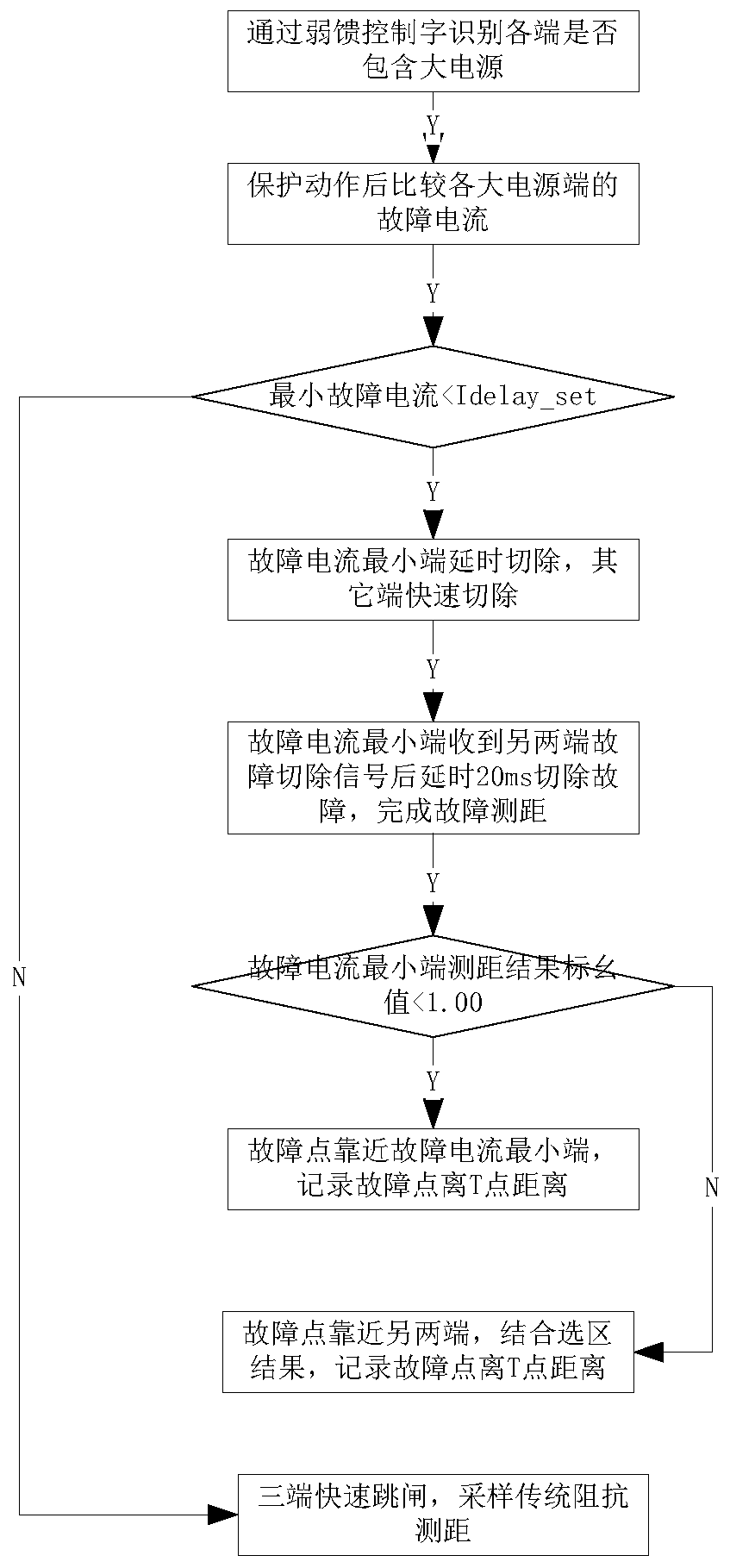
T link fault distance measurement method
A technology of fault distance measurement and line connection, which is applied to the fault location, fault detection according to the conductor type, and electrical measurement. The effect of distance accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
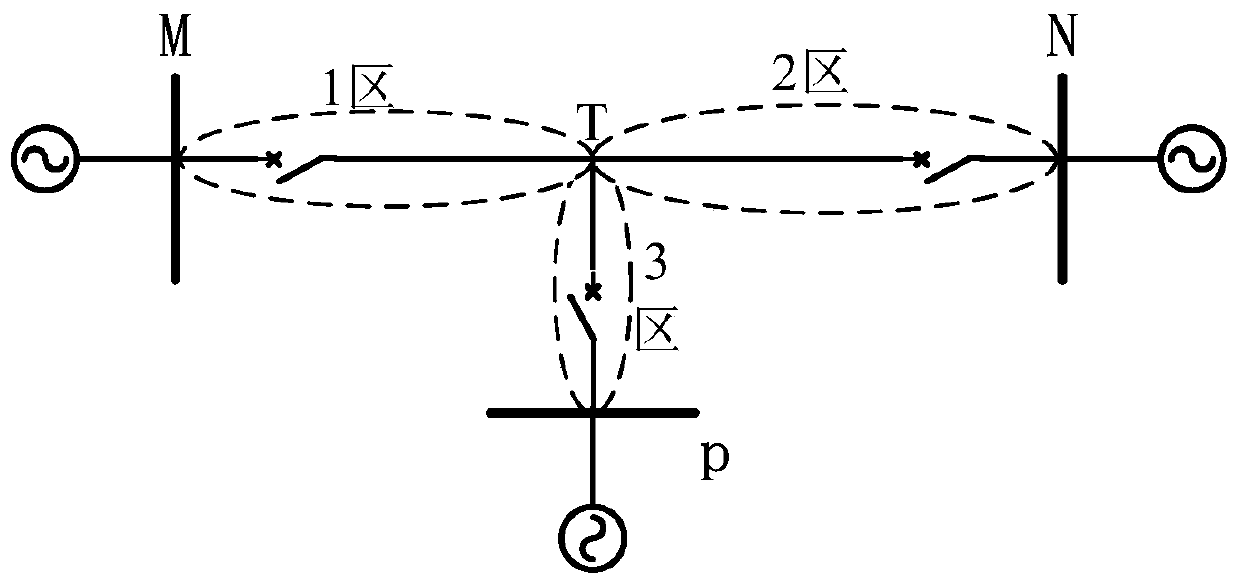
[0071] established as Figure 4 The RTDS simulation model shown, the model parameters are shown in Table 1:
[0072] Table 1 Model parameters
[0073] project parameter unit Positive sequence resistance 0.147 Ω / km positive sequence inductance 0.430 Ω / km Positive sequence parallel capacitive reactance 0.530 MΩ*km Zero sequence resistance 0.500 Ω / km Zero sequence inductance 1.200 Ω / km Zero-sequence parallel capacitive reactance 0.786 MΩ*km Line length MT (zone 1) 20 km Line length NT (Zone 2) 30 km Line length PT (zone 3) 40 km
[0074] If the simulated fault point K1 is 50% away from the M side, the theoretical T point distance measurement result is 20*0.5=10kM; the simulated fault point K2 is 50% away from the N side fault, and the theoretical T point distance measurement result is 30*0.5=15kM; simulated fault The point K3 is 30% away from the fault on the P side, and the theoretical ran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com