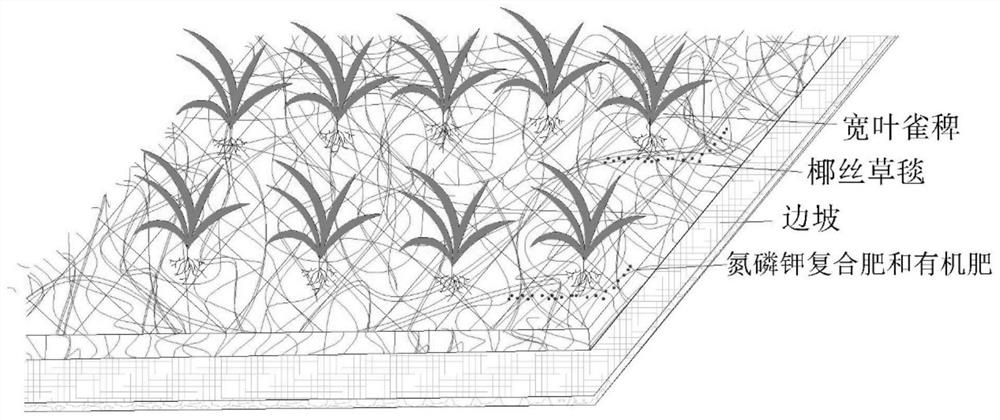
A method for repairing abandoned rare earth mines based on paspalum cultivation
A rare earth and mining technology, applied in the field of abandoned rare earth mine restoration, can solve problems such as unsuitable for large-scale abandoned rare earth mine restoration, unfavorable large-scale promotion, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve good social benefits, convenient and fast construction, and the effect of alleviating erosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
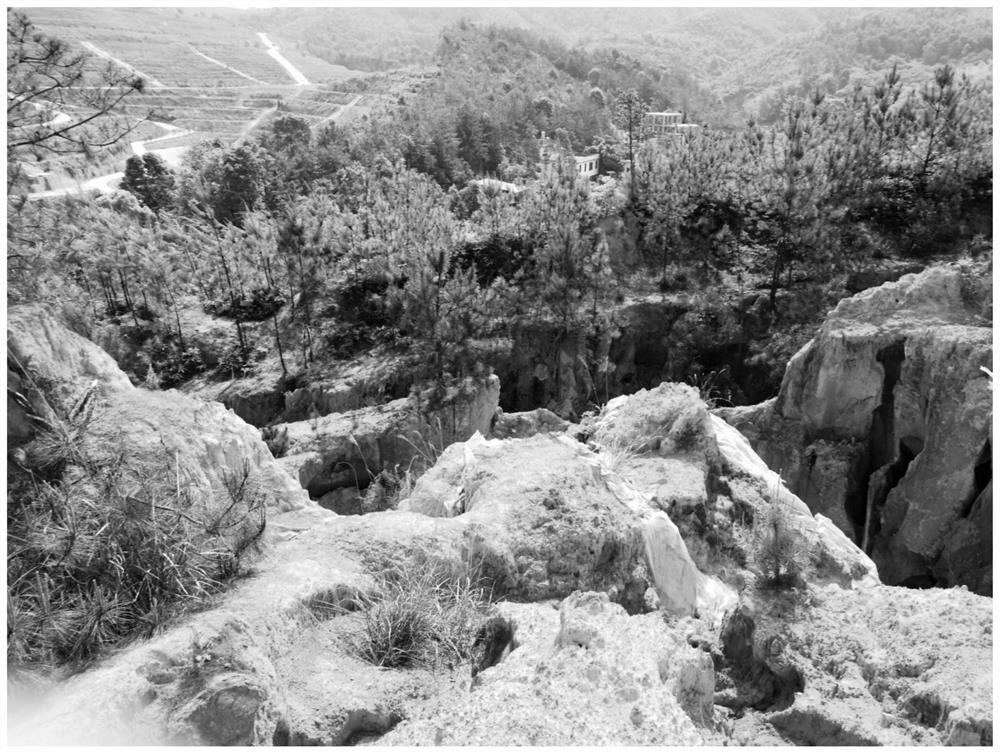
[0027] In this embodiment, ecological restoration is carried out by taking the mining and stripping area of the abandoned rare earth mine in Zhanggong District, Ganzhou City as the restoration object.
[0028] 1. Development of ecological restoration
[0029] S1. Build vegetation:
[0030] Soak paspalum grass seeds in water at 50-60 °C for 4 hours, air-dry them naturally, and spray them evenly in the mining and stripping areas of abandoned rare earth mines. The specific operation of spraying is as follows:
[0031] (1) Collect the soil in the soil area to be repaired for impurity removal and sieving to remove garbage, weeds, large grains of gravel, and soil clods in the soil, so as to be used for spraying; (2) Take organic fertilizer (farmyard manure) , grass fiber, water-retaining agent (acrylamide-acrylate copolymer), binder (polyacrylamide) and the soil powder obtained in step (1) to prepare a soil matrix, which contains organic fertilizer 100 g / kg, grass fiber 300 g / kg...
Embodiment 1
[0045] 1. How to set up the treatment group
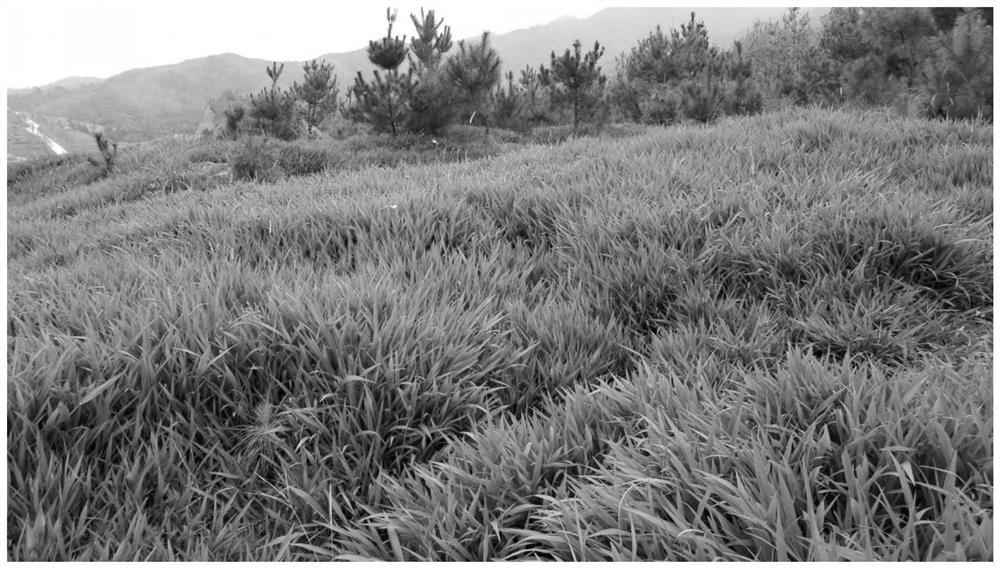
[0046] This embodiment is set as the control treatment of embodiment 1, to reflect the impact of the setting of the grass blanket on the restoration effect. In this example, two treatment groups were set up: treatment I, no grass blanket was used in the process of ecological restoration; treatment II, paspalum broad-leaved grass blanket was covered on the surface of the soil area sown with broad-leaved paspalum. In addition to the above variable settings, the location of the soil area selected for treatment I and treatment II and the ecological restoration measures carried out on the soil area were strictly consistent with those in Example 1.
[0047] 2. Repair effect
[0048] Table 2 shows the evaluation parameters for the ecological restoration effect of the mining and stripping areas of abandoned rare earth mines carried out in this example. The state evaluation parameters of each treatment group before restoration and after re...
Embodiment 2
[0051] 1. How to set up the treatment group
[0052] This embodiment is set as the control treatment of Embodiment 1 to reflect the influence of the sowing method on the restoration effect. In this example, one treatment group was set up: treatment III, sowing paspalum paspalum frontosa seeds in the soil area to be repaired in the traditional sowing form of manual sowing. In addition to the above variable settings, the location of the soil area selected for treatment III and the ecological restoration measures carried out on the soil area are strictly consistent with those in Example 1.
[0053] 2. Repair effect
[0054] Table 3 shows the evaluation parameters for the ecological restoration effect of the mining and stripping areas of abandoned rare earth mines carried out in this example. Compared with before restoration, after restoration, the average content of rare earth elements in the soil area selected for treatment III decreased, and the rare earth elements in the soil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com