Detection of nerves in a series of echographic images
A series of technologies in images, applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve problems such as difficulties in automatic detection process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] In practice, the anesthesiologist scans areas of the patient's body with an ultrasound probe to identify nerves and determine the areas where the anesthetic product is to be injected. The ultrasound device operates continuously under the control of the anesthesiologist or another practitioner (surgeon, etc.) and generates a stream of images (ie, video) that are displayed on a monitor in real time. Thereby, scans performed by the anesthetist can be undertaken based on what the anesthetist sees on the monitor.
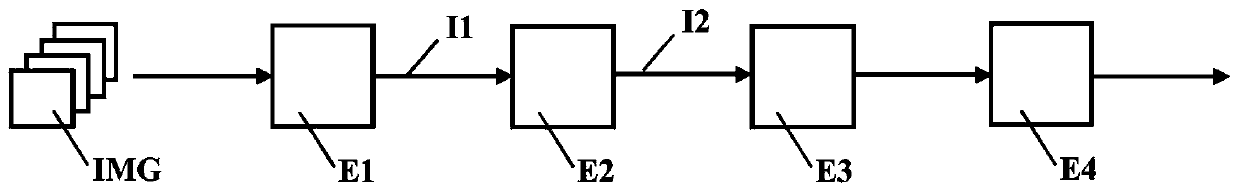
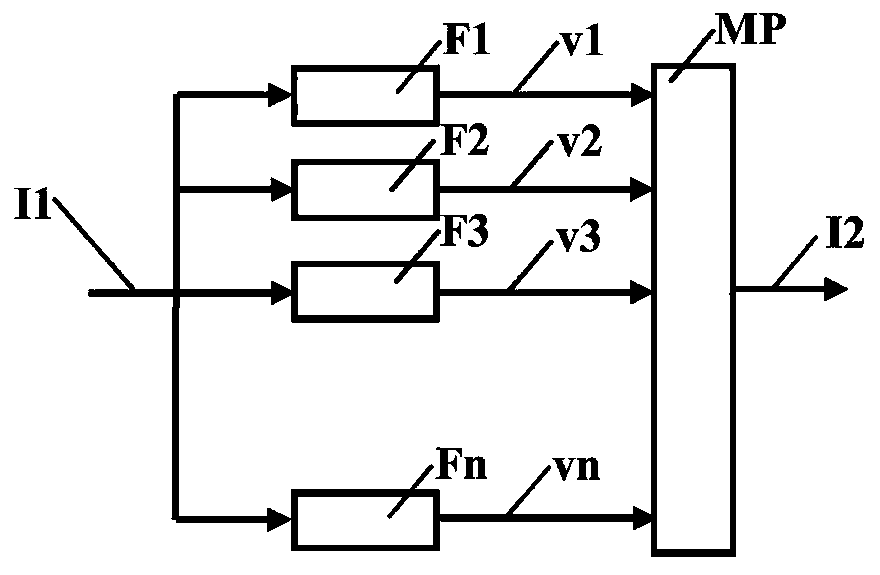
[0027] The method according to the invention is based on a processing chain which acquires as input a stream of echographic images and supplies as output the detection of nerves on this stream.
[0028] Typically, the detection may include highlighting the nerve as overexposed on the stream of echographic images displayed on the monitor. For example, such protrusions may include enclosing the detected nerve or even precisely defining a contour. It can be done in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com