Beam structure damage identification method based on support counterforce and deflection curvature
A technology for bearing reaction force and damage identification, which is used in machine/structural component testing, elasticity testing, measuring devices, etc., to solve problems such as the inability to identify the degree of structural damage and the need for pre-damage information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
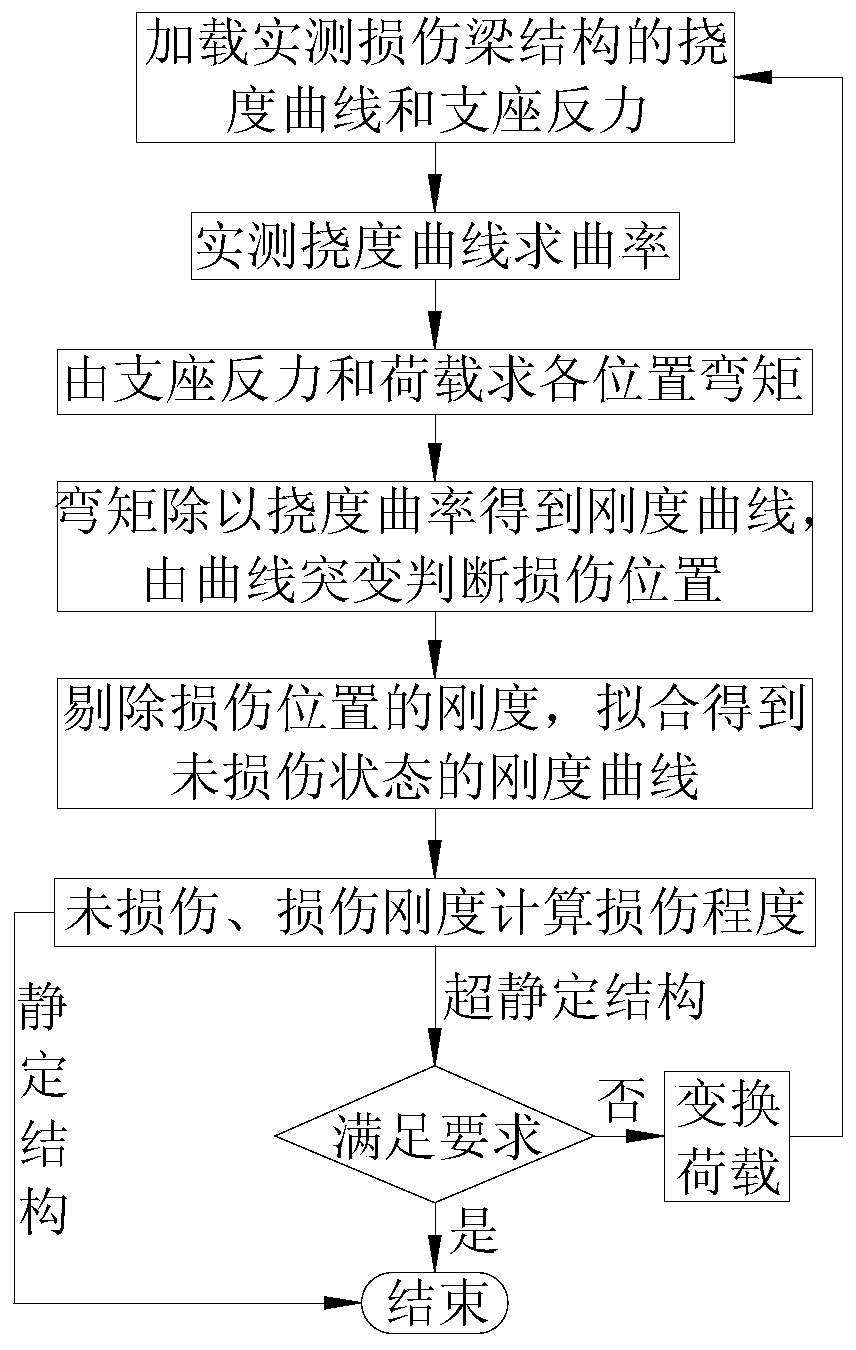
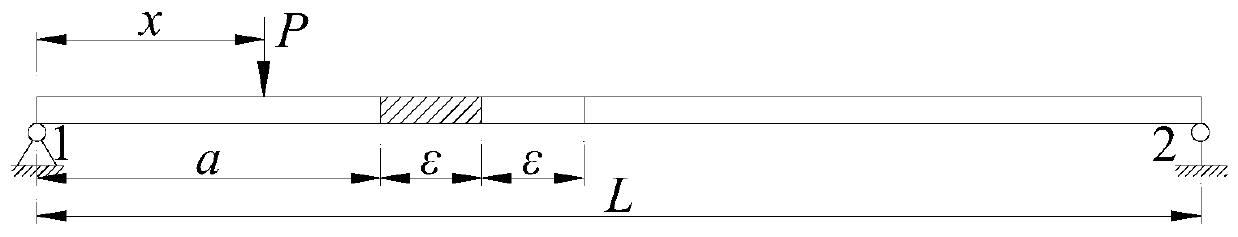
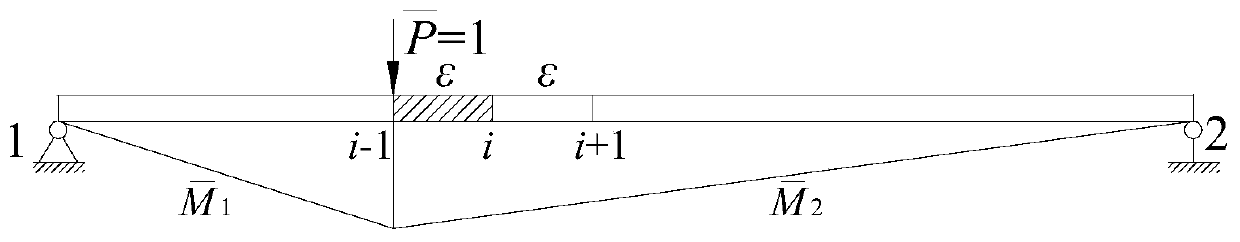
[0174] Embodiment one: see Figure 17 , the span of the simply supported beam is 100cm, and a unit is divided by 5cm, with a total of 20 units and 21 measuring points (the number in the upper circle in the figure is the unit number, and the lower number is the measuring point number). The cross-sectional size of the plate is b×h=4.5cm×1.5cm, and the elastic modulus of the material is 2.7×10 3 MPa, Poisson's ratio is 0.37, density is 1200kg / m 3 .
[0175] The damage in the actual engineering structure, such as the generation of cracks, material corrosion or the reduction of elastic modulus, generally only causes a large change in the structural stiffness, but has little impact on the quality of the structure. Therefore, in the finite element calculation, it is assumed that the damage of the structural element only causes the decrease of the stiffness of the element, and does not cause the change of the mass of the element. Damage to elements is simulated by a reduction in th...
Embodiment 2
[0184] Embodiment two: see Figure 22 , the span of the cantilever beam is 100cm, and a unit is divided by 5cm. There are 20 units and 21 measuring points in total (the numbers in the upper circle in the figure are unit numbers, and the numbers in the lower row are measuring point numbers). The cross-sectional size of the plate is b×h=4.5cm×1.5cm, and the elastic modulus of the material is 2.7×10 3 MPa, Poisson's ratio is 0.37, density is 1200kg / m 3 .
[0185] Considering that the fixed support end unit 1, the mid-span unit 10, and the free end unit 20 have different degrees of damage, the damage conditions are shown in Table 2.
[0186] Table 2 Multiple damage conditions of cantilever beam
[0187]
[0188] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0189] Step 1: Apply a concentrated load of 10N to the No. 21 measuring point at the cantilever end of the damaged cantilever beam to obtain the measured deflection curve of the cantilever beam after damage, and th...
Embodiment 3
[0195] Embodiment three: see Figure 27 , the span layout of the three-span continuous beam is 100+150+100cm, and 10cm is divided into one unit, a total of 35 units and 36 measuring points (the numbers in the upper circle in the figure are the unit numbers, and the lower numbers are the support numbers) . The cross-sectional size of the plate is b×h=4.5cm×1.5cm, and the elastic modulus of the material is 2.7×10 3 MPa, Poisson's ratio is 0.37, density is 1200kg / m 3 .
[0196] Unit 7 is located near the 0 point of the side span bending moment (ie, the inflection point of deflection curvature) under the action of a uniform load, unit 13 is located near the 0 point of the bending moment under the concentrated load of the mid-span, unit 18 is the mid-span unit of the middle span, and unit 26 is the third span The damage conditions of the maximum negative bending moment unit are shown in Table 3.
[0197] Table 3 Damage conditions of three-span continuous beams
[0198]
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com