Discovery method and device based on servitization architecture
A technology for discovering requests and services, applied in the field of discovery methods and devices based on service-oriented architecture, can solve the problem of high communication complexity, and achieve the effect of reducing communication complexity and communication times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] image 3 Shown is the implementation flow chart of a service-based architecture-based discovery method provided in Embodiment 1 of the present application, see image 3 shown, including:
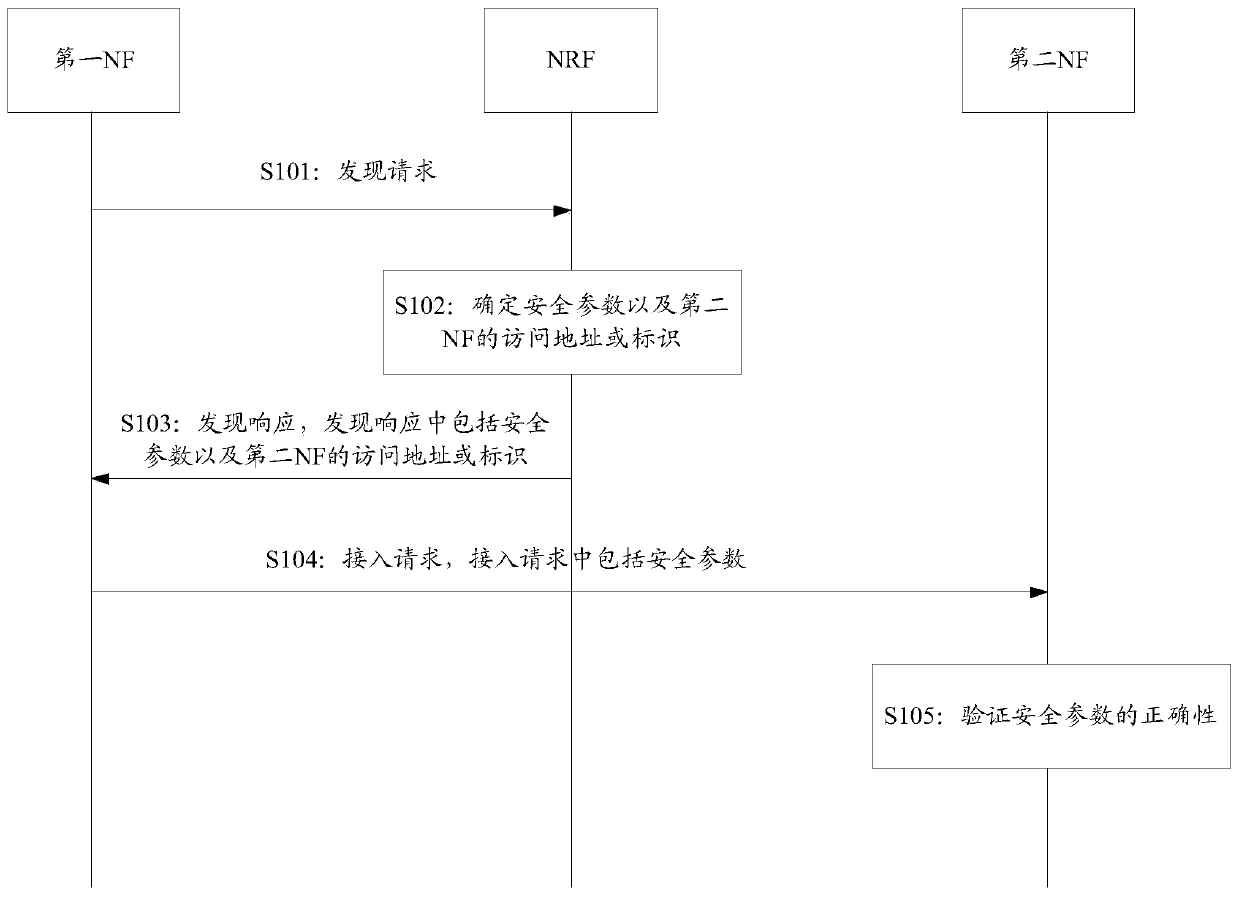
[0111] S201: The first NF determines that a service needs to be requested, and the service can be determined through a service parameter, for example, the service parameter can be a service identifier (service ID). In the following embodiments, the service parameter is taken as an example for illustration, and the implementation process of other service parameters is similar, and will not be repeated here.
[0112] S202: The first NF sends a discovery request to the NRF, and the discovery request may include the identifier of the first NF (ID_NF1), and information such as the service ID of the service requested by the first NF, and may also include the type information of the second NF (NF2type )Wait.
[0113] In the embodiment of the present application, the discovery request may ...
Embodiment 2
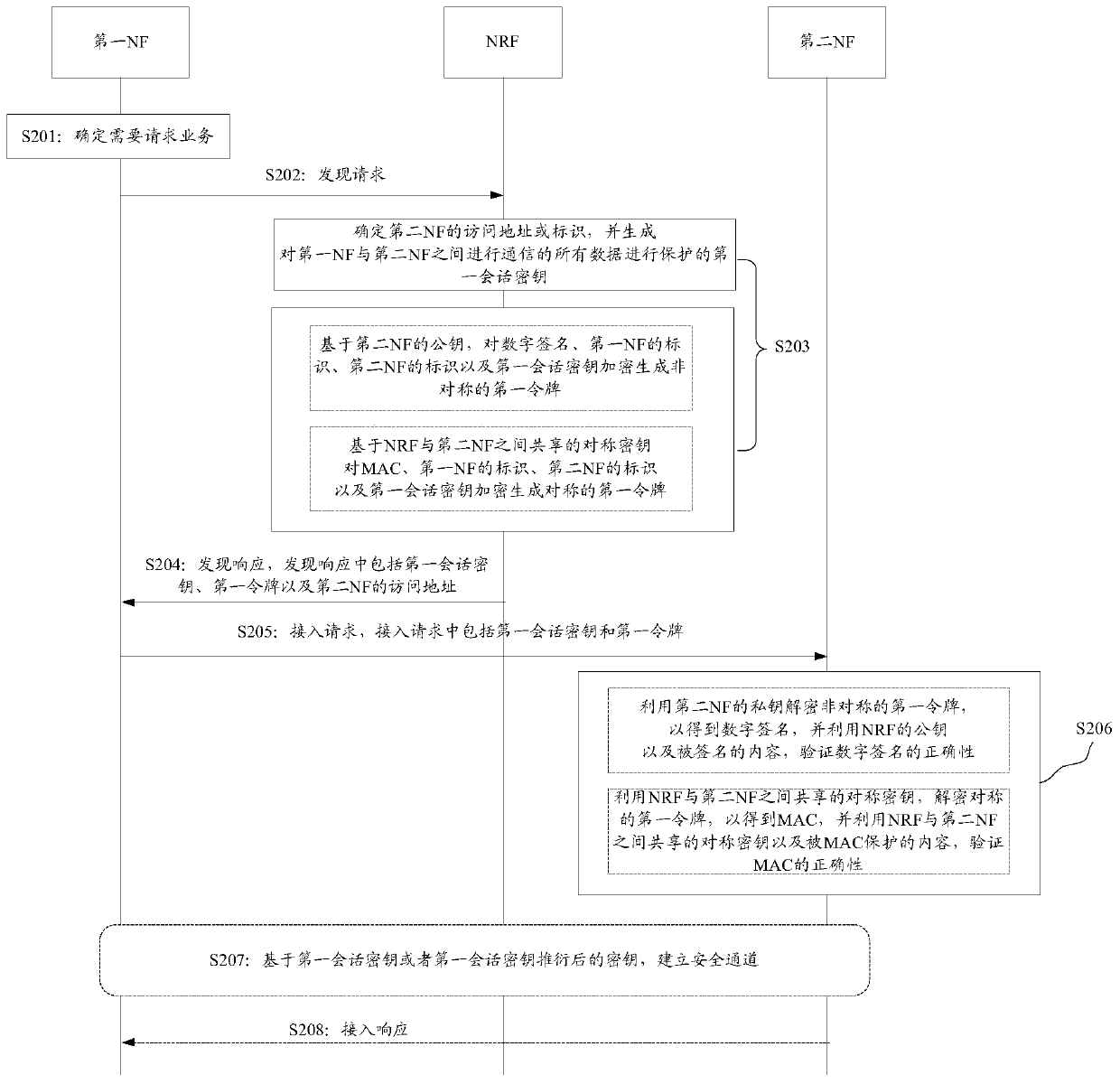
[0145] Figure 4 Shown is a flowchart for implementing a service-based architecture-based discovery method provided in Embodiment 2 of the present application. Figure 4 In the above, the execution steps of S301 and S302 are the same as the execution steps of S201 and S202 in the first implementation and will not be repeated here, and only the differences will be described below.
[0146] S303: The NRF receives the discovery request sent by the first NF, and determines the access address or identifier (ID_NF2) of the second NF, and determines the security parameters.
[0147] Wherein, the implementation process of determining ID_NF2 by the NRF is similar to the above embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
[0148] In the embodiment of this application, when the NRF determines the K_session shared between the first NF and the second NF, it can distinguish the services requested by the first NF and generate K_sessions respectively. It can be understood that there is a one-t...
Embodiment 3
[0174] Figure 5 Shown is a flowchart for implementing a service-based architecture-based discovery method provided in Embodiment 3 of the present application. Figure 5 , the execution steps of S401 and S402 are the same as the execution steps of S301 and S302 in the second implementation, and the implementation process of determining ID_NF2 and generating the second K_session in S303 is also the same as the implementation process of determining ID_NF2 and generating the second K_session in the second embodiment They are the same, so they will not be repeated here, and only the differences will be described below.
[0175] S403: The NRF generates a third token based on each generated second K_session.
[0176] In this embodiment of the present application, the third token may be a symmetrical third token or an asymmetrical third token.
[0177] In a possible implementation manner, in the embodiment of the present application, the NRF can encrypt the digital signature, ID_NF...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com