Unmanned surface vehicle environment sensing method based on single-line laser radar
A single-line laser radar and environmental perception technology, which is applied in the field of unmanned vehicle environmental perception, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory detection of short-distance small targets and maneuvering targets, large size of marine radar, and inability to effectively detect the outline of targets.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] see Figure 1~6 , in an embodiment of the present invention, a single-line lidar-based method for unmanned boat environment perception, comprising the following steps:
[0045] Step 1: Test the perception range and detection ability of the lidar in the real scene environment, and filter out the invalid point cloud according to the results;
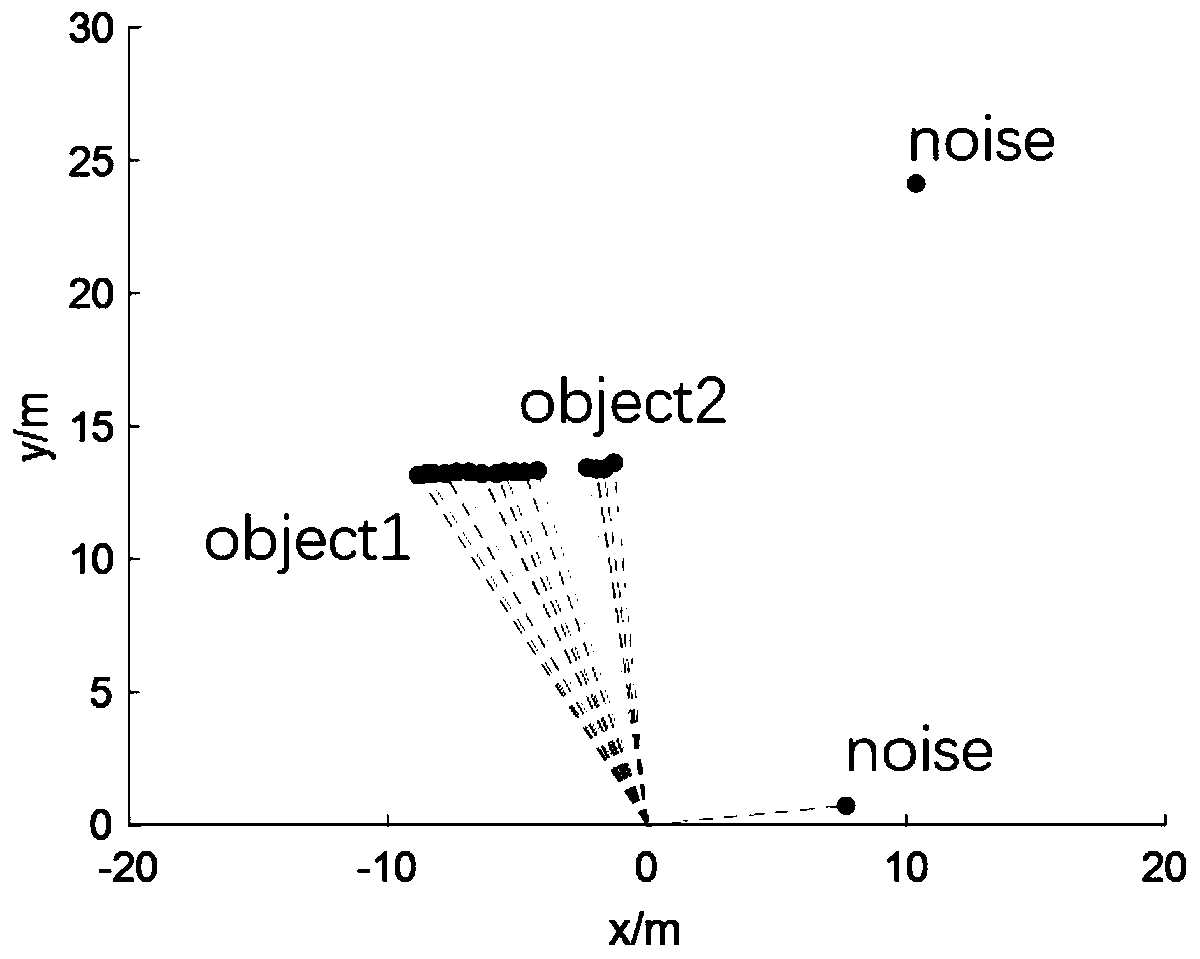
[0046] Step 2: After filtering invalid point clouds, use the DBSCAN algorithm for point cloud clustering;
[0047] Step 3: Use the nearest neighbor data association method to perform inter-frame data matching;
[0048] Step 4: Under the framework of the linear Kalman filter, use the interactive multi-model to estimate the state of the moving target, and adjust the process noise covariance matrix adaptively according to the maneuverability of the target.
Embodiment 2
[0050] In this embodiment, the laser radar in the first step is a Lase-2000D laser radar.
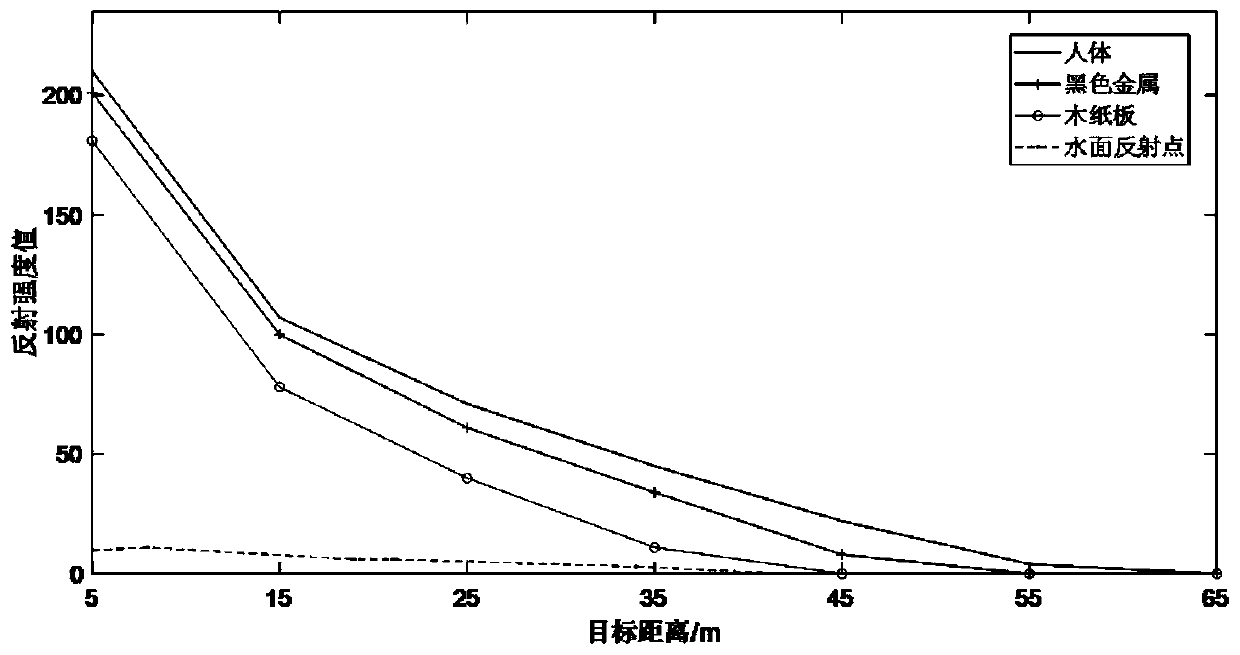
[0051] In this embodiment, the test under the real scene in the step 1 includes selecting the surface of the human body, ferrous metal, and wooden cardboard under the outdoor natural light environment on land for measurement, and the measurement distance is 5-65 meters, once every 10 meters, and It is obtained that the reflection intensity value below 10 is regarded as an invalid point cloud.
[0052] In this embodiment, the parameters that affect the segmentation result in step 2 are the neighborhood range ε and the number of samples in the neighborhood minpts, and the arc length 1 of equidistant adjacent points is used as a reference to set the segmentation parameters. The formula for the segmentation parameters is:
[0053]
[0054] where d is the linear distance from the target to the lidar, and σ is the horizontal resolution of the lidar.
[0055] In this embodiment, in the s...
Embodiment 3
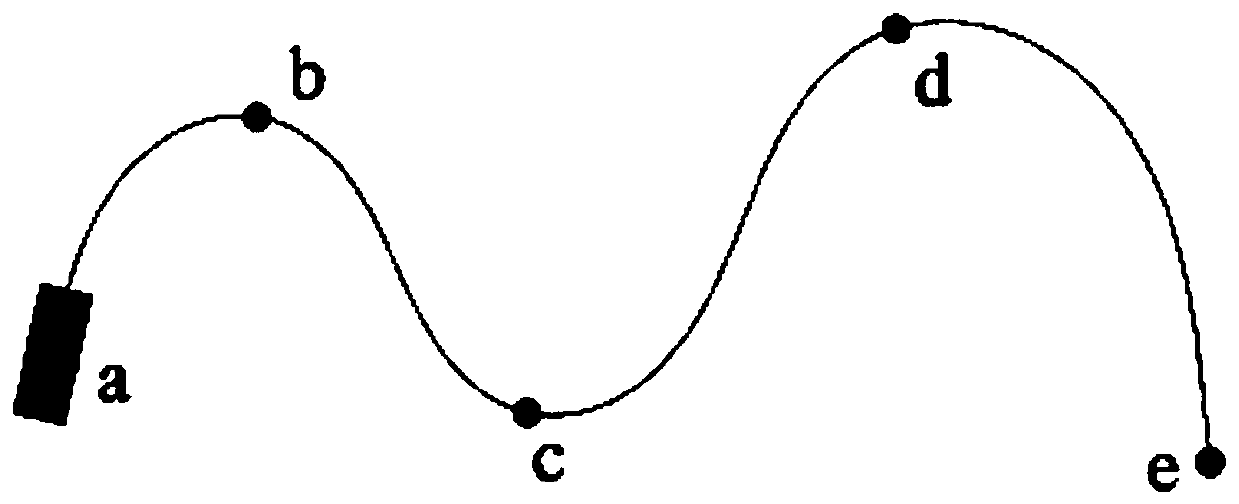
[0071] In order to verify the rationality of parameter selection, a simulation experiment is designed in a uniformly variable speed scenario, and the target speed is considered to be 1m / s and 25m / s respectively. image 3 Driving with variable speed in the path c shown, the result is as follows:
[0072] (a) is Q=0.05I 2*2 Due to the improvement of the trust degree of the observation model, the speed estimation results can be quickly updated to the actual speed of the target near the path points b and c where the target acceleration and heading change, although there is a A few frames of data with large errors, but the overall speed estimate is relatively accurate. However, in terms of heading estimation, since the speed of the target at waypoint b is only 1m / s, there is a large error in the results around the 200th frame, which is consistent with the conclusion of the previous simulation experiment. As the value increases, the heading estimation results are more accurate.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com