A method for in-situ stabilization and remediation of lead-contaminated sediment with iron-based materials and microorganisms
An iron-based material and lead-contaminated technology is applied in the fields of iron-based materials and microorganisms for the repair of lead-contaminated sediment, lead-contaminated sediment repair reagents, and lead-contaminated sediment repair reagents to improve bioavailability, The effect of broad application prospects and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The lead-contaminated sediment was taken from the sediment of Qingshui Pond in the Xiangjiang section of Zhuzhou, and the samples were air-dried and screened (60 mesh).
[0029] Table 1 Basic properties of sediment
[0030] pH 7.8 Organic carbon (g / kg) 7.88 Organic matter (g / kg) 13.59 Cation exchange capacity CEC (cmol / kg) 21.6 Total lead (mg / kg) 733.68
[0031] Preparation of iron-based materials: mix fayalite and oxalic acid dihydrate in a ratio of 2:1, place them in a reactor, add deionized water according to a liquid-solid ratio of 4:1, seal, heat up to 90 °C for reaction for 36 hours , after the completion of the reaction, washing, filtering and drying.
[0032] Culture of sulfate-reducing bacteria: Desulfovibrio sp. ATCC 7757 was inoculated in anaerobic medium (KH 2 PO 4 0.5g / L, NH 4 Cl 1g / L, CaCl 2 0.1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 (O 2.5g / L, sodium lactate 3.5g / L), the pH value is adjusted to 6.5, when it grows to the logarithmic...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The sample is the same as in Example 1.
[0039] Preparation of iron-based material: Biotite and oxalic acid dihydrate were mixed in a ratio of 3:2, placed in a reactor, deionized water was added according to the liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, after sealing, the temperature was raised to 80 ° C for 12 hours, and the reaction When finished, wash, filter and dry.
[0040] Culture of sulfate-reducing bacteria: Desulfovibrio sp. ATCC 7757 was inoculated in anaerobic medium (KH 2 PO4 0.5g / L, NH 4 Cl 1g / L, CaCl 2 0.1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 (O 2.5g / L, sodium lactate 3.5g / L), the pH value is adjusted to 6.5, when it grows to the logarithmic phase, the cell density is 3.2*10 8 pcs / mL.
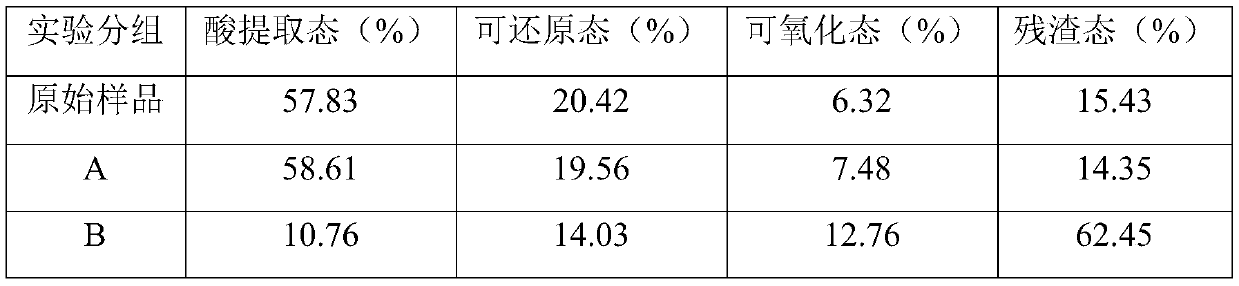
[0041] Remediation of lead-contaminated sediment in a simulated anaerobic environment. The remediation experiments were carried out in a 10L reactor, into which 2kg of sediment samples and 4L of deionized water were successively added, and the reactors were divided into four groups: A, B, C and D. ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The sample is the same as in Example 1.
[0044] Preparation of iron-based material: phillips and oxalic acid dihydrate were mixed in a ratio of 1:2, placed in a reactor, deionized water was added according to the liquid-solid ratio of 4:1, after sealing, the temperature was raised to 90 °C for reaction for 24 hours. When finished, wash, filter and dry.
[0045] Table 3 Morphological changes of lead-contaminated sediment before and after immobilization reaction
[0046]
[0047]
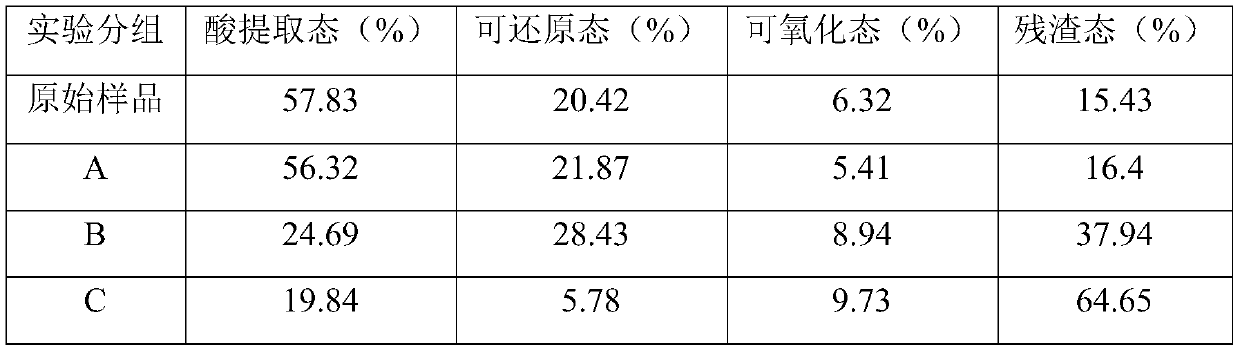
[0048] Culture of sulfate-reducing bacteria: Desulfovibrio sp. ATCC 7757 was inoculated in anaerobic medium (KH 2 PO 4 0.5g / L, NH 4 Cl 1g / L, CaCl 2 0.1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 (O 2.5g / L, sodium lactate 3.5g / L), the pH value is adjusted to 6.5, when it grows to the logarithmic phase for later use, the cell density of the bacterial liquid is 3*10 8 pcs / mL.
[0049] Remediation of lead-contaminated sediment in a simulated anaerobic environment. The remediation experiments were carried ou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com