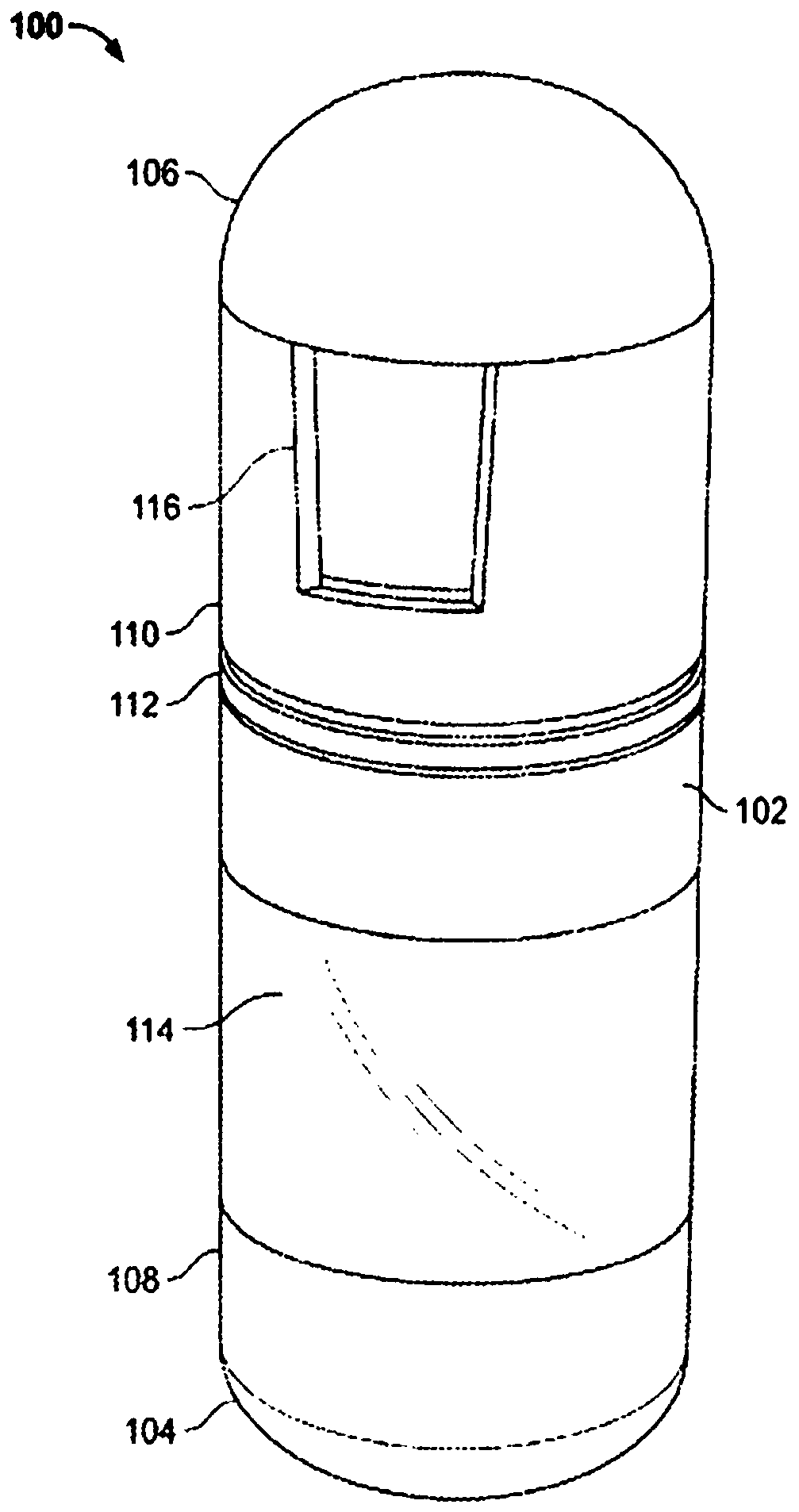
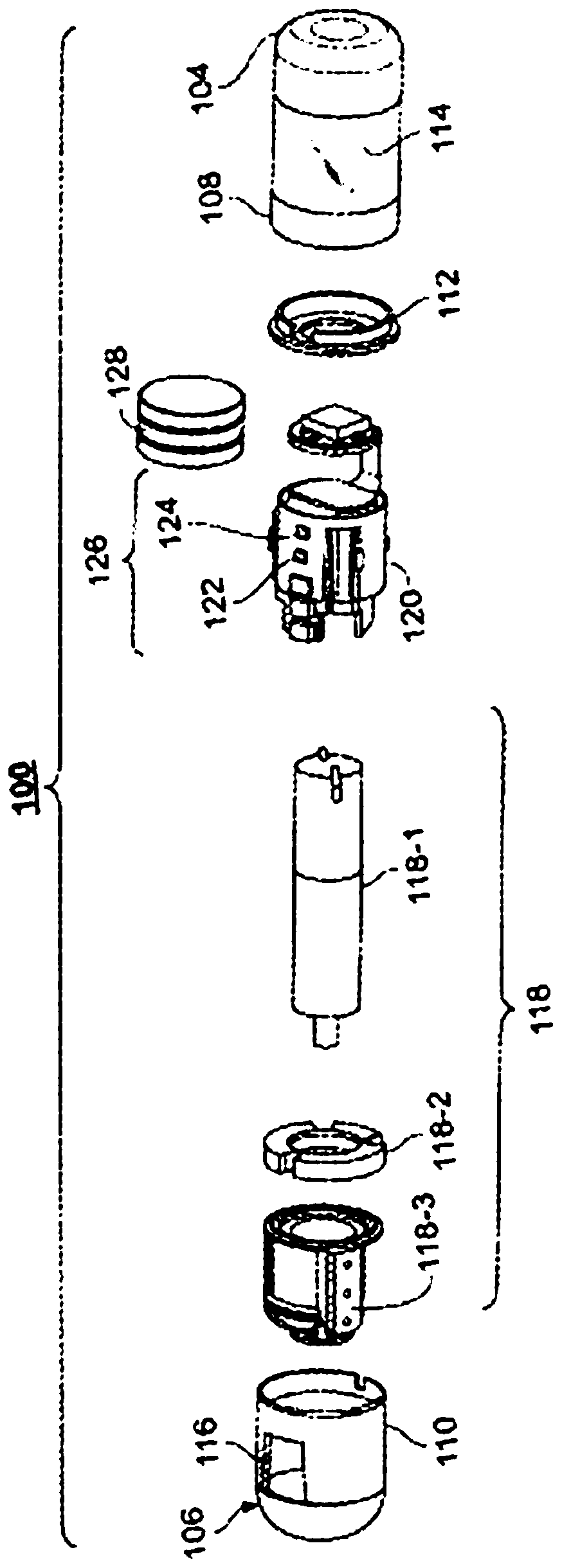
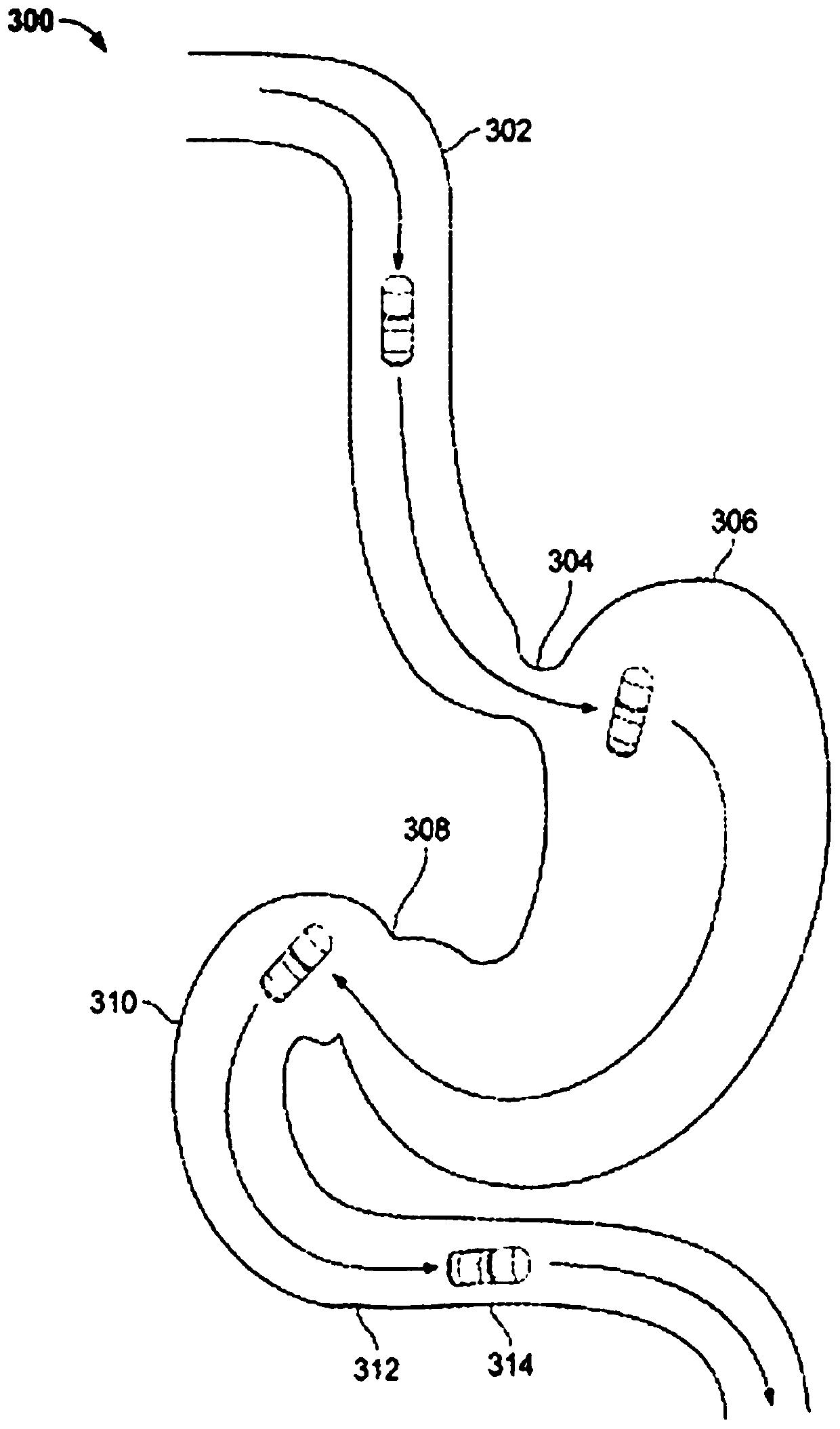
Treatment of a disease of the gastrointestinal tract with a TNF inhibitor
A technology for gastrointestinal diseases and gastrointestinal tract, which is applied in the field of using TNF inhibitors to treat gastrointestinal diseases, and can solve problems such as difficulties in dispensing therapeutic drugs and dispensing drugs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[1215] Example 1 - Preclinical mouse colitis model
[1216] Experimental induction of colitis
[1217] Colitis was experimentally induced in mice by the dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induced colitis model. This model is widely used because of its simplicity and many similarities to human ulcerative colitis. Briefly, mice were administered DSS (which is thought to be directly toxic to the colonic epithelial cells of the basal crypts) via cecal catheterization for several days until colitis was induced.
[1218] group
[1219] Depending on the agent administered, mice were assigned to one of the following seven groups:
[1220] 1. Control (no drug)
[1221] 2. Adalimumab (2.5mg / kg)
[1222] 3. Adalimumab (5mg / kg)
[1223] 4. Adalimumab (10mg / kg)
[1224] Control or agents were administered to the damaged mucosal surface of the intestine by cecal catheter administration at the dose levels described above.
[1225] Additionally, for each group, animals were divided into two...
Embodiment 2a
[1229] Example 2a - Development of a Preclinical Porcine Colitis Model
[1230] Experimental induction of colitis
[1231] Female pigs weighing approximately 35 to 45 kg were fasted for at least 24 hours at the beginning of the study before intrarectal administration of trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS). Animals were lightly anesthetized during drug administration and endoscopy. If necessary, use a colon-cleaning enema. One animal was administered 40 ml of 100% EtOH mixed with 5 g of TNBS diluted in 10 ml of water by enema using a bulb tip catheter. The enema is deposited in the proximal portion of the descending colon just past the curvature of the transverse colon. TNBS was retained at the administration site for 12 minutes by using two Foley catheters with a 60 ml balloon placed in the middle part of the descending colon below the administration site. The second animal was treated similarly, but using a solution containing 10 grams of TNBS. Prior to TNBS administrati...
Embodiment 2
[1235] Example 2b - Pharmacokinetics / pharmacodynamics and bioavailability of adalimumab following topical administration
[1236] group
[1237] Sixteen (16) pigs (approximately 35 to 45 kg at the start of the study) were assigned to one of five groups:
[1238] 1. Vehicle control: (3.2mL normal saline); in rectum; (n=2)
[1239] 2. Treatment control: Adalimumab (40 mg in 3.2 mL saline); subcutaneous; (n=2)
[1240] 3. Adalimumab (low): Adalimumab (40 mg in 3.2 mL saline); intrarectally; (n=4)
[1241] 4. Adalimumab (medium): Adalimumab (80 mg in 3.2 mL saline); intrarectally; (n=4)
[1242] 5. Adalimumab (high): Adalimumab (160 mg in 3.2 mL saline); intrarectally; (n=4)
[1243] On day 0, the test articles were administered intrarectally or subcutaneously to the damaged mucosal surface of the intestine at the above dose levels and volumes by a veterinarian.
[1244] Clinical Observations and Body Weight
[1245] Clinical observations were performed at least once a day. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com