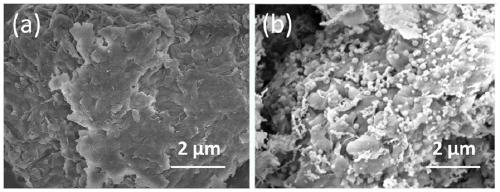
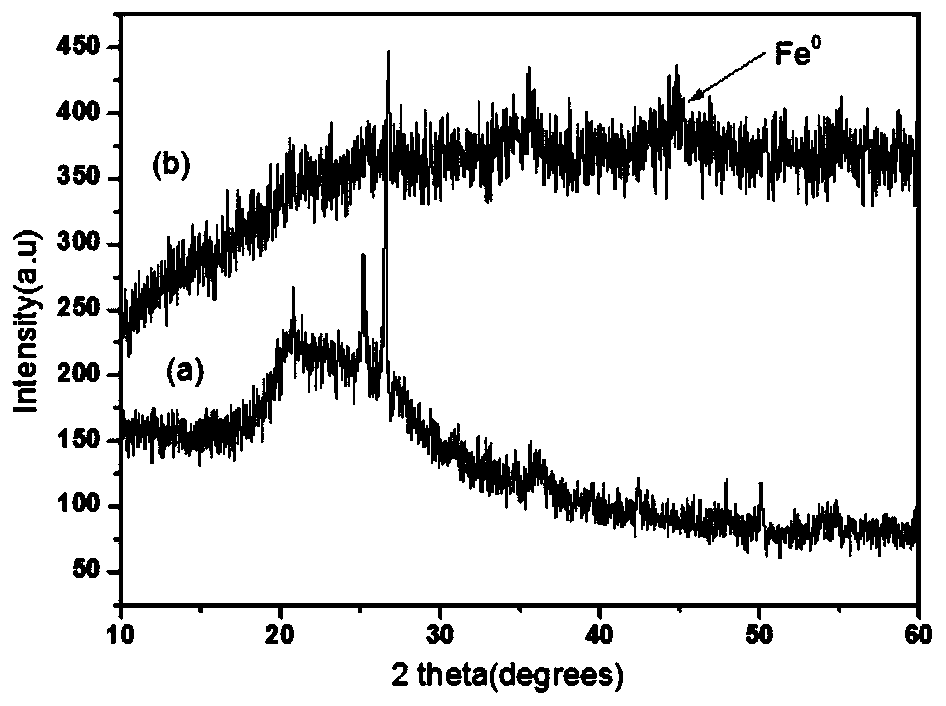
Clay mineral loaded nanometer zero valent iron, and preparation method and use thereof
A nano-zero-valent iron and clay mineral technology, applied in the field of environmental chemistry, can solve the problems of high price of the reducing agent sodium borohydride, residual pollution of neonicotinoid pesticides, high toxicity, etc., and achieves increasing reactive sites and improving reduction. performance, reducing the effect of agglomeration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Preparation of clay mineral-loaded nanometer zero-valent iron
[0035] (1) Dried tobacco stems or green walnut peels and pulverized them, crossed a 40-60 mesh sieve, and added mass fraction of 70-80% ethanol aqueous solution to the powder of tobacco stems or green walnut peels, the solid-to-liquid ratio of the two was 1g: 10-30mL, ultrasonically extract at 40°C for 10-20min, heat to reflux at 65-85°C for 1-2h, filter, and collect the filtrate for later use;
[0036] (2) After dissolving 4.0-6.0 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate with 50-100 mL of ethanol aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 20-40%, add 2-4 g of clay minerals, and ultrasonically disperse for 5-10 minutes to obtain a mixed solution;
[0037] (3) Add the filtrate obtained in step (1) dropwise to the mixed solution described in step (2), the volume ratio of the filtrate and the mixed solution is 2:1, mechanically stir under nitrogen protection 1h;
[0038] (4) washing the solution obtained in ...
preparation example 1
[0040] Preparation example 1 Montmorillonite loaded nanometer zero-valent iron
[0041] (1) Dried tobacco stems or green walnut peels, crushed them, passed through a 40-mesh sieve, and added 70% ethanol water solution with a mass fraction of 70% to the powder of tobacco stems or green walnut peels. Ultrasonic extraction for 20 minutes, heated to reflux at 65°C for 2 hours, filtered, and the filtrate was collected for later use;
[0042] (2) After dissolving 4.0 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate with 50 mL of 40% ethanol aqueous solution, add 2 g of montmorillonite, and ultrasonically disperse for 5-10 min to obtain a mixed solution;
[0043] (3) Add the filtrate obtained in step (1) dropwise to the mixed solution described in step (2), the volume ratio of the filtrate and the mixed solution is 2-4:1, under nitrogen protection Mechanical stirring for 1-2h;
[0044] (4) washing the solution obtained in step (3) with absolute ethanol and deionized water for 2-4 times, and freeze-d...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2 Different materials compare the removal effect of neonicotinoid pesticides
[0061] The initial concentration of three neonicotinoid pesticides was set to 20mg / L, the reaction temperature was 35°C, the initial pH value of the solution was 3, and the material dosage was 2g / L. The removal effects of the clay mineral-loaded nano-zero-valent iron prepared by the present invention and the conventional clay mineral-loaded nano-zero-valent iron prepared with sodium borohydride as a reducing agent on three neonicotinoid pesticides are shown in Table 1.
[0062] Table 1 The removal effect of different materials on neonicotinoid pesticides
[0063]
[0064]
[0065] It can be seen from the data in the above table that the removal rates of the three neonicotinoid pesticides are all low for the clay minerals montmorillonite, attapulgite and kaolin, and the removal rate of the three neonicotinoid pesticides by nano-zero-valent iron is only 74.1% %, 65.2% and 79.8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com