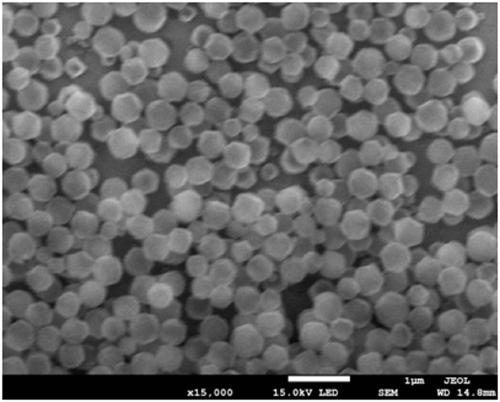
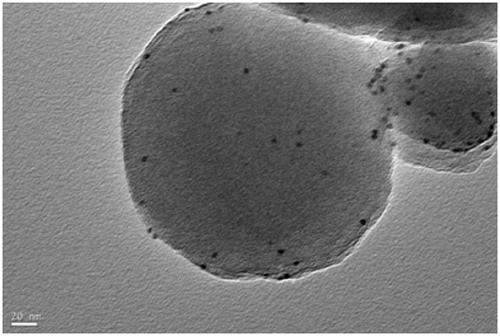
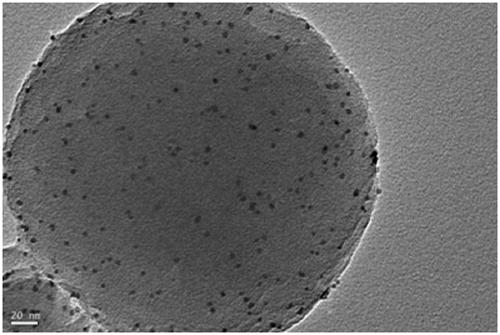
Pt@PCN-224 photocatalyst for preparing artemisinin from dihydroarteannuic acid and preparation method of Pt@PCN-224 photocatalyst
A technology of dihydroartemisinic acid and photocatalyst, which is applied in the direction of organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, chemical instrument and method, physical/chemical process catalyst, etc., which can solve the problem of high cost, yield and conversion rate Low-level problems, to achieve high porosity, reduce production costs, and good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 120mg Zr 6 The metal clusters are dissolved in 5 ml of a mixed solution A of N,N-dimethylacetamide and acetic acid. The volume ratio of N,N-dimethylacetamide and acetic acid in solution A is any one of 0:5 to 4:1. 60 mg of tetracarboxylic phenylporphyrin was dissolved in 2.5 ml of N,N-dimethylacetamide to obtain a mixed solution B. Pt nanoparticles (1mg, 3mg, 5mg) were dissolved in 2.5ml of N, N-dimethylacetamide to obtain mixed solution C. The three are completely mixed under stirring conditions with a magnetron rotating speed of 900 revolutions per minute, stirring at 25 degrees Celsius, the stirring time is controlled between 0.5-24 hours. The preliminary product was collected by centrifugation, washed with N, N-dimethylacetamide three times, washed once with acetone, and dried to obtain pure phases Pt@PCN-224-1, Pt@PCN-224-3, Pt@PCN-224-5. For the final product.
Embodiment 2
[0035] 120mg Zr 6 The metal clusters were dissolved in 5 ml of a mixed solution A of N,N-dimethylacetamide and acetic acid, and the volume ratio of N,N-dimethylacetamide and acetic acid in solution A was 2:3. Dissolve 60 mg of TCPP-Zn (or TCPP-Co, TCPP-Ni) in 2.5 ml of N, N-dimethylacetamide to obtain a mixed solution B. Dissolve 1 mg of Pt nanoparticles in 2.5 ml of N, N-dimethylacetamide to obtain a mixed solution C. The three are completely mixed under stirring conditions with a magneto rotating speed of 900 revolutions per minute, and stirring at 25 degrees Celsius for 9 hours. The preliminary product was collected by centrifugal separation, washed with N, N-dimethylacetamide three times, washed once with acetone, and dried to obtain pure phases Pt@PCN-224-Zn, Pt@PCN-224-Co, Pt@PCN-224-Ni For the final product.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Dihydroartemisinic acid (25mg, 0.106mmol), Pt@PCN-224 or its derivatives obtained in Example 1 and Example 2 (0.002mmol, based on porphyrin), trifluoroacetic acid (8μL), dispersed in 5ml A mixed solution is obtained in methyl chloride. The mixed solution was slowly bubbling with oxygen for 3 hours under LED light illumination. Remove the dichloromethane contained in the reactant and pass 1 H NMR further proved the conversion rate of dihydroartemisinic acid. Finally, the conversion rate of Pt@PCN-224-1 was 98%, and the yield rate was 45%. The conversion rate of Pt@PCN-224-3 was 99%, and the yield was 50%. The standardization rate of Pt@PCN-224-5 is 99%, and the yield is 51%. The conversion rate of Pt@PCN-224-Zn is 99%, the yield is 54%, the conversion rate of Pt@PCN-224-Co is 99%, the yield is 53%, and the conversion rate of Pt@PCN-224-Ni is 99%. , The yield is 52%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com