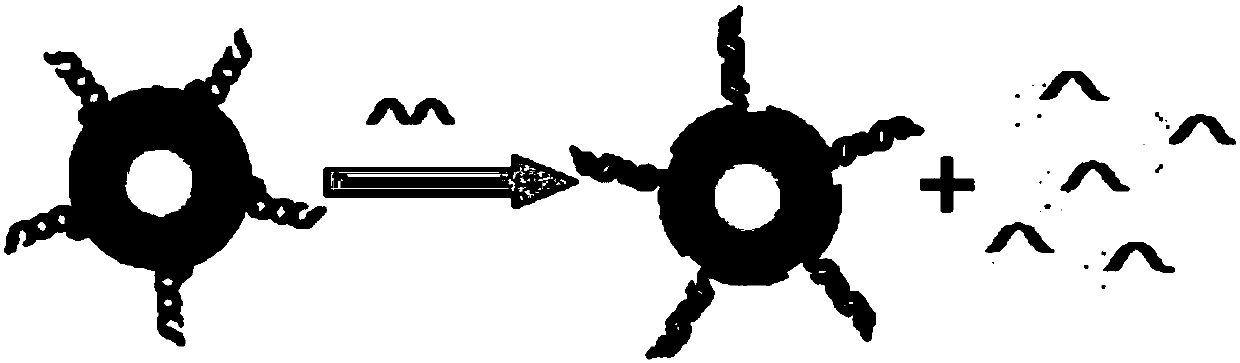
Construction and application of double-block DNA-based regulable nanogold probe
A nano-gold probe and double-stranded probe technology, applied in the biological field, to achieve the effect of solving non-specific adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
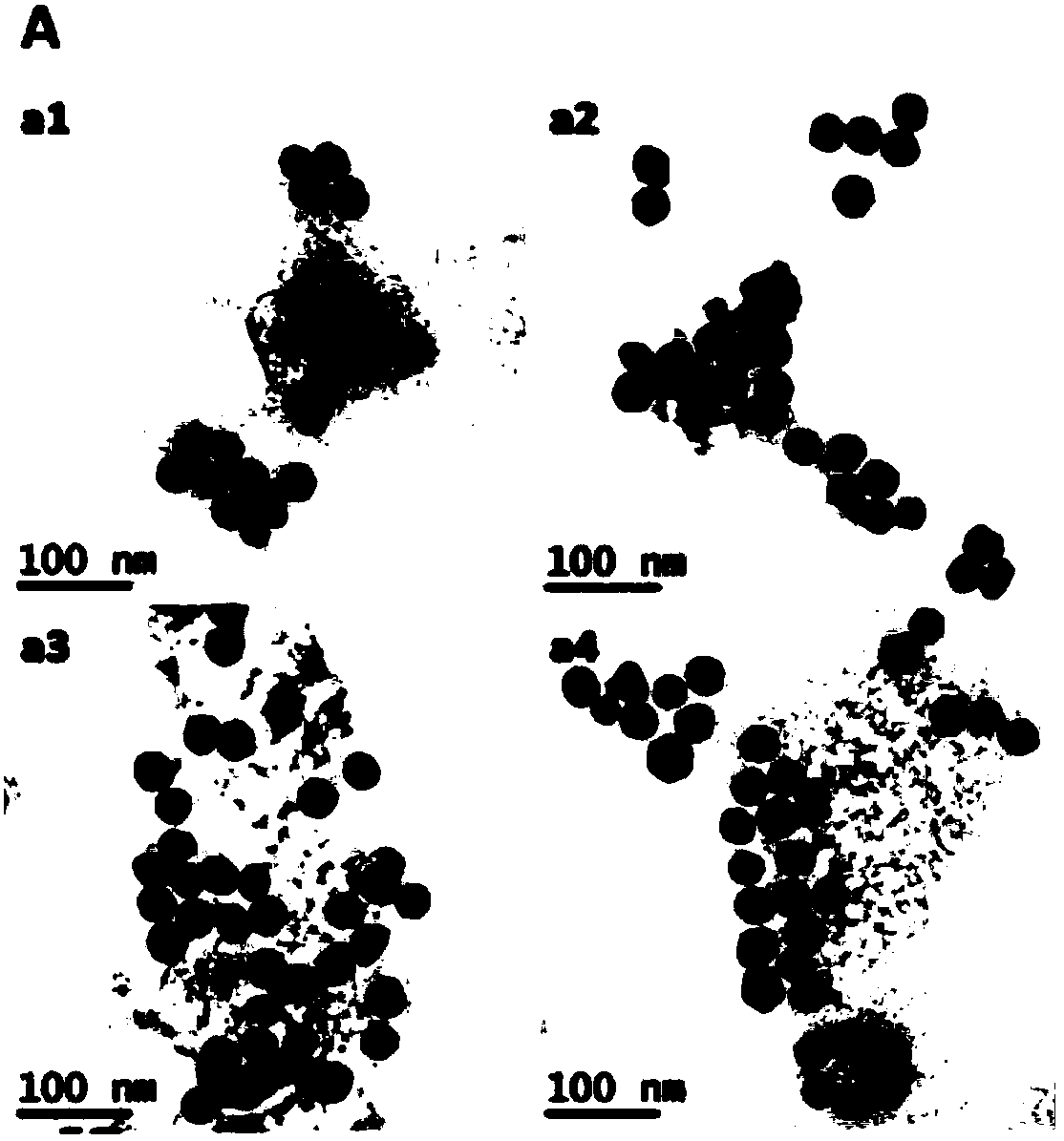
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] (1) Materials and equipment
[0050] Reagents used in this embodiment: trisodium citrate (C6H5Na3O7.2H2O), phosphate, NaCl, MgCl2 and KCl and other reagents were purchased from Sinopharm.
[0051] The above reagents were of analytical grade without further purification.
[0052] The water used in this embodiment is MilliQ water; MilliQ water: 18.2 MΩ.cm (Millipore). The equipment used in this example includes a transmission electron microscope (TEM), an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Hitachi U-3010), a fluorescence spectrophotometer (F-900, Edinburg), a pH meter, and a refrigerated high-speed centrifuge (Hitachi).
[0053] The diblock DNA, reporter molecule and target molecule used in the embodiment of the present invention were purchased from Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. and purified by high performance liquid chromatography.
[0054] The embodiment of the present invention uses three diblock DNAs, namely 2blockPolyA30 (SEQ ID NO.1), 2blockPolyA40 (SEQ ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] In this example, the regulation of the number of assembled gold nanoparticles on the surface of the diblock DNA with different Poly A lengths is discussed.
[0068] The diblock DNA nano-gold probe solutions with different lengths of Poly A prepared in Example 1 were first quantified by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer. The calculation formula is CAuNPs-PolyA=A520nm*2.79*10-10M. The diblock nano-gold probe (0.15 nM final concentration) was added to mercaptoethanol (20 mM final concentration) and shaken overnight at room temperature. Then the supernatant fluorescently labeled DNA (fluorophore FAM, excitation wavelength 494nm, emission wavelength 520nm) was collected by centrifugation, and the fluorescence intensity was detected. Finally, the fluorescence value was substituted into the previous standard curve to calculate the concentration of fluorescently labeled DNA. like Figure 4 As shown, (A) As the length of PolyA increases, the number of diblock DNA assembled on ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] In this example, the regulation of the recognition ability of the target sequence by diblock DNA with different numbers of Poly A nucleotides is discussed.
[0071] Nanogold probes with different lengths of Poly A provided in Example 1 were used. Add different concentrations of target molecules to different groups of nano-gold probes, respectively: 0, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 10, 50, 100, 150, 200nM, and detect the fluorescence intensity of each group after incubation. Each experiment was repeated three times. In this embodiment, the sequence of the target molecule is shown in SEQ ID NO.11, specifically 5' AGCCC CTGCC CACCG CACAC TG3'.
[0072] The result is as Figure 5 As shown, the intensity of the fluorescent signal increases with the addition of target molecules, and finally reaches a plateau. Different poly A numbers have a regulatory effect on the minimum detection limit of the probe. As the number of adenine nucleotides in PolyA increases, the detection limi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com