Power-off maintaining three-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric directional adjustment device and platform control method
A technology for adjusting devices and degrees of freedom, which is applied in the direction of generators/motors, piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, electrical components, etc. Small and other problems, achieve the effect of low location layout requirements, reduce power consumption, and self-compensate installation errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
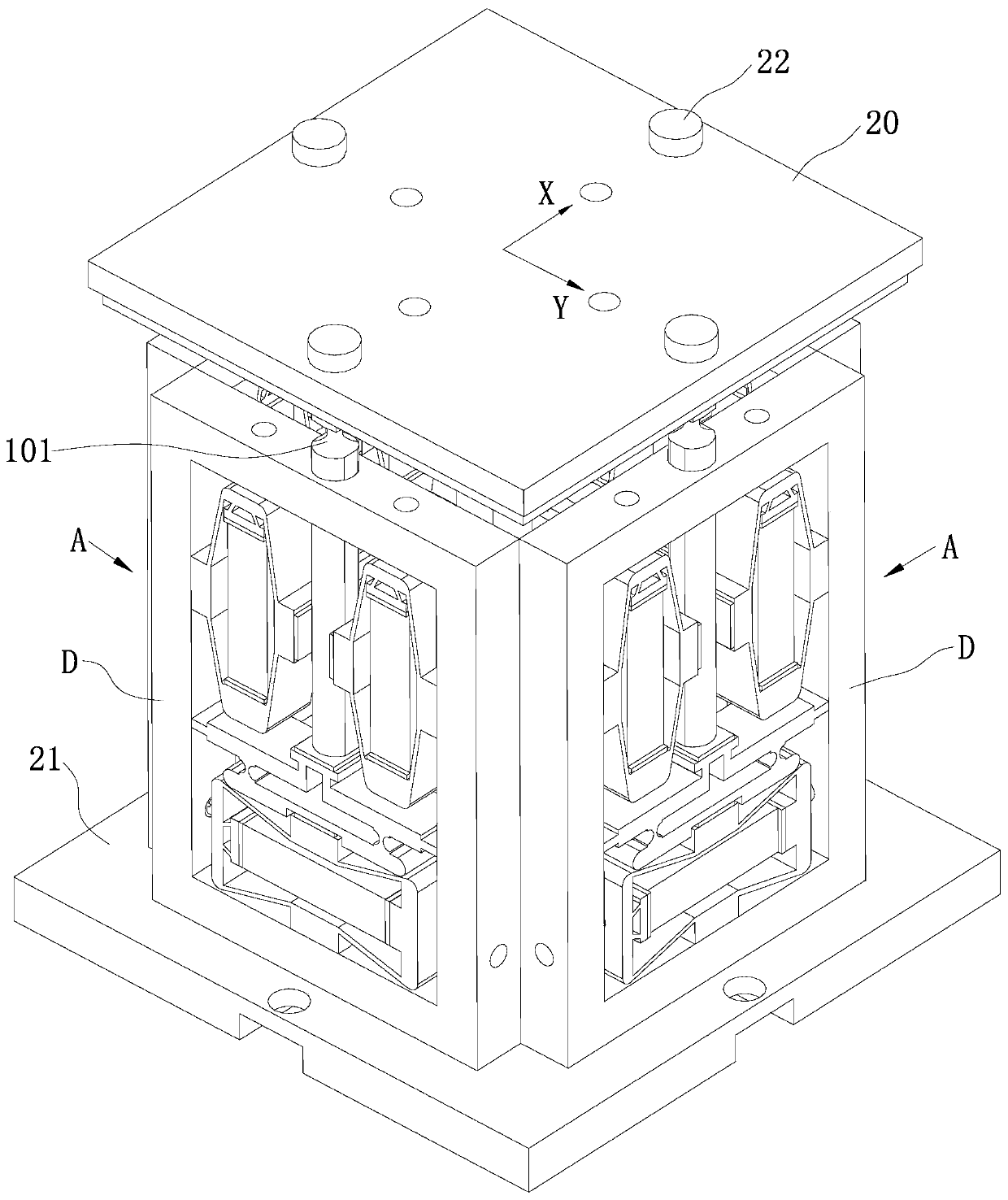
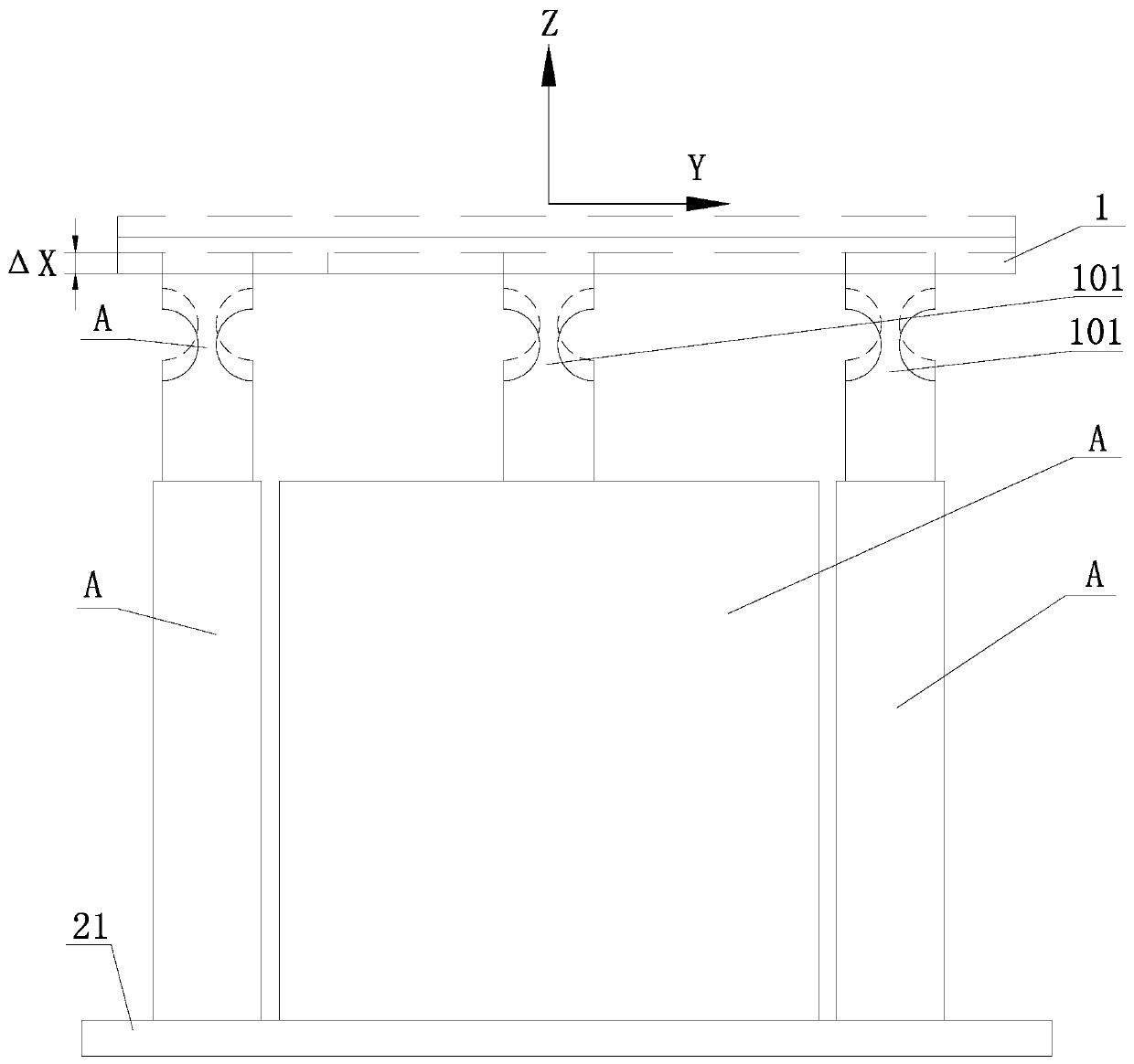
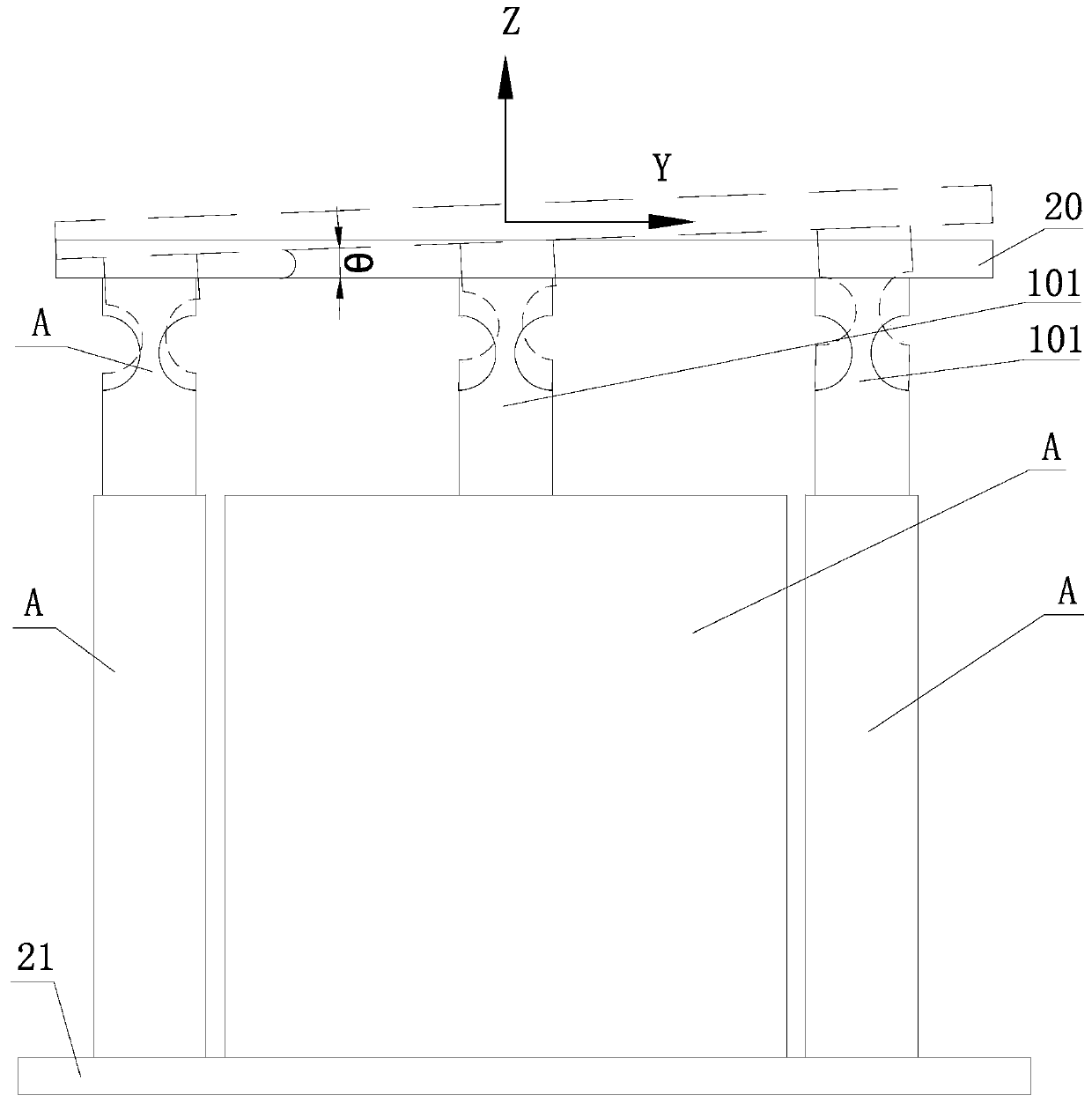
[0055] Example 1, see Figure 5-Figure 7 As shown, the driving piezoelectric stack 9 of each adjustment mechanism A in this embodiment is arranged horizontally and perpendicular to the length direction of the two braking piezoelectric stacks 12, and the braking piezoelectric stack 12 horizontal arrangement;
[0056] Each adjustment mechanism A includes a push rod 1, a driving mechanism, a braking mechanism and a support body D;
[0057] The drive mechanism includes a drive piezoelectric stack 9 and a micro-displacement amplification structure B;
[0058] The braking mechanism includes two braking triangular amplification structures 11 and two braking piezoelectric stacks 12;
[0059] A braking piezoelectric stack 12 is arranged in each braking triangular amplification structure 11, and the opposite output terminals of the two braking triangular amplification structures 11 are fixedly connected to the support body D, and the phases of the two braking triangular amplification ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2, such as Figure 8 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the micro-displacement amplifying structure B is a driving triangular amplifying structure 5, and a driving piezoelectric stack 9 is installed in the driving triangular amplifying structure 5, and the driving triangular amplifying structure 5 and The driving piezoelectric stacks 9 are respectively connected to the support body D, and the output end of the driving triangular amplifying structure 5 is in contact with the bottom end of the ejector rod 1 . The working principle is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3, such as Figure 9 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiments 1 and 2 is that the driving piezoelectric stack 9 is vertically arranged and perpendicular to the length direction of the two braking piezoelectric stacks 12, and the braking piezoelectric stack The stack 12 is arranged horizontally; the micro-displacement amplifying structure B is a lever amplifying structure 4, the lever amplifying structure 4 is connected to the support body D, and one end of the driving piezoelectric stack 9 is in contact with the input end of the lever amplifying structure 4, and the driving pressure The other end of the electrical stack 9 is connected to the support body D, and the output end of the lever amplification structure 4 is in contact with the bottom end of the push rod 1 . The lever amplifying structure 4 is a symmetrical design. Such as Figure 15As shown, this embodiment is a power-off maintenance orthogonal adjustment mechanism, and its wo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com