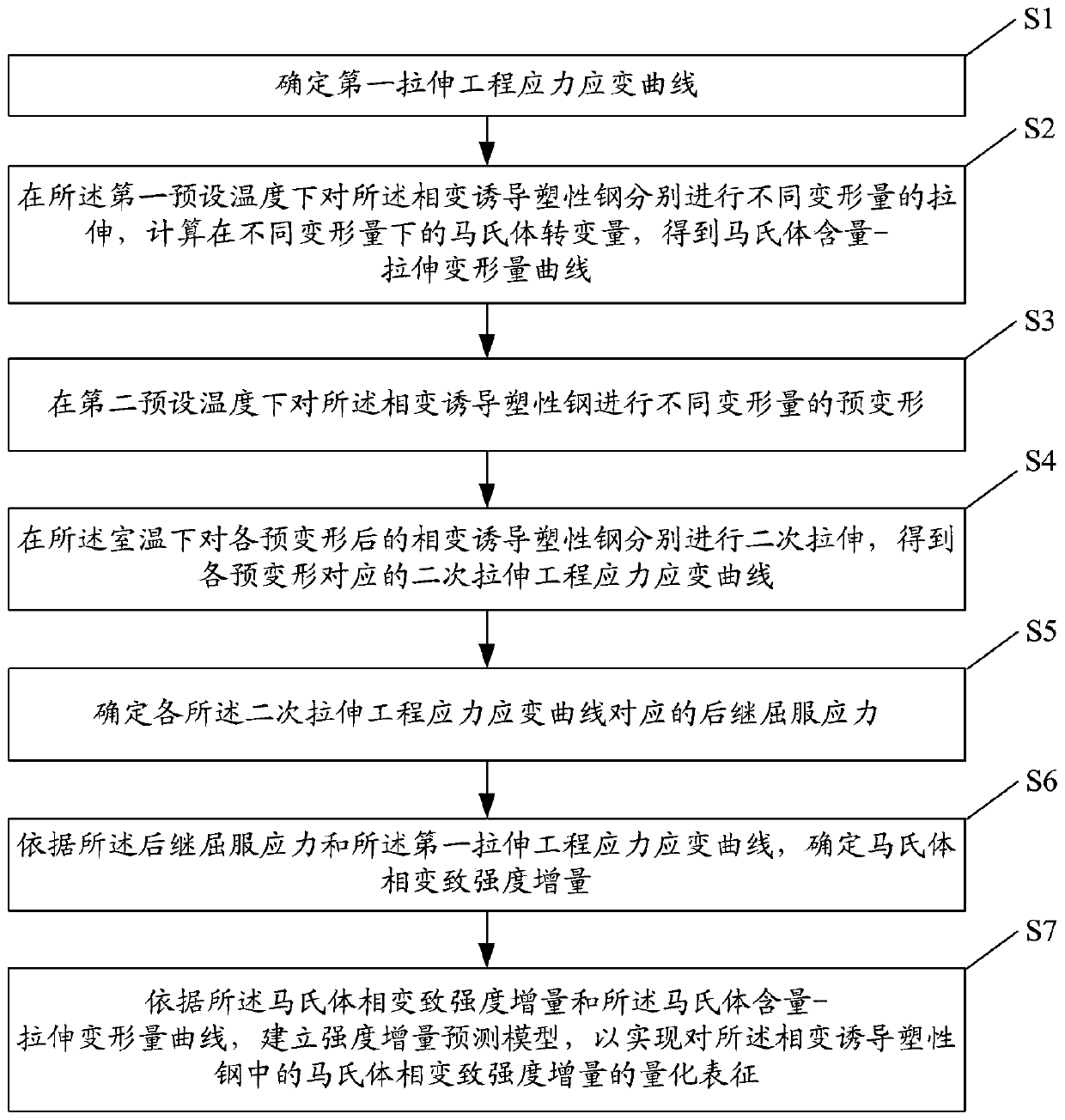
Method and system for characterization of martensitic transformation strength increment in phase transformation-induced plasticity steel
A technology of transformation-induced plasticity and martensitic transformation, applied in the field of mechanical properties to solve the problem of quantitative characterization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
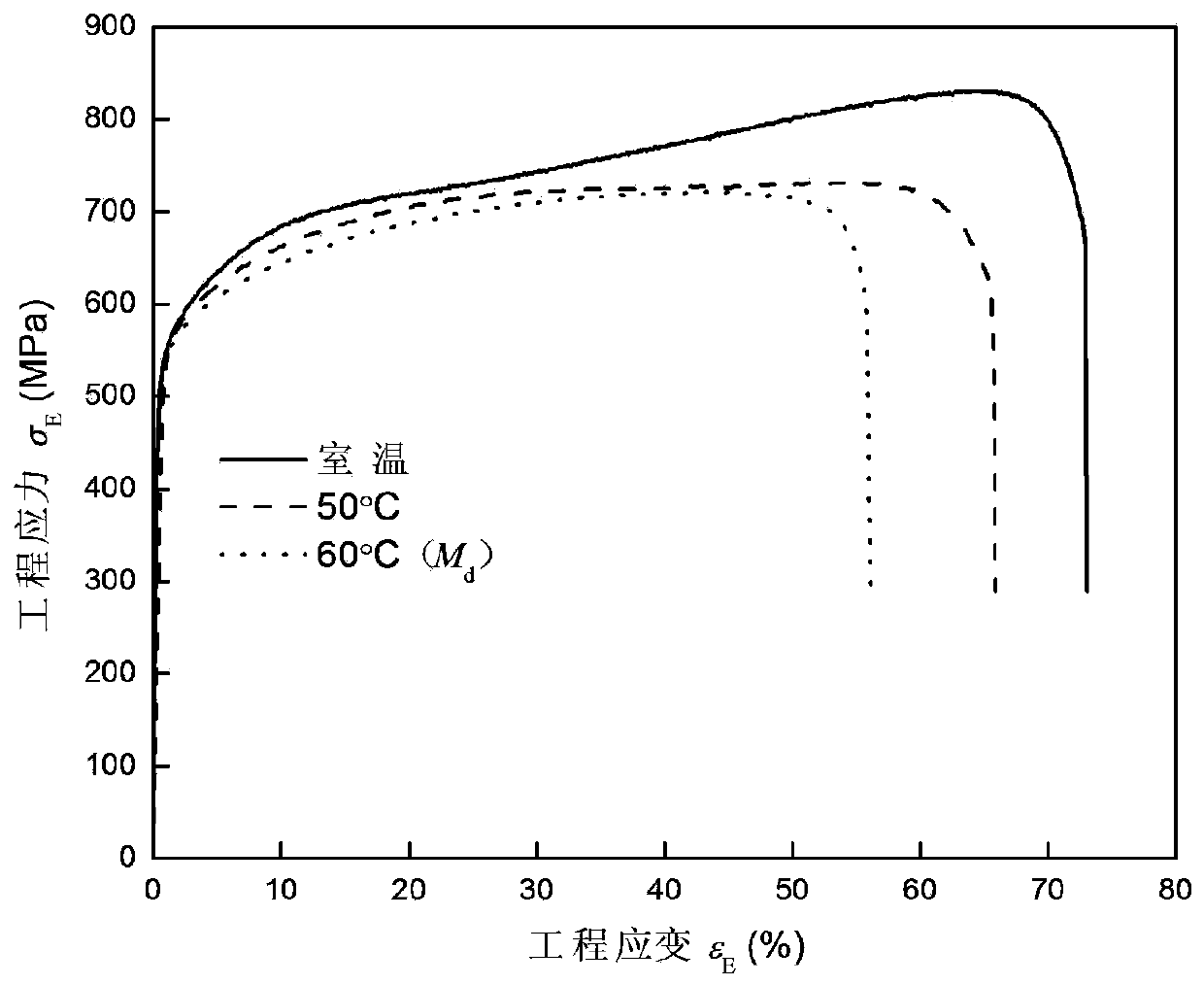
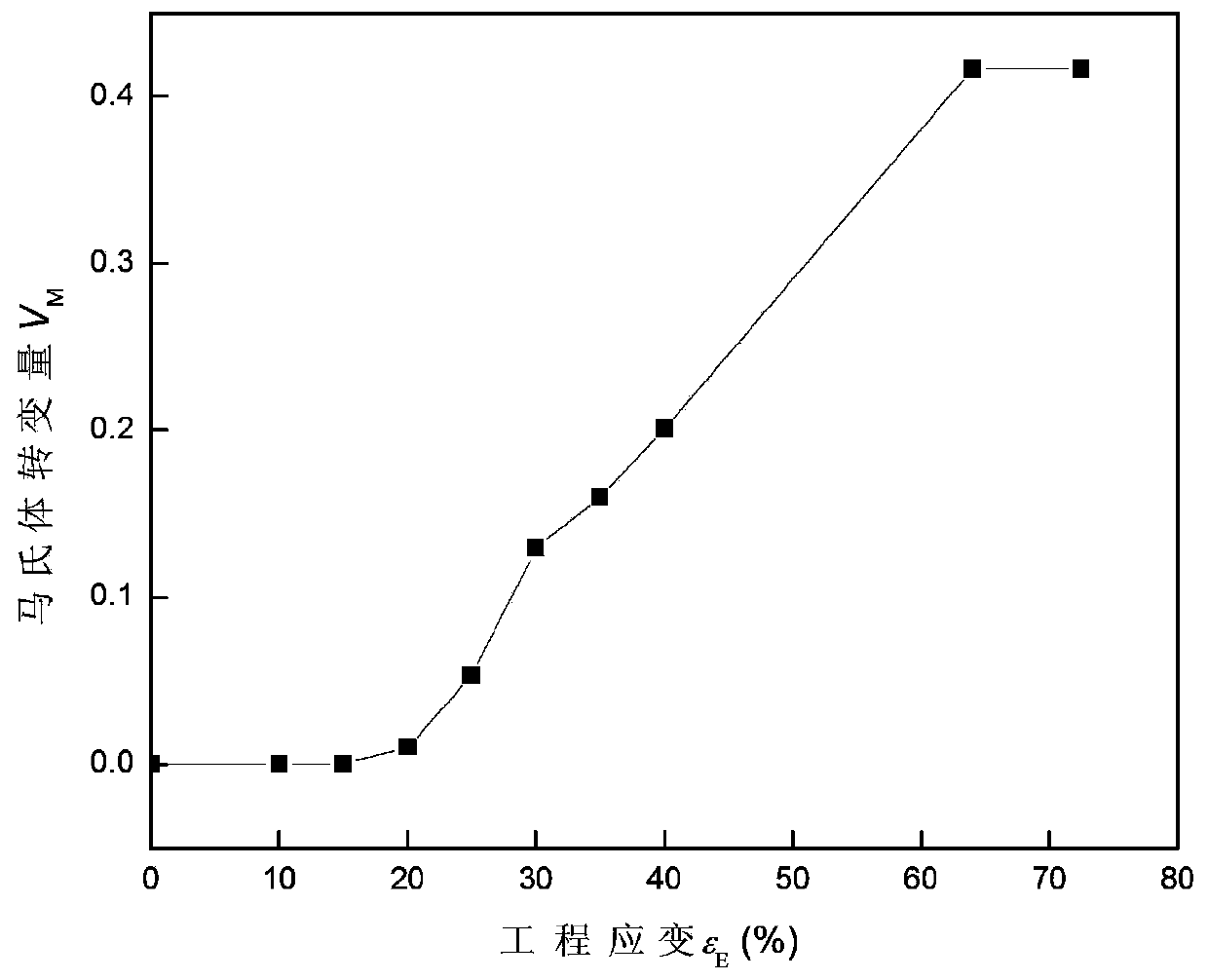
[0073] ① Explore M d value. m d The value is the critical deformation temperature of the martensite transformation of the transformation-induced plasticity steel in the process of uniaxial stretching. When the deformation temperature is lower than this temperature value, the material will experience different degrees of TRIP effect (the stress caused by the martensitic transformation The value rises twice); when the deformation temperature is higher than this temperature value, the TRIP effect of the material disappears, and no phase change occurs at this time. This critical value (generally not higher than 100°C) can be obtained by carrying out a series of high-temperature tensile tests with different deformation temperatures (in this embodiment, the strain rate is all 0.001s -1 ) to obtain the high-temperature tensile engineering stress-strain curve of phase transformation-induced plasticity steel, such as figure 2 shown. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the cri...
Embodiment 3
[0088] This example provides a characterization system for the strength increment of the martensitic phase transformation of the phase transformation-induced plasticity steel, Figure 9 It is a schematic structural diagram of the characterization system for the strength increment of the martensitic transformation of the transformation-induced plasticity steel in Example 3 of the present invention.
[0089] see Figure 9 , the phase transformation-induced plasticity steel martensitic transformation strength increment characterization system of this embodiment includes:
[0090] The first curve determination module 901 is used to determine the first tensile engineering stress-strain curve; the first tensile engineering stress-strain curve is the relationship between the tensile deformation and the stress of the phase transformation induced plastic steel at the first preset temperature Relational curve; the first preset temperature is room temperature.
[0091] The second curve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com