Cultivation system used for generation of chemically induced pluripotent stem cell and chemical reprogramming method using the same
A technology of pluripotent stem cells and culture system, applied in the direction of artificially induced pluripotent cells, non-embryonic pluripotent stem cells, cell culture active agents, etc. The effects of animal-free culture system, reduced cell loss, simplified collection and molecular mechanism analysis of competent stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
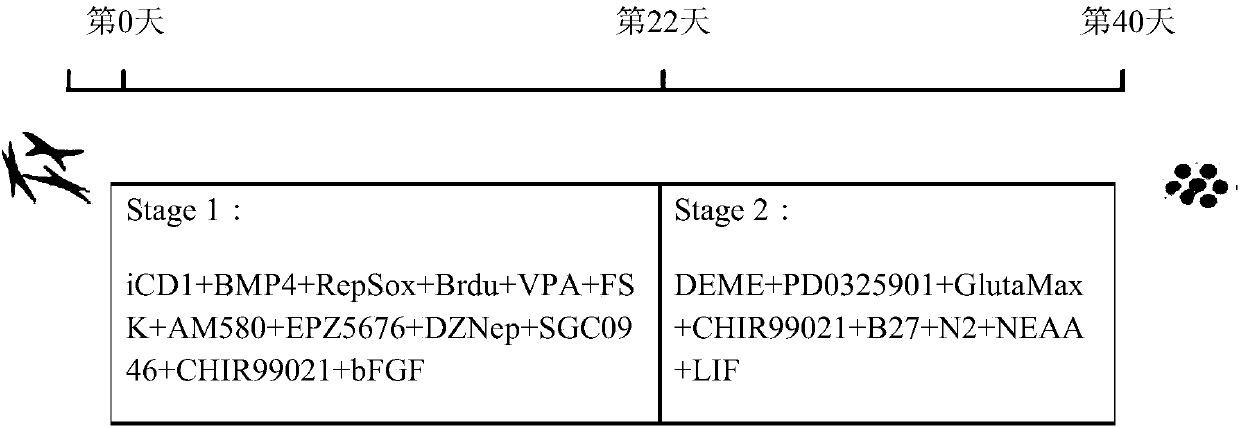
[0134] Example 1. Generation of pluripotent stem cells in a culture system for generation of chemically induced pluripotent stem cells
[0135] The above mouse embryonic fibroblasts, mouse neoplastic fibroblasts, mouse lung fibroblasts, mouse tail tip fibroblasts and mouse neural stem cells were mixed at a density of 20,000 cells / well (12 wells) or 50,000 Cells / well (6 wells) density, mouse hepatocytes were seeded at 5,000,000 / well (6-well plate) in the following chemical reprogramming medium for chemical induction of pluripotent stem cells. The medium contains iCD1 medium as basal medium and 10 ng / ml BMP4, 10 μM Brdu, 5 μM RepSox, 10 μM Forsklin, 0.1 mM VPA, 0.05 μM AM580, 5 μM EPZ5676, 0.05 μM M DZNep, 5 μM MSGC0946, 50 μg / ml vitamin C, 3 μM CHIR99021 and 10 ng / ml basic fibroblast growth factor. The medium was replaced every day, and after 22 days of culture, the above chemical reprogramming medium was replaced with the following containing N2 (100X), B27 (50X), GlutMax (...
Embodiment 2
[0136] Example 2. Characterization of chemically induced pluripotent stem cells
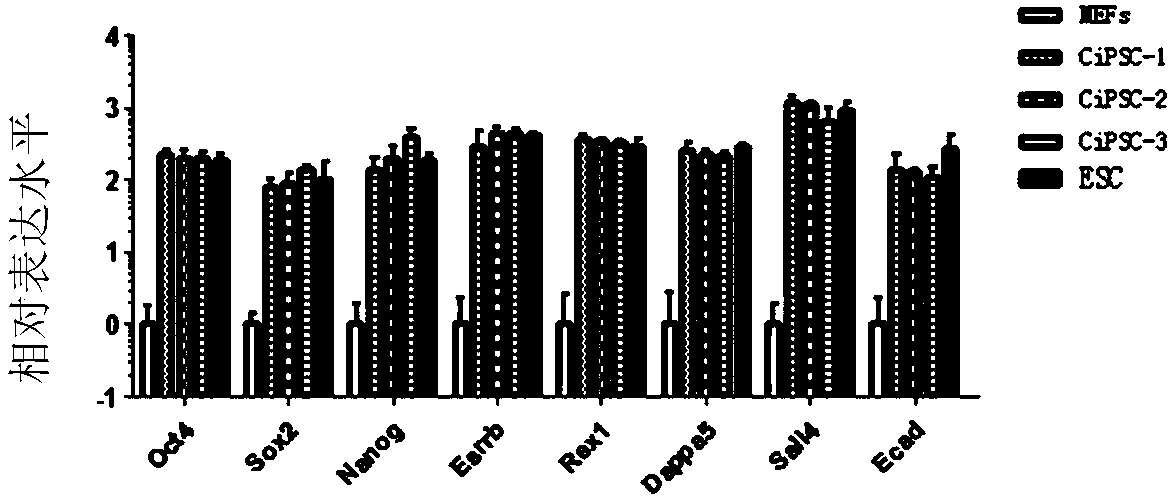
[0137] The expression levels of endogenous pluripotency genes Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, Esrb, Rex1Dappa5, Sall4 and Cdh1 in ciPSCs were monitored by quantitative RT-PCR technique. Such as figure 2 As shown, the expression levels of these endogenous pluripotency genes were the same as the expression levels of endogenous pluripotency genes Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, Esrb, Rex1Dappa5, Sall4 and Cdh1 detected in mouse embryonic stem cells.
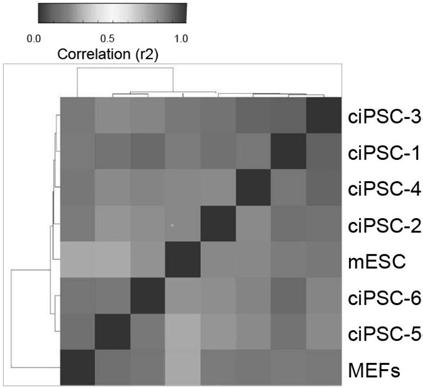
[0138] The transcriptomic properties of ciPSCs were detected by RNA-seq analysis. Such as image 3 As shown, the transcriptomic properties of ciPSCs were identical to those of mouse embryonic stem cells.
[0139] Further, as Figure 4 As shown, protein expression levels of pluripotency genes Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, Esrb and Rex1 in chemically induced pluripotent stem cells were confirmed by immunofluorescence.
Embodiment 3
[0140] Example 3. In vivo differentiation properties of chemically induced pluripotent stem cells in mice
[0141] The ciPSCs obtained in Example 1 were subcutaneously injected into NOD-SCID mice. Such as Figure 5 As shown, ciPSCs formed teratomas in mice and differentiated into cells of the three germ layers (cartilage: mesoderm; muscle: mesoderm; nerve: ectoderm; gut-like epithelium: endoderm). Such as Figure 6 As shown, ciPSCs maintained a normal karyotype during passaging. Inject ciPSCs into mouse blastocysts as Figure 7 As shown, the offspring mice are chimeric mice.
[0142] It can be seen from the above characterization results of Examples 2 and 3 that, according to the method of the present invention, the chemically induced pluripotent stem cells cultured in the culture system of the present invention have full pluripotency. It can be seen that the culture system of the present invention can effectively reprogram somatic cells to generate pluripotent stem cel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com