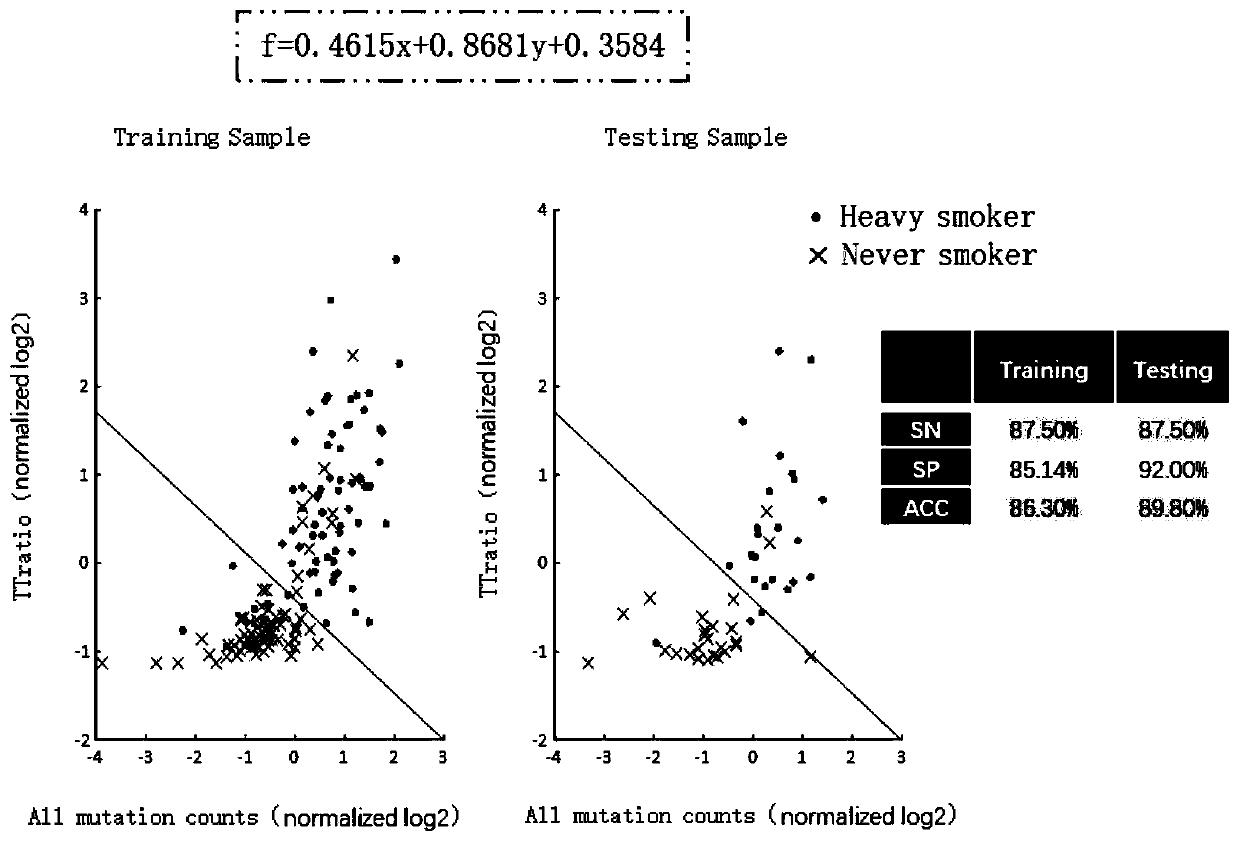
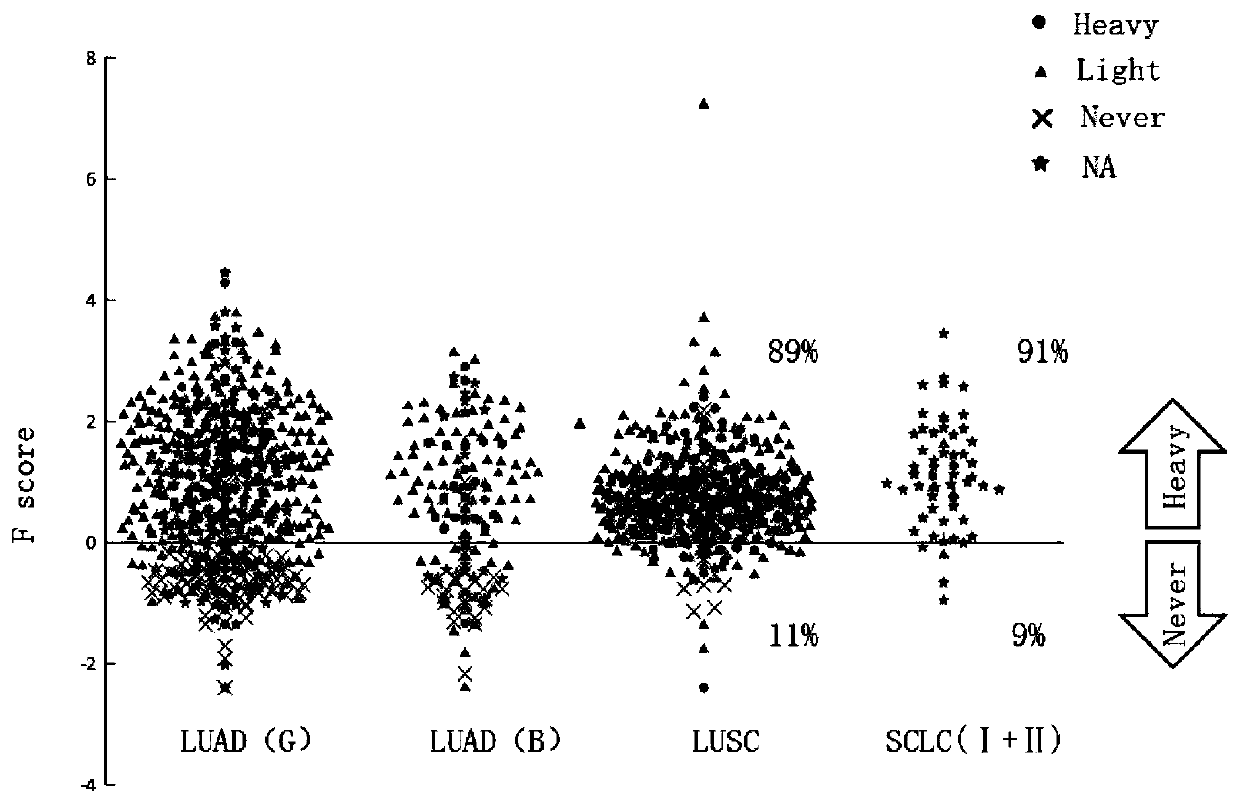
Method for quantitative evaluation of molecule mutation degree by tobacco
A quantitative evaluation and molecular technology, applied in instrumentation, genomics, proteomics, etc., can solve the problems of single index and inaccurate evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0024] This invention mainly has the following steps:
[0025] (1) Acquire data. The present invention is mainly aimed at lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). LUAD has two independent datasets: the GDC dataset is downloaded from the genome data sharing website (https: / / portal.gdc.cancer.gov / ), which is the whole exome data of somatic mutations. This data set contains a total of 567 samples as a training set for modeling; another data set comes from a literature with a total of 183 LUAD tumor samples, of which 159 exome data samples are selected as a test set (Imielinski M, et al.Mapping the Hallmarks of LungAdenocarcinoma with Massively Parallel Sequencing, in which 159 exome data are clinical data WES, which can be obtained in the supplementary file of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com