Multi-species coevolution method for solving warehousing operation optimization problem with aisles
A technology for job optimization and co-evolution, applied in logistics, biological models, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of taking into account breadth, improving diversity, improving solution accuracy and convergence efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
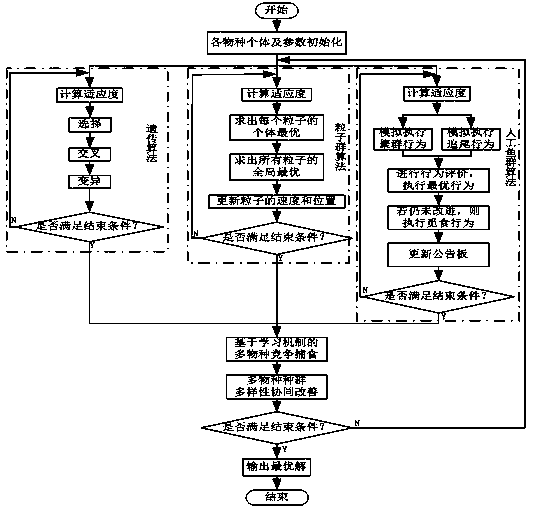
[0033] see figure 1 , the multi-species co-evolution method for solving the optimization problem of storage operations with aisles proposed by the present invention is characterized in that the following specific steps:
[0034] (1) Analyze the constraints existing on the storage site and the goals to be optimized, and abstract them into a mathematical model with constraints;
[0035] (2) Initialization parameters: overall maximum evolution algebra G_max , the maximum evolutionary algebra of each species G_pmax , evolutionary algebraic counter t , population size M, crossover probability p c , mutation probability p m , inertia weight , learning factor and , step length stepsize , the field of view of the artificial fish visual , number of attempts Try_number , crowding factor , to initialize the individual population of each species;
[0036] (3) global search, t = t +1;
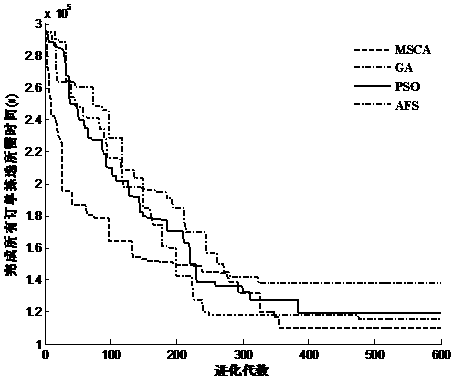
[0037] (4) Local search, genetic algorithm, particle swarm algorithm and artific...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0050] The optimization model established in the step (1) is established based on the following considerations: optimizing the picking path of the stacker for the purpose of saving energy and reducing consumption. The goal to be optimized is to complete the given order picking operation in the shortest time, and its mathematical model is expressed as follows:
[0051]
[0052] in For the target to be optimized, O A collection of picking tasks for an order, R A collection of picking paths for the stacker, It is the time required for the stacker to pass through two storage positions to be picked continuously; Indicates whether the stacker passes through the storage space continuously in a certain path and location mark of Indicates the location Is it a subpath .
Embodiment 3
[0054] see figure 1 , the multi-species co-evolution method for solving the optimization problem of storage operations with aisles proposed by the present invention, its specific steps are as follows:
[0055] 1. Establish goals and establish optimization models
[0056] The multi-aisle storage operation optimization problem in this example storage operation has the following characteristics:
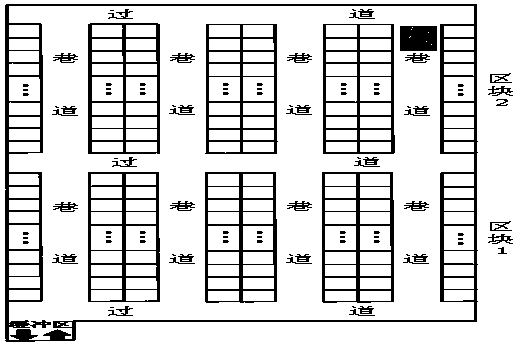
[0057] There are m relevant positions corresponding to a certain batch of orders, and their positions in the warehouse are denoted as p 1 , p 1 ,...,p m . , the storage layout of this type is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0058] Let the average speed of horizontal movement and vertical movement of the stacker be respectively , , and the horizontal and vertical movements are independent of each other, the maximum loading capacity of the stacker is C , and the length, width and height of each storage bin are respectively recorded as L , W and H . The roadway width is W 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com