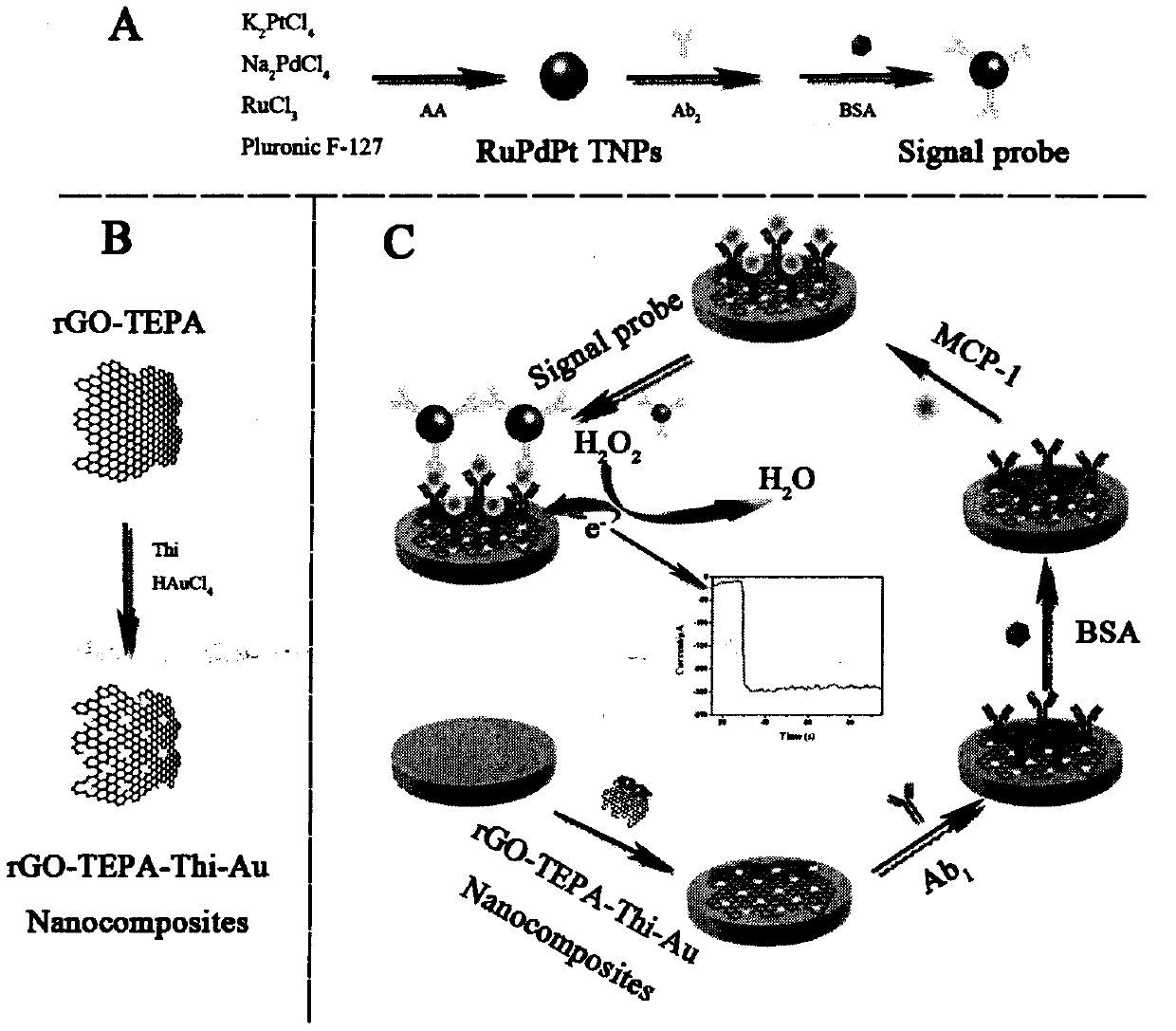
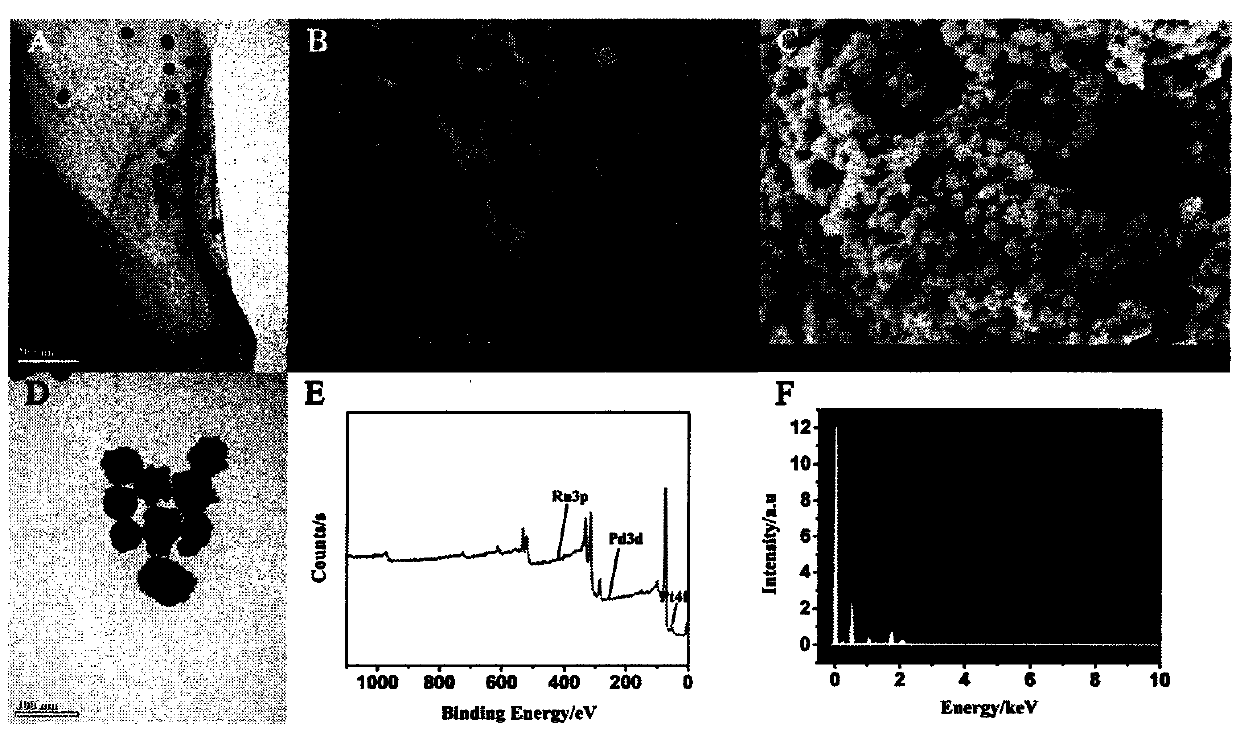
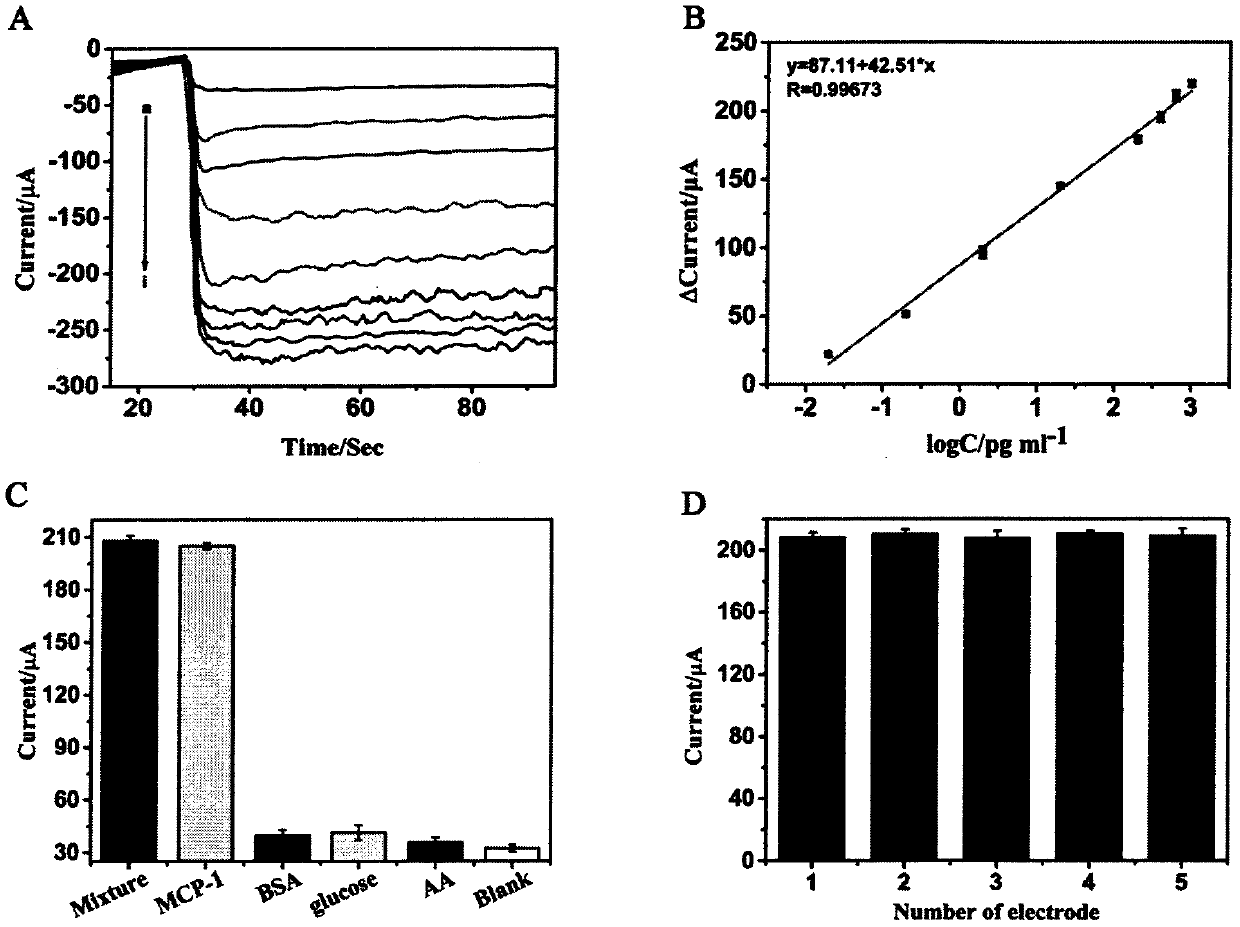
Preparation method of novel electrochemical biosensor for detecting monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
A chemoattractant protein and monocyte technology is applied in the field of preparation of a new electrochemical biosensor for detecting monocyte chemotactic protein-1, which can solve the problems of small current signal and insufficient sensitivity, and achieves improved sensitivity and detection range. , promote development, improve the effect of solid load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Step 1. First, 3mL rGO-TEPA solution (1mg mL -1 ) sonicate for at least 30 minutes. Then, 3 mL Thi (0.5 mM) and 25 μL 1% HAuCl 4 The solution was added to the above rGO-TEPA solution and vigorously stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The resultant was then collected by centrifugation at 9000 rpm for 15 minutes and washed three times with ultrapure water. The product collected by centrifugation was dissolved in 1 mL of ultrapure water and stored in a 4°C refrigerator.
[0037] Step 2. Use 0.3 and 0.05 μm Al respectively 2 o 3 Polish the electrode into a mirror surface with powder, then ultrasonically ultrasonicate the electrode for 5 minutes each in the order of ultrapure water, absolute ethanol, and ultrapure water, and dry at room temperature for later use;
[0038] Step 3. Add 10 μL of electrode modification material reduced graphene oxide tetraethylenepentamine-thionine-gold nanoparticles (rGO-TEPA-Thi-Au) composite dropwise on the surface of the electrode, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com