Independent suspension wheel type intelligent steering method
An intelligent steering, independent suspension technology, applied in the steering mechanism of the deflectable wheel, steering mechanism, non-electric variable control and other directions, can solve the problems of complex steering process, easy tire wear, large steering radius, etc., to improve flexibility. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
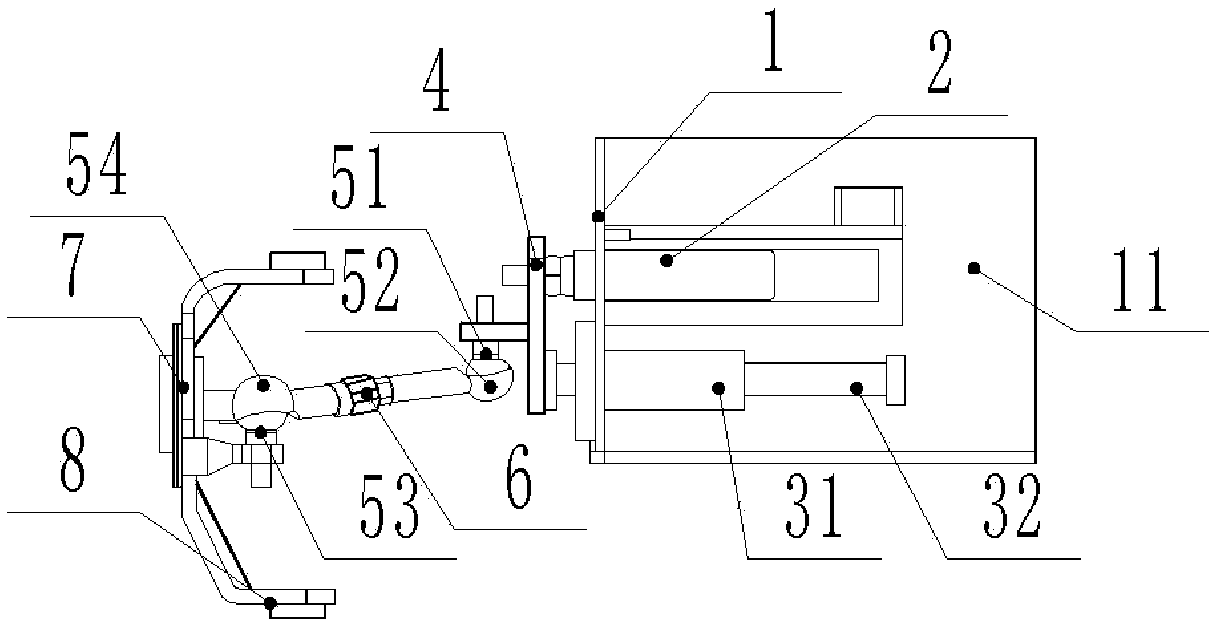
[0029] An independent suspension wheel-type intelligent steering method, which is used to control the driving mechanism of the inspection robot to drive the wheel set to realize steering. Each wheel of the wheel set is equipped with a wheel independent push rod steering system, including the following steps:
[0030] Step 1, the inspection control circuit sends a steering control signal to the drive mechanism;
[0031] Step 2, the driving mechanism drives the wheel independent push rod steering system to act separately, and the wheel independent push rod steering system controls each wheel of the wheel set to rotate independently;
[0032] Step 3: After the wheel rotation is completed, the driving mechanism drives the wheel set driving motor to work, and the wheel set driving motor drives the wheels of the wheel set to rotate to complete the steering of the wheels.
[0033] The steering method of this embodiment can not only complete the common steering mode of the inspection ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Compared with the first embodiment, this embodiment differs in that the present embodiment also includes an intelligent inspection trolley, and the intelligent inspection trolley also includes a steering adjustment mechanism.
[0048] The intelligent inspection robot has two steering methods, one is to turn on the spot, and the other is to turn while traveling. When turning in situ, the wheels are only pushed by the thrust of the push rod motor; when turning in motion, the wheels need to overcome the inertia force of the vehicle motion under the premise that the wheels are subjected to the force of the push rod motor. Therefore, the in situ steering is compared with the steering in motion , the force required when turning on the spot will be smaller, and the magnitude of the inertial force overcome by the wheels at different speeds when turning while moving is also different, and the thrust required for turning is also different. If the thrust of turning in place is sat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com