Method for realizing whole cell transformation to synthesize L-phenyllactic acid by genetic engineering strain
A genetically engineered bacteria and gene technology, applied in the field of genetically engineered strains to realize whole-cell transformation and synthesis of L-phenyllactic acid, can solve problems such as complicated operation, consumption of coenzymes, product separation, etc., and achieve broad application prospects, reduce production costs, and reduce additives. amount of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
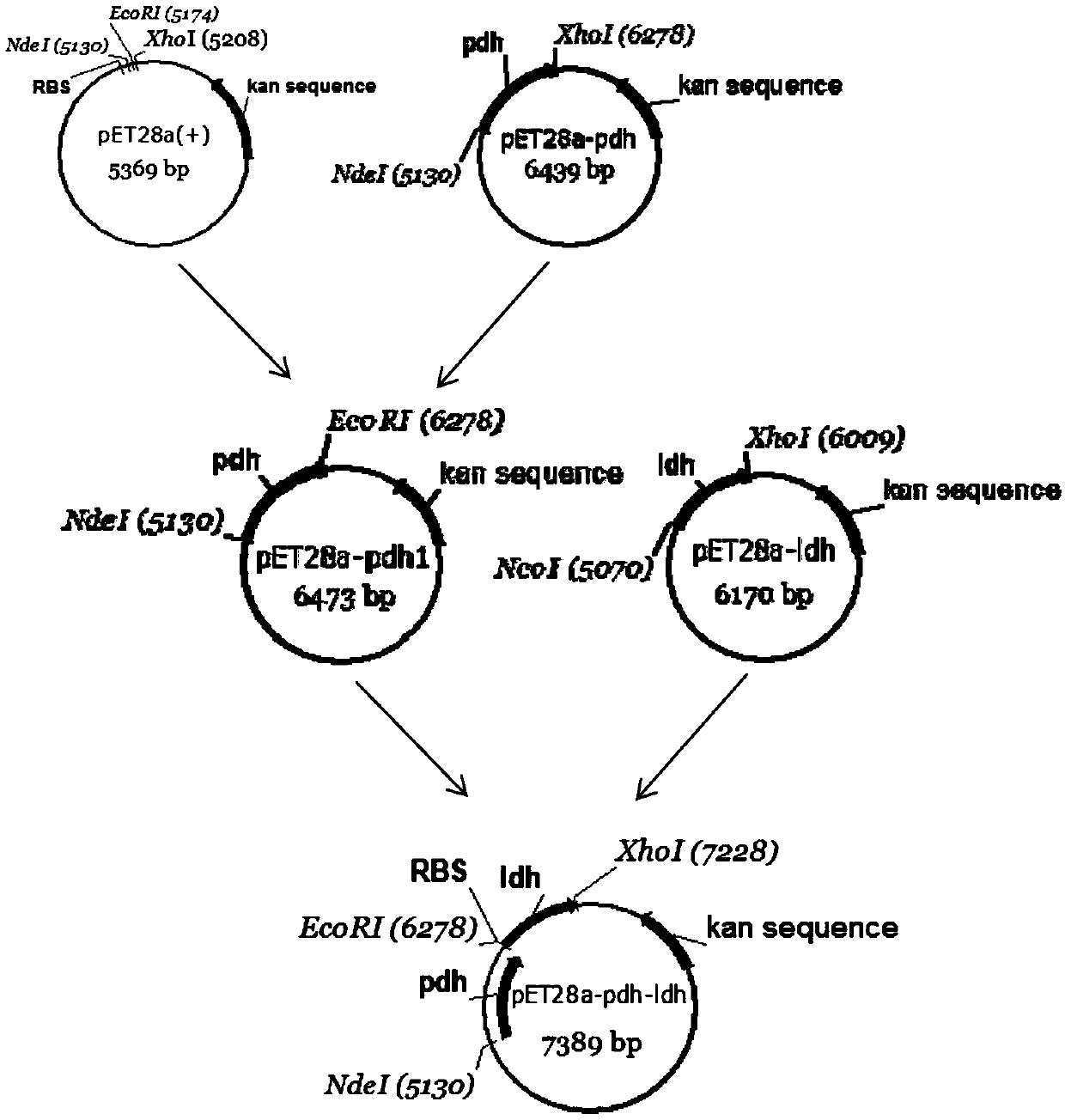
[0029] Example 1 Construction of co-expression plasmid pET28a-pdh-ldh
[0030] The phenylalanine dehydrogenase gene pdh and the L-hydroxyisocaproate reductase gene ldh were artificially synthesized. PCR amplification reaction system (50.0μL): dd h 2 O 35.5 μL, 5×Phusion HF Buffer 10.0 μL, dNTPs 1.0 μL, pdh-up / ldh-up 1.0 μL, pdh-down / ldh-down 1.0 μL, template plasmid 1.0 μL, Phusion enzyme 0.5 μL. Reaction conditions: 1) Pre-denaturation at 98°C for 30s; 2) Denaturation at 98°C for 10s; 3) Primer annealing at 68°C (pdh) / 58.5°C (ldh) for 30s; 4) Primer extension at 72°C for 35s (pdh) / 50s (ldh) (Repeat steps 2-4, cycle 30 times); 5) Continue to extend at 72°C for 7 minutes. After the PCR product was verified by agarose gel electrophoresis, impurities were removed with an agarose gel recovery kit, and the purified target gene was stored at 4°C for future use.
[0031] Table 1 Primers for amplifying gene pdh and ldh
[0032] Primer name
Primer sequence
pdh-...
Embodiment 2
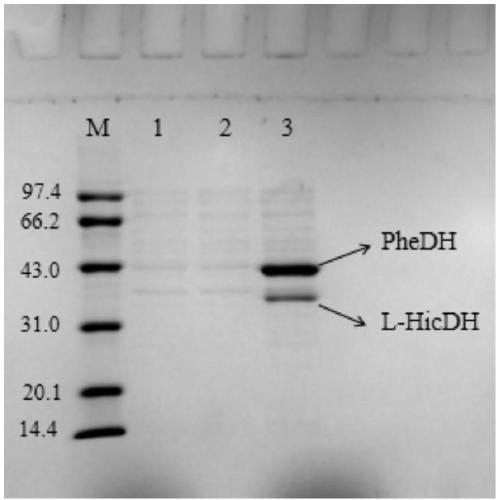
[0039] Example 2 Construction and induced expression of co-expression strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-pdh-ldh
[0040] After activating and culturing the recombinant strain E.coli DH5α / pET28a-pdh-ldh, extract the plasmid, transfer the co-expression plasmid pET28a-pdh-ldh into E.coli BL21(DE3) competent cells, and name the obtained co-expression strain is E.coliBL21(DE3) / pET28a-pdh-ldh.
[0041] The co-expression strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-pdh-ldh was inoculated into LB (containing 1.0mmol / L kanamycin) liquid medium, cultivated overnight at 37°C and 160rpm, as the seed solution. Inoculate the seed liquid into 100.0mL LB (containing 1.0mmol / L kanamycin) liquid medium with 1.0% inoculum size, shake and cultivate to OD 600 0.6, add 0.8mmol / L isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG), and cultivate at 22°C for 14h. The cultured bacterial solution was centrifuged at 4° C., 8000 rpm for 10 minutes to remove the supernatant and collect the bacterial cells. The bacterial cells were wa...
Embodiment 3
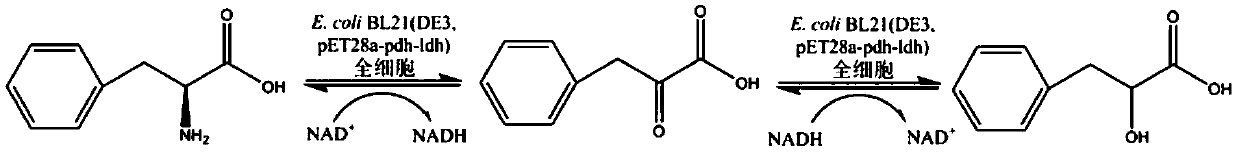
[0042] Example 3 Co-expression strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-pdh-ldh whole cell transformation to synthesize L-phenyllactic acid
[0043] Using L-phenylalanine as a substrate to convert and synthesize L-phenyllactic acid is divided into two steps: deamination reaction and reduction reaction ( image 3 ). Deamination reaction: Phenylalanine dehydrogenase deaminates L-phenylalanine to phenylpyruvate, accompanied by NAD + Conversion to NADH. Reduction reaction: L-hydroxyisocaproate reductase reduces phenylpyruvate to L-phenyllactate, at the same time, accompanied by NADH to NAD + change. Therefore, the tandem reaction of phenylalanine dehydrogenase and L-hydroxyisocaproate reductase is used to convert and synthesize L-phenyllactic acid, which can realize the cofactor NAD + and NADH self-circulation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com