Dispersion containing citrus fibers
A citrus fiber, aqueous dispersion technology, applied in animal husbandry, food science, animal feed, etc., can solve problems such as less ideal, affecting product properties and quality, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0058] ● Preparation of aqueous dispersion: by dissolving 1.00 g NaCl and 0.15 g CaCl with Type 1 RO water (18.2 MΩ / cm resistivity) 2 .2H 2 O (to make up to 1 L) to prepare standardized tap water. The conductivity was 2.21 (±0.07) mS / cm at 25°C.
[0059] Moisture content (MC) and dry matter (DS): The moisture content of fibers with a moisture content of less than 20% is determined by an automatically timed infrared moisture balance at 105°C, typically by placing 3 to 5 grams of fiber in an aluminum pan to cover its entire bottom. The moisture content of the fibers is expressed in weight percent (wt %). For fibers with higher moisture content or co-processed with food ingredients, the infrared method may be the optimized oven method, as recommended in "Develop a drying method. Reference paper. Method collection. Mettler-Toledo AG December 2014". DS is calculated according to the following formula:
[0060] DS(%)=100%-MC(%)
[0061] ●c* and stiffness: determined according ...
Embodiment 1 and 2
[0085] Citrus fibers were produced according to the examples of WO2012 / 016190 using orange pulp and lemon peels as input materials.
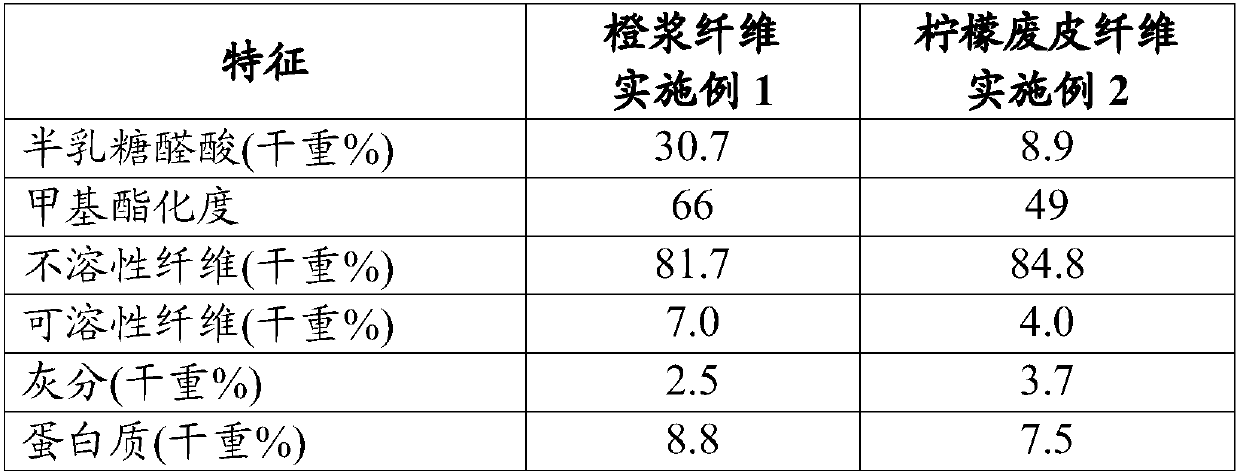
[0086] The characteristics of the orange pulp fiber and lemon peel fiber are shown in Table 1 below.
[0087] Table 1
[0088]
[0089] The normalized c* and stiffness in tap water for orange pulp fibers and lemon husk fibers are shown in Table 2 below. The fibers were dispersed in standardized water using a low shear mixer (4 blade propeller mounted on a RWD20 digital IKA mixer set at 900 rpm).
[0090] Table 2
[0091] feature
Embodiment 3
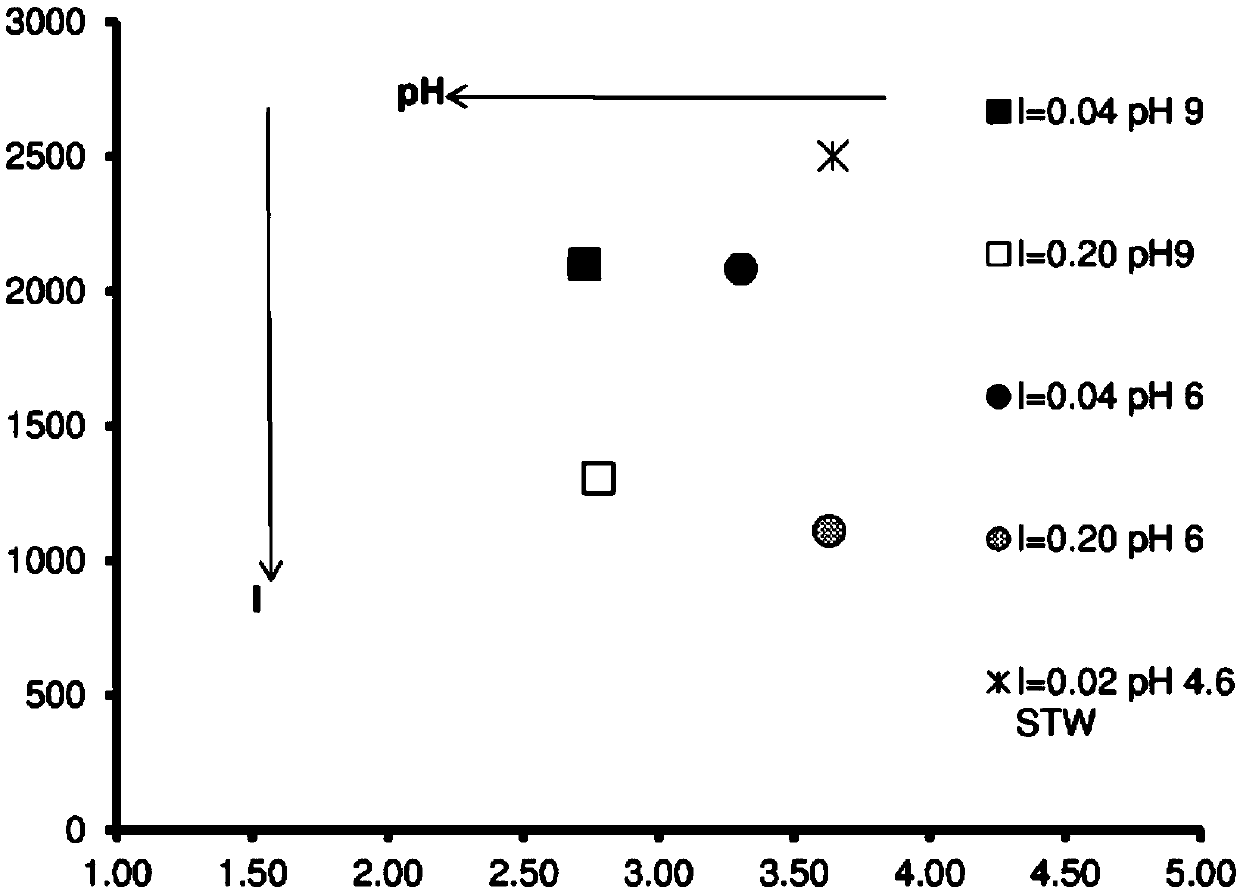
[0093] The effects of the pH value and ionic strength of the dispersion medium on the c* and stiffness of the lemon peel fibers of Example 2 were studied. An aqueous dispersion with lemon husk fibers was prepared by dispersing the fibers in standardized water with a low shear mixer (4 blade propeller mounted on a RWD20 digital IKA mixer set at 900 rpm).
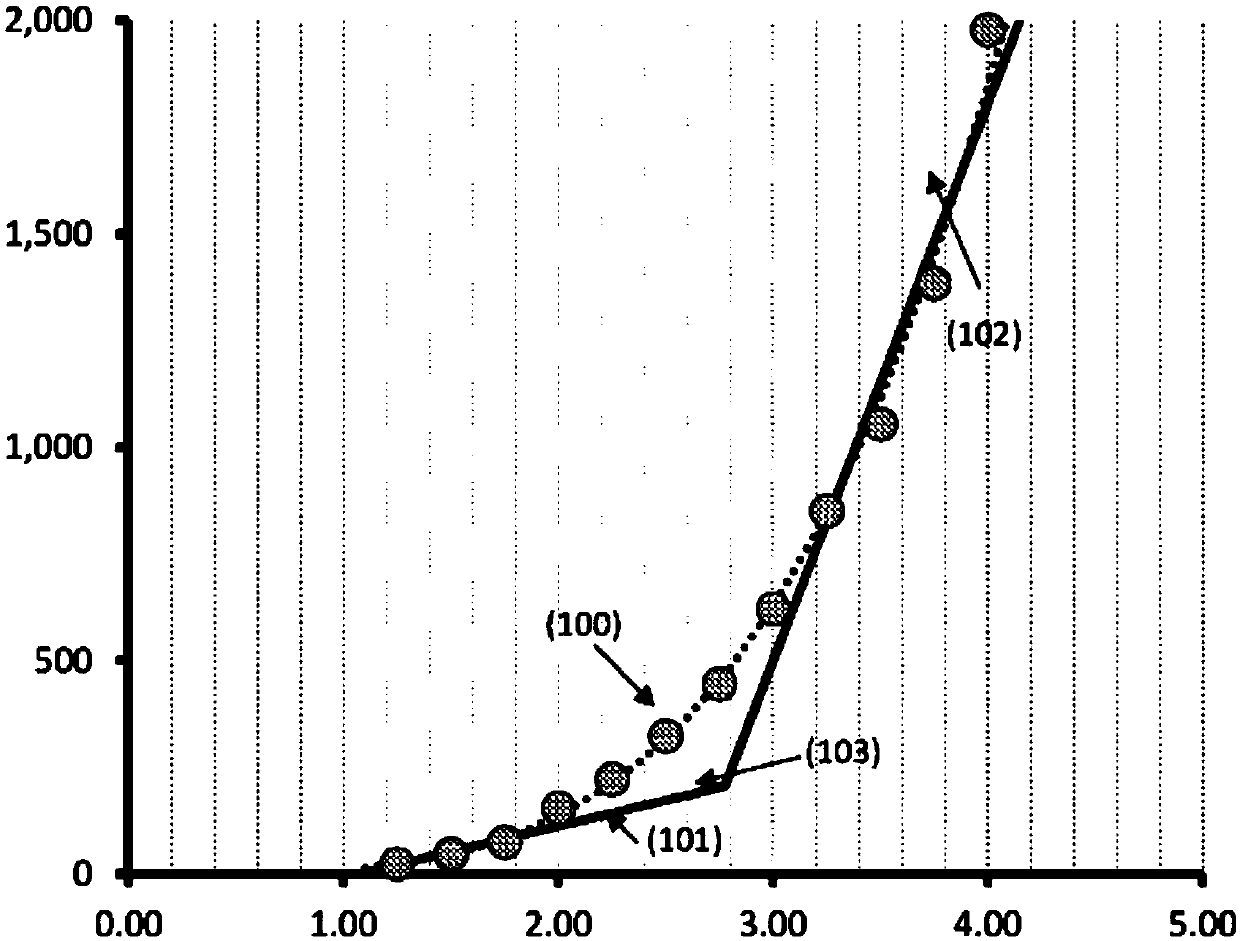
[0094] figure 2 Results are shown for stiffness versus c* as a function of both pH (pH was set to 4.6, 6.0 and 9.0) and ionic strength (I was set to 0.02-0.04-0.20). The obtained c* is between 2.72 wt% and 3.64 wt%, while the obtained stiffness is between 1109 Pa / (wt%) and 2502 Pa / (wt%). The inventors have observed that, by being able to adjust the stiffness, food designers may be able to control the textural properties of the dispersion and adjust the functional properties of the dispersion, such as dispersion stability, pumpability, etc. It may also be possible to reduce the sensitivity of the dispersion's texture to v...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com