A transfer learning method from macro expression to micro expression
A transfer learning and micro-expression technology, applied in the field of computer vision and pattern recognition, can solve problems such as limited binding force, weak strength, and unsatisfactory recognition effect, and achieve the effect of improving the recognition rate and overcoming the limited number of samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
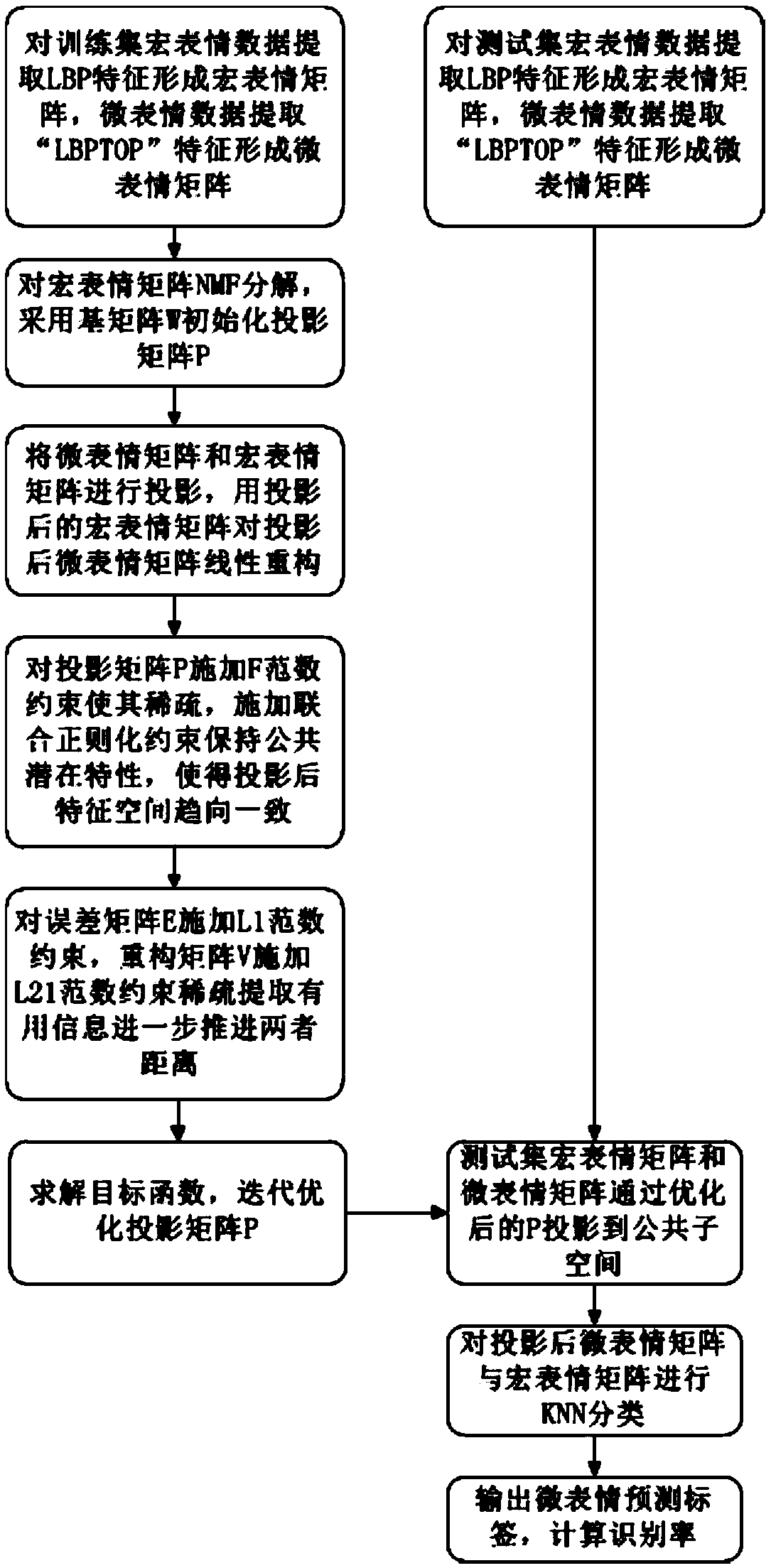
[0078] A transfer learning method from macro-expression to micro-expression, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0079] (1) Extract macro-expression features and micro-expression features respectively: extract LBP features from macro-expression to form macro-expression feature representation matrix X a , micro-expression extraction LBP-TOP features to form a micro-expression feature representation matrix X b , and take the average of the three orthogonal planes of the LBP-TOP feature. The original LBP-TOP feature is the LBP feature extracted from the three orthogonal planes of XY, XT, and YT, forming a 3*59-dimensional feature. Here, for two The dimensions of expression are unified, and the LBP features on the three orthogonal planes are accumulated and averaged to form a 59-dimensional LBP-TOP feature, forming a micro-expression representation feature that is unified with the macro-expression dimension;
[0080] (2) Project the micro-expression feature ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] According to a method of transfer learning from macro-expressions to micro-expressions described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that,
[0086] In step (2), the objective function is as shown in formula (I):
[0087]
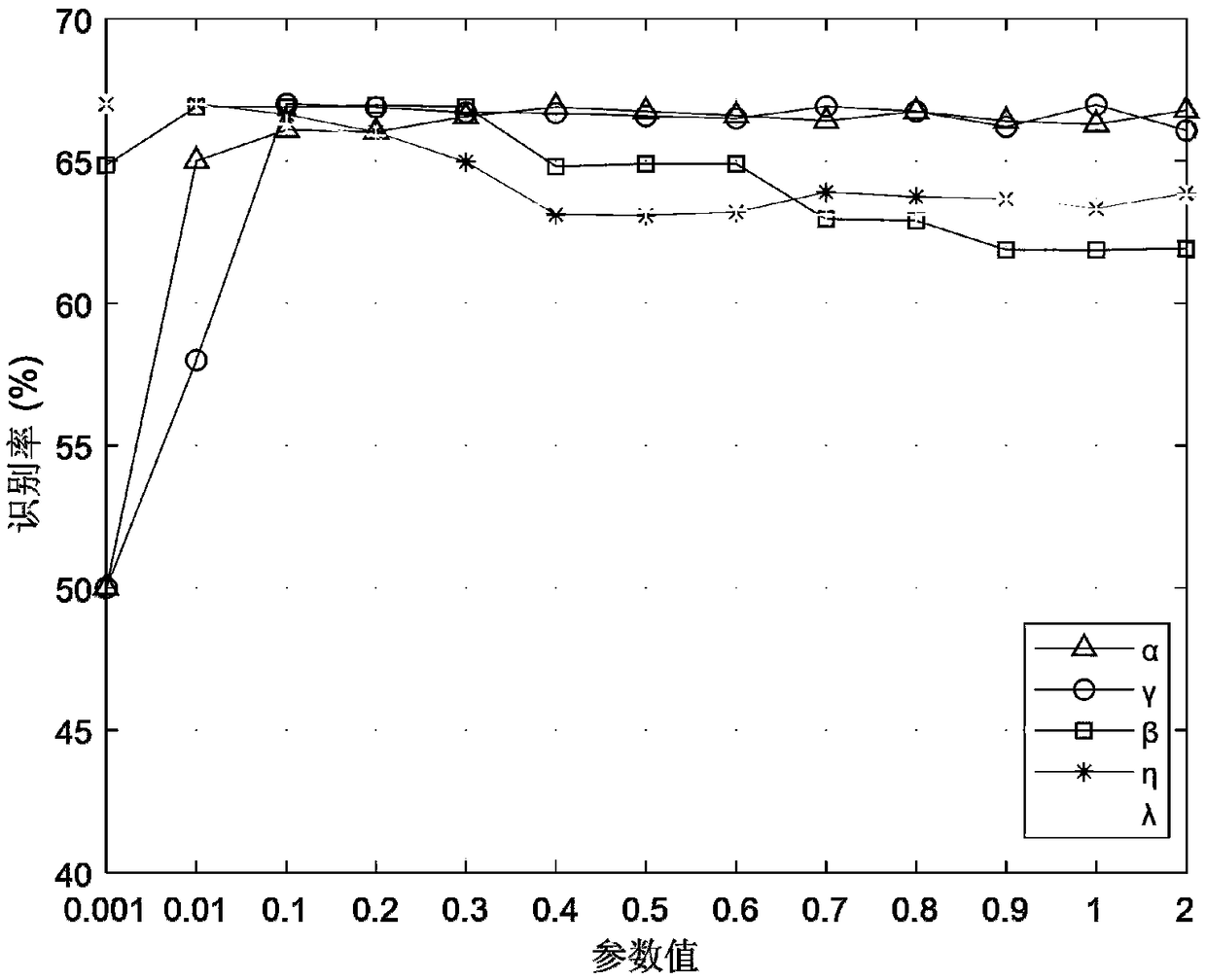
[0088] In formula (I), α, β, γ are balance coefficients, α>0, β>0, γ>0;
[0089] x a is the macro-expression feature matrix, n a Represents the number of macro expression samples, d represents the feature dimension;
[0090] x b is the micro-expression feature matrix, n b Represents the number of dimension expression samples, and d represents the feature dimension;
[0091] P∈R d×np , P is the projection matrix, np is the subspace dimension;
[0092] V is the reconstruction coefficient matrix (equivalent to the secondary projection matrix);
[0093] E is an error matrix, which stores the respective characteristic components in the macro-expression and micro-expression, and the characteristic components include their unique characteri...
Embodiment 3
[0112] According to a method of transfer learning from macro-expression to micro-expression described in embodiment 1 or 2, the difference is that
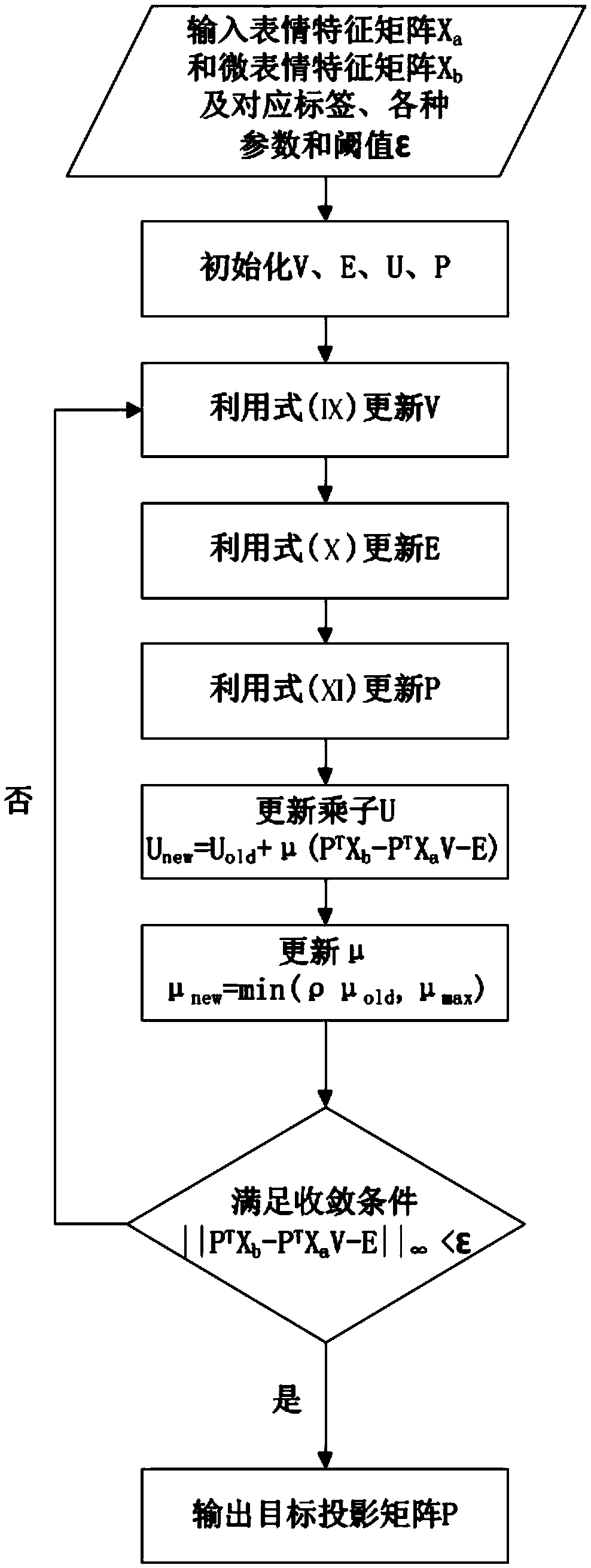
[0113] In step (3), the projection matrix P is initialized by NMF, and the target projection matrix is iteratively optimized by solving the objective function, and the target projection matrix P is output when the convergence condition is met. 1 , including the following steps:
[0114] E. Convert the objective function into an approximate form for solution: such as figure 2 said;
[0115] The objective function is shown in formula (Ⅵ):
[0116]
[0117] Considering various constraints, the objective function is non-convex, and the objective function is transformed into an approximate form, as shown in formula (VII):
[0118]
[0119] In formula (VII), Y is by the eigenvector that WY=ΛDY problem solves as the matrix that row vector forms, Λ is to form diagonal matrix as diagonal element by corresponding eigenvalue;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com