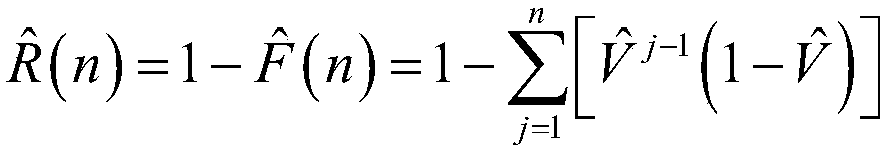Reliability evaluation method for using weapons by order
A technology of reliability and equipment, applied in the direction of instruments, special data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems that the distribution function of continuous variables cannot accurately describe the frequency variable, the theory is incomplete, and the physical meaning does not match.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
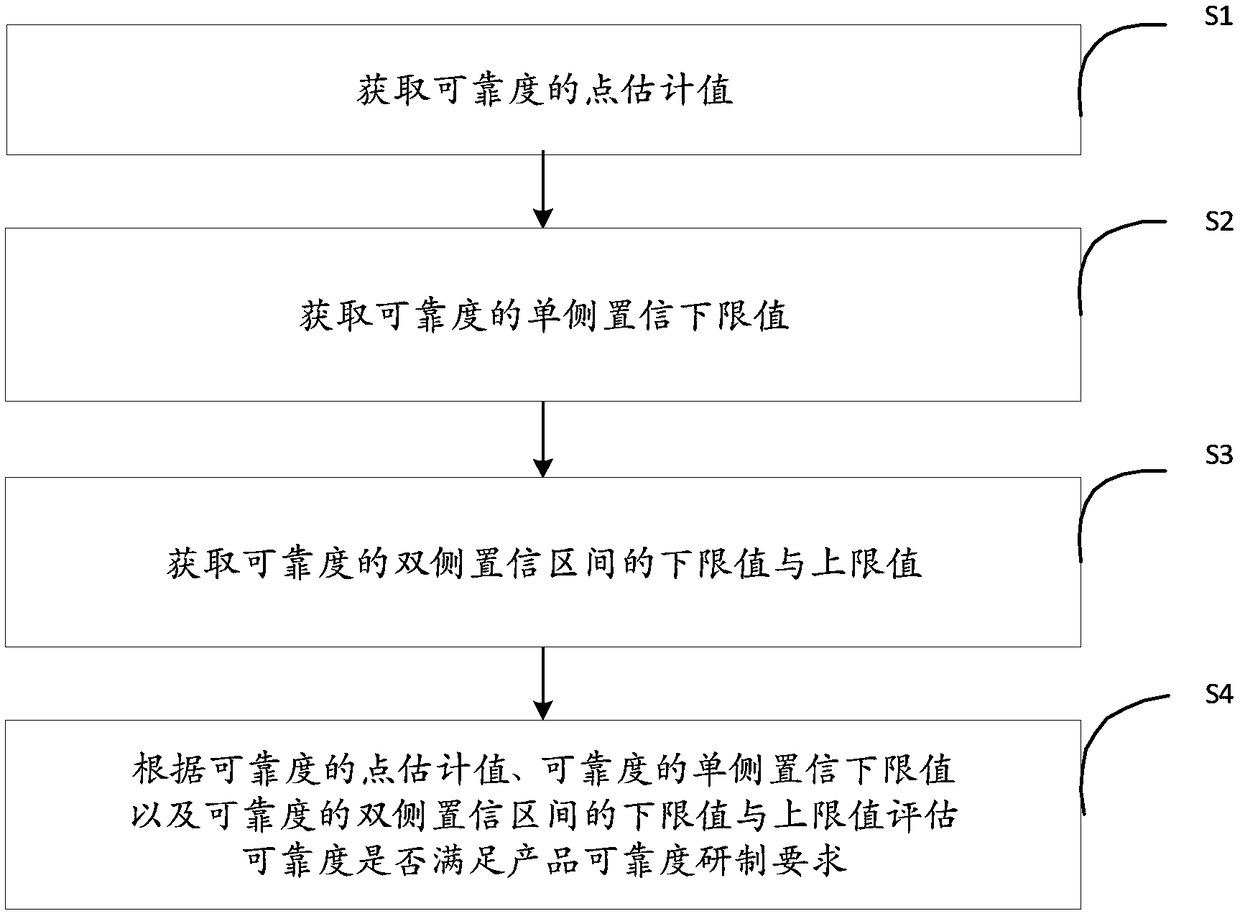
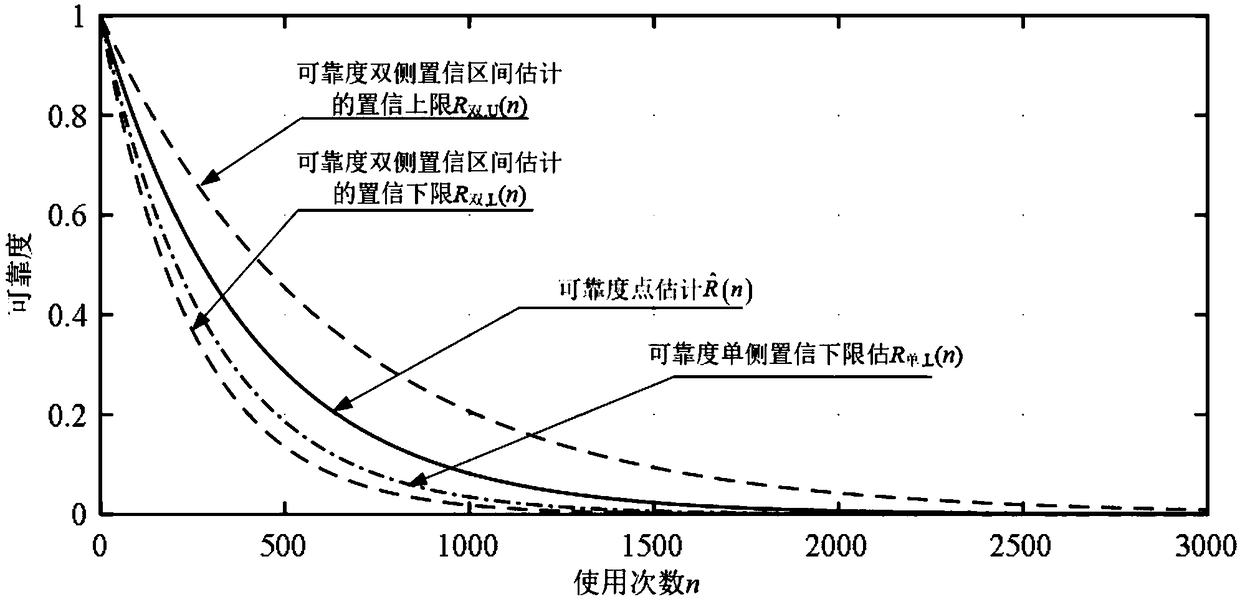
[0042] see figure 1 , which is a flow chart of a reliability evaluation method for use-by-use weaponry provided in this embodiment. A reliability assessment method for use-by-use weapons and equipment, comprising the following steps:
[0043] S1: Obtain point estimates of reliability
[0044]
[0045] in, is the probability that the weapon will fail when it is used n times, is the maximum likelihood estimate of the probability V of the armament being used without failure in a single use.
[0046] Further, the maximum likelihood estimation value of the probability V of the non-failure of the weapon equipment in a single use The way to get it is:
[0047] S101: Construct the maximum likelihood function L(V):
[0048] L(V)=V (N-Z) W Z (2)
[0049] Among them, N is the total number of effective reliability tests conducted by the weaponry, Z is the cumulative number of failures of the weaponry in N reliability tests, and V is the number of failures of the weaponry...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Based on the above embodiments, this embodiment evaluates the reliability of the catapult of a certain aircraft carrier (example needs, not real data).
[0103] Step 1. Analyze and process reliability test data
[0104] ①Assume that a carrier-based aircraft catapult has carried out a total of N=2000 reliability tests, and Z=5 failures occurred during the period (required for examples, not real data).
[0105] ② The total number of tests corresponding to the 1st to 5th failures is shown in Table 3:
[0106] table 3
[0107] Sequence of failure
1
2
3
4
5
total number of trials
F 1 =438
F 2 =981
F 3 =1415
F 4 =1792
F 5 =1996
[0108] According to the above table, the 1st to 5th failure events are counted as probability events A 1 ,A 2 ,...,A 5 , and calculate the number of continuous tests without failure before each failure, as shown in Table 4:
[0109] Table 4
[0110]
[0111] Step 2. Establish a probability ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com