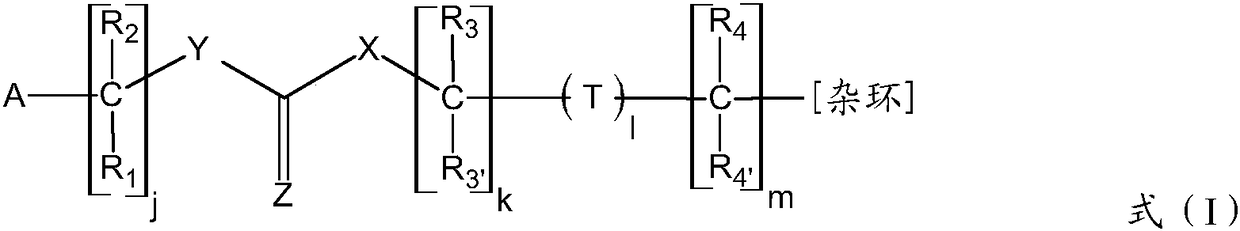
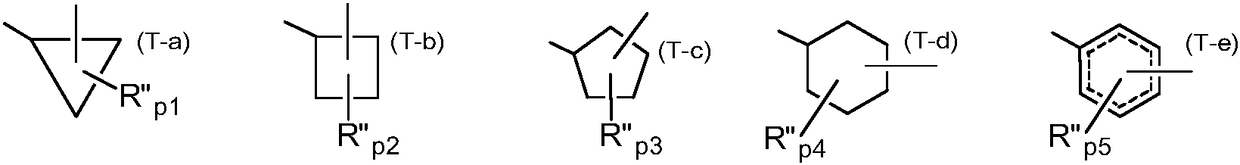
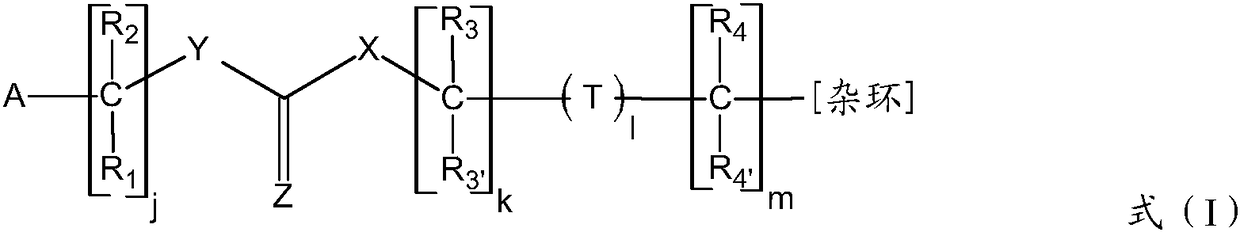
Adenine derivatives as protein kinase inhibitors
A technology for kinase inhibitors, compounds, used in medicinal chemistry and pharmaceuticals to address the problems of decline in compliance, limited efficacy, emergence of tolerance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0288] Example 1: General method for the synthesis of carbamate acyclic purine nucleoside analogs
[0289] The following procedures illustrate the preparation of several carbamate acyclic purine nucleoside analogs, and the synthetic routes are outlined below. The synthesis begins with an appropriate haloalkyl acetate at the N of the adenine ring in step (1). 9 Alkylation of the purine is performed in position and the carboethoxy group is removed in step (2). In step (3) (the final step), the carbamate acyclic nucleoside (3) is prepared by activation of the corresponding alcohol with carbonyldiimidazole (CDI), followed by reaction with an appropriate amine. The synthesis of various amine intermediates, such as that used in step (3), is shown in Example 6 below. Examples of final compound structures can be found in Table 1 below.
[0290]
[0291] Step (1): To a stirred mixture of the appropriate purine (1 eq) and cesium carbonate (1.2 eq) in anhydrous DMF (1.5 mL / mmol) wa...
Embodiment 2A
[0309] Example 2A: General method for the preparation of 2-substituted alkyl or aryl purine acyclic nucleoside analogs
[0310]
[0311] To a stirred solution of 4-(6-amino-2-chloro-purin-9-yl)butyl-carbamate derivative (0.2 mmol, 1 equiv) in dioxane (2 mL) was added (hetero ) aryl or alkyl boronic acid (R-B(OH) 2 ) or pinacol ester (R-Bpin) (0.3mmol, 1.5eq) and aqueous cesium carbonate (1M, 0.6mmol, 3eq). The reaction mixture was purged three times with nitrogen, then Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 (23mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1 equiv). The reaction mixture was warmed to 100°C overnight. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and the crude mixture was purified by flash column chromatography (0-10% MeOH in DCM) to give the expected compound.
[0312] The following compounds are exemplified to illustrate the method:
[0313] Prepared from 4-(6-amino-2-chloro-purin-9-yl)butyl N-(1,3-benzobisoxazol-5-ylmethyl)carbamate 4-[6-Amino-2-(3-furyl)purin-9-yl]butyl N-(1,3-benzobisoxazol-5-ylmeth...
Embodiment 2B
[0319] Example 2B: General method for the preparation of 2-alcoholate purine acyclic nucleoside analogs
[0320]
[0321] Step 1: Add the appropriate alcohol (30 eq) and sodium tert-butoxide (3 eq) to 4-(6-amino-2-chloro-purin-9-yl)butan prepared in step 2 of Example 1 -1-ol (1 equivalent). NOTE: In the case of methoxy, sodium methoxide (7.5 eq.) was used. The reaction mixture was heated in microwave to 100-150°C until completion (10-90 min). The solvent was then evaporated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified by flash column chromatography (0-10% MeOH in DCM) to give the expected compound.
[0322] The following compounds are exemplified to illustrate step 1:
[0323] Prepared from 4-(6-amino-2-chloro-purin-9-yl)butan-1-ol (241 mg, 1.0 mmol) after microwave irradiation at 100 °C for 10 min 4-(6-Amino-2-methoxy-purin-9-yl)butan-1-ol . Yield: 172 mg (73%) of the title compound as a white powder. ESI-MS: 238.3 (M+H) + .
[0324] Prepared from 4-(6-amin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com