Method for optimizing public traffic network
A technology of public transportation and optimization methods, applied in genetic rules, instruments, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as falling into local optimal solutions, achieve the effect of overcoming common shortcomings, improving convergence conditions, and avoiding falling into local optimal solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
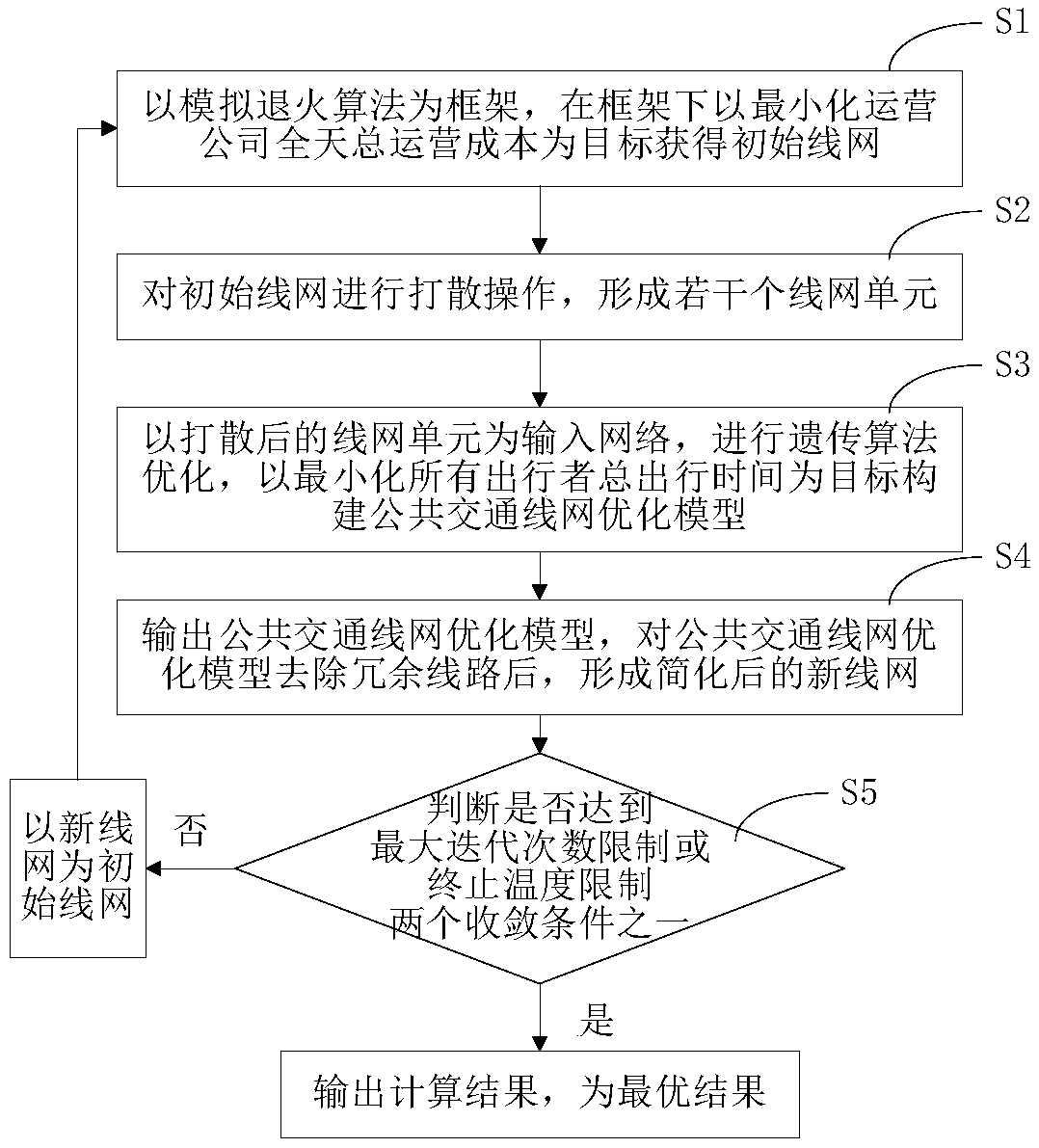
[0052] This embodiment provides a method for optimizing a public transportation network. The method optimizes the public transportation network on the basis of the original network, and has the characteristics of dual temperature control, reversible network, genetic nested simulated annealing, and the like. figure 1 Shown is a schematic flow chart of the public transportation network optimization method described in this embodiment. Such as figure 1 Shown, described public transport line network optimization method comprises the following steps:
[0053] Step S1, using the simulated annealing algorithm as the framework, under the framework to minimize the total operating cost of the operating company throughout the day to obtain the initial network;
[0054] Step S2, performing a disintegration operation on the initial wire mesh to form several wire mesh units;
[0055] Step S3, taking the dispersed network units as the input network, constructing a public transportation net...
no. 2 example
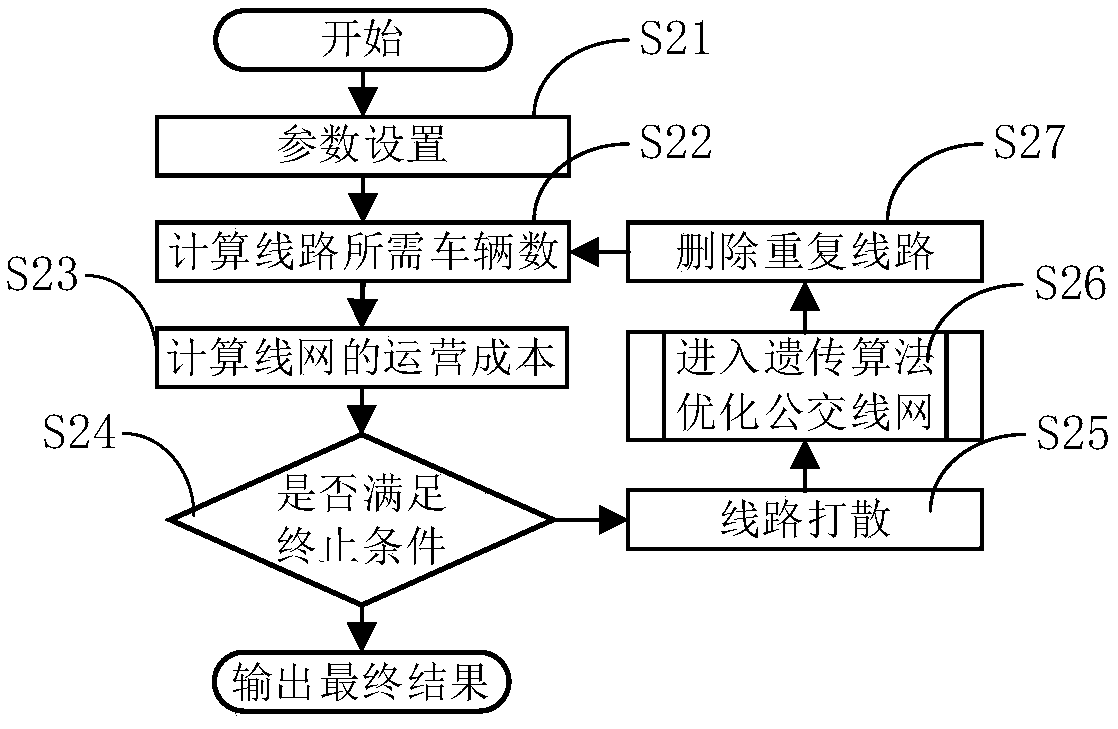
[0061] This embodiment provides a method for optimizing a public transport network, figure 2 Shown is a schematic flow chart of the method for optimizing the public transport network described in this embodiment. Such as figure 2 As shown, the public transport network optimization method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0062] Step S21, parameter setting.
[0063] Further, in this step, the following parameters are set: initial temperature (T 0 ), termination temperature (T stop ), the maximum number of iterations (I 1 ), annealing control rate (D 1 ), control temperature (T c ), return temperature (T p ), iteration return rate (D 2 ) and cost difference control variable (C A ).
[0064] Preferably, set T in this embodiment 0 The value is 100, T stop The value is 0, I 1 The value is 500, D 1 The value is 0.97, D 2 The value of 0.94; C A It is 33.00% of the operating cost of the smallest line network that has been found.
[0065] I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com