Radix angelicae sinensis and radix astragali treatment reagent for treating early diabetic nephropathy and preparation method
A technology for treating diabetic nephropathy and a therapeutic agent is applied in the field of therapeutic agent and preparation of Angelica astragalus for the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy, and can solve the problems of inability to effectively regulate the condition, inability to stop antihypertensive drugs at will, and high medical expenses, and to improve the clearance of creatinine. rate, reduced nephrotoxic damage, reduced damage effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
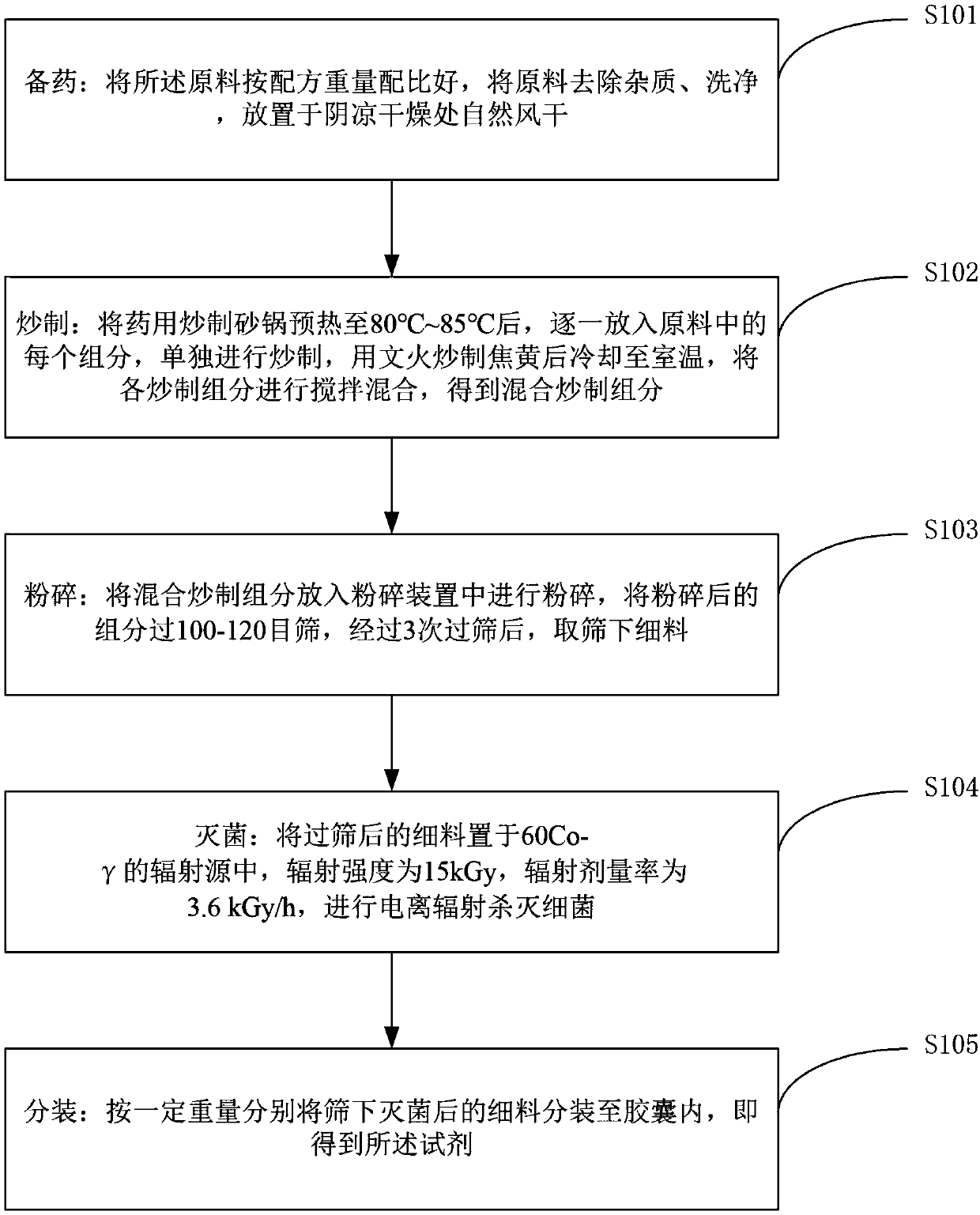
[0049] like figure 1 As shown, the preparation method of the Chinese medicine compound reagent for the prevention and treatment of gout provided by the embodiments of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0050] S101: Prepare the medicine: mix the raw materials according to the weight ratio of the formula, remove impurities from the raw materials, wash them, and place them in a cool and dry place to dry naturally;
[0051] S102: Frying: Preheat the medicinal frying casserole to 80°C to 85°C, put each component in the raw material one by one, fry separately, stir fry with a slow fire until it turns brown, cool to room temperature, and fry each component The components are stirred and mixed to obtain the mixed and fried components;
[0052] S103: Pulverization: put the mixed and fried components into a pulverization device for pulverization, pass the pulverized components through a 100-120 mesh sieve, and after 3 times of sieving, take the fine material under t...
Embodiment 1
[0103] Example 1: 10 parts of angelica, 11 parts of astragalus, 8 parts of Poria cocos, 3 parts of ginseng, 4 parts of codonopsis, 8 parts of Atractylodes macrocephala, 2 parts of corn silk, 6 parts of tangerine peel, 10 parts of cohosh, 10 parts of bupleurum, and 8 parts of licorice , 15 parts of japonica rice, 12 parts of Anemarrhena, 4 parts of Ophiopogon japonicus, 15 parts of kudzu root, 15 parts of Rehmannia glutinosa, 9 parts of Achyranthes bidentata, 15 parts of plantain, 10 parts of Chuanxiong, 10 parts of salvia miltiorrhiza, and 7 parts of fairy grass.
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2: 15 parts of angelica, 11 parts of astragalus, 8 parts of Poria cocos, 4 parts of ginseng, 6 parts of codonopsis, 7 parts of Atractylodes macrocephala, 4 parts of corn silk, 10 parts of tangerine peel, 12 parts of cohosh, 13 parts of bupleurum, and 10 parts of licorice , 18 parts of japonica rice, 12 parts of Anemarrhena, 8 parts of Ophiopogon japonicus, 15 parts of kudzu root, 15 parts of Rehmannia glutinosa, 13 parts of Achyranthes bidentata, 10 parts of plantain, 6 parts of Chuanxiong, 8 parts of salvia miltiorrhiza, and 8 parts of fairy grass.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com