Groove avoiding method for two-dimensional lidar patrol robot
A two-dimensional laser radar and inspection robot technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as inability to obtain groove information, inability to operate safely, and inability to obtain groove data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
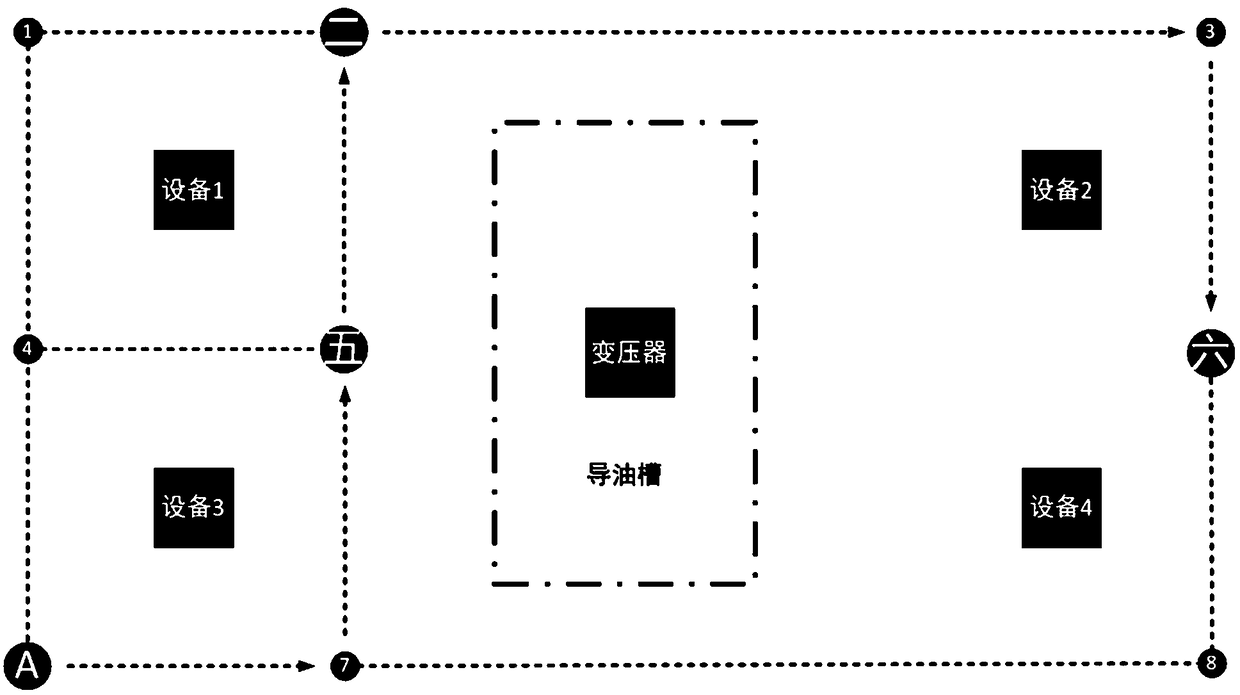
[0034] The present invention proposes a method for a two-dimensional laser radar inspection robot to avoid the groove, which realizes that when the inspection robot switches from the manual operation mode to the automatic inspection mode, it can smoothly return to the position defined by the network structure diagram, thereby continuing the inspection robot Automatic inspection work, such as figure 1 As shown, the following setting method is adopted in particular: In the automatic mode, the inspection robot merges the groove electronic map into the electronic map scanned by the inspection robot through the SLAM algorithm before path planning, and then performs path planning.
[0035] As a preferred design solution, when the manual mode is converted to the automatic mode, in the automatic mode, the inspection robot merges the groove electronic map into the electronic map scanned by the inspection robot through the SLAM algorithm before path planning, and then Carry out path plan...
Embodiment 2
[0037] This embodiment is further optimized on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments. In order to better realize the present invention, the following setting method is adopted in particular: the electronic map of the groove is added on the input side of the path planning module, as a preferred In the design scheme, an electronic map of grooves is added on the input side of the path planning module, so that the purpose of reducing the amount of computation in the path planning and screening process can be achieved.
Embodiment 3
[0039] This embodiment is further optimized on the basis of any of the above-mentioned embodiments. Further, in order to better realize the present invention, the following configuration method is adopted in particular: the method includes the following specific steps:
[0040] 1) The inspection robot scans the electronic map through the SLAM algorithm, SLAM algorithm, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) real-time positioning and map construction algorithm;
[0041] 2) Load the groove electronic map in the electronic map obtained in step 1); when loading the groove electronic map, use robot positioning + manual collection to form an xml file as the groove electronic map;
[0042] 3) Engineers lay out the network structure diagram on the basis of the electronic map formed in step 2; when laying out the network structure diagram, use robot positioning + manual collection, and then form it by manual editing;
[0043] 4) The inspection robot performs path planning in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com