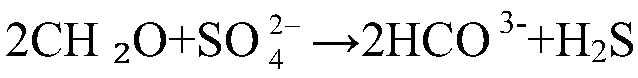Microbial remediation method of heavy-metal-contained waste residue stockpiling site
A microbial remediation and heavy metal technology, applied in the restoration of contaminated soil, etc., can solve the problems of slow heavy metal removal speed, short storage time, low plant survival rate, etc., and achieve the effect of optimizing large-scale cultivation, high efficiency, and quick results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
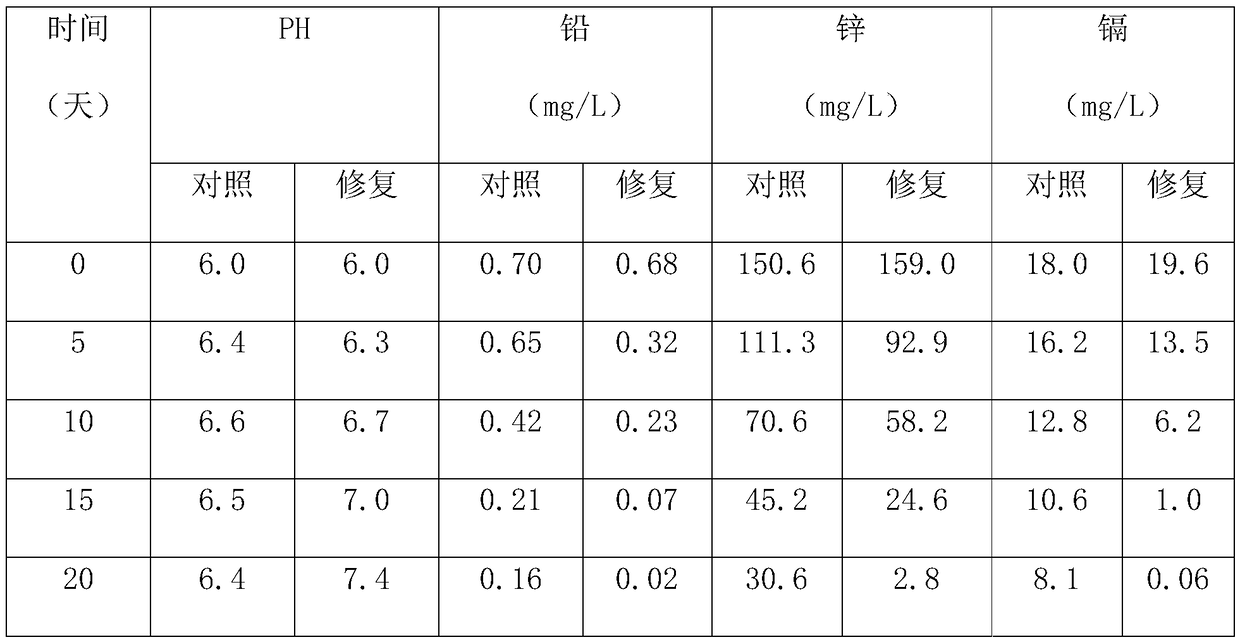
[0037] a. Acidophilic bacteria and sulfate-reducing bacteria were collected from the soil of tailing ponds of Guangxi nonferrous metal beneficiation enterprises;
[0038] b. Crush sweet sorghum stalks and place them in a fermenter, mix them with lactic acid bacteria at a ratio of 200:1, add water and stir evenly, keep the water at 50%, and ferment in a sealed container for 3 days for later use;
[0039]c. After the fermentation is completed, take out the sweet sorghum stalk fermentation liquid, add magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.4g / L, ammonium sulfate 1.2g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.6g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.4g / L , slowly and intermittently add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 6, the preparation of the medium is completed, and the medium is placed in an anaerobic culture bottle for high-pressure steam sterilization, the sterilization pressure is 105kPa, the temperature is 118°C, and the sterilization is 25min;
[0040] d. Mix the soil contaminated by ...
Embodiment 3
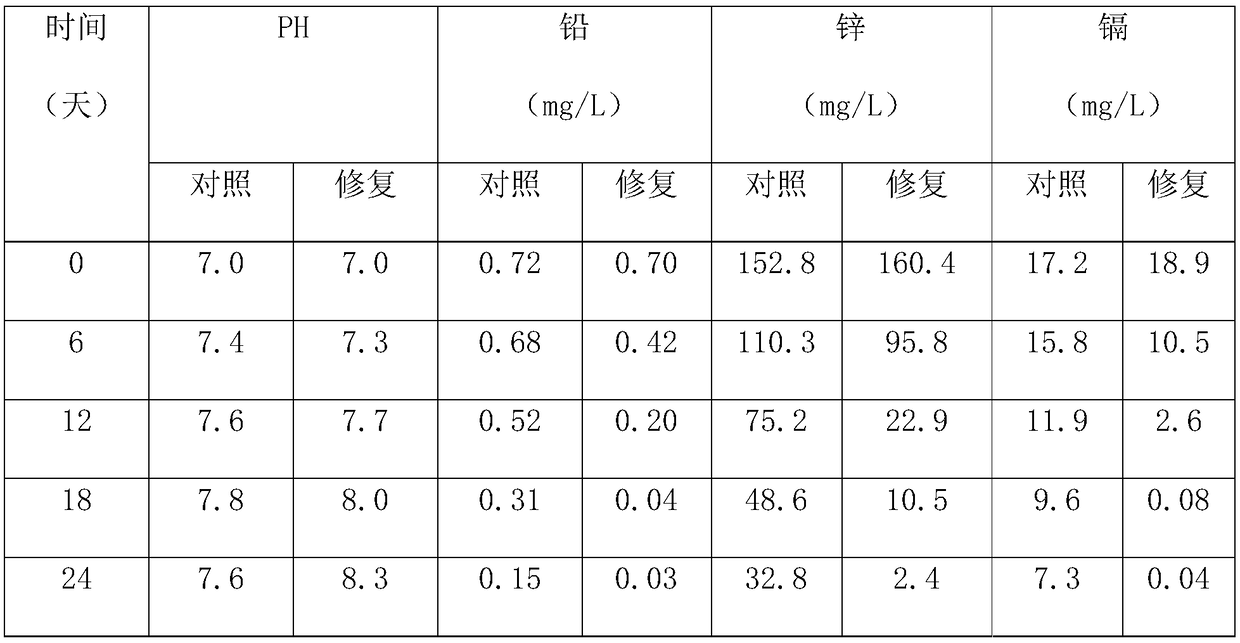
[0057] a. Acidophilic bacteria and sulfate-reducing bacteria were collected from the soil of tailing ponds of Guangxi nonferrous metal beneficiation enterprises;
[0058] b. Crush sweet sorghum stalks and put them in a fermenter, mix them with lactic acid bacteria at a ratio of 250:1, add water and stir evenly, keep the water at 40%, and ferment naturally for 4 days for later use;
[0059] c. After the fermentation is complete, take out the fermented sweet sorghum stalk, add magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.5g / L, ammonium sulfate 1.0g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.5g / L , slowly and intermittently add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 7, the preparation of the medium is completed, and the medium is placed in an anaerobic culture bottle for high-pressure steam sterilization with a sterilization pressure of 103kPa and a temperature of 121°C for 20 minutes;
[0060] d. Mix the soil polluted by heavy metal waste slag with the culture me...
Embodiment 4
[0067] a. Acidophilic bacteria and sulfate-reducing bacteria were collected from the soil of tailing ponds of Guangxi nonferrous metal beneficiation enterprises;
[0068] b. Crush sweet sorghum stalks and place them in a fermenter, mix them with lactic acid bacteria at a ratio of 250:1, add water and stir evenly, keep the water at 50%, and ferment naturally for 4 days for later use;
[0069] c. After the fermentation is complete, take out the fermented sweet sorghum stalk, add magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.5g / L, ammonium sulfate 1.1g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.5g / L , slowly and intermittently add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 7, the preparation of the medium is completed, and the medium is placed in an anaerobic culture bottle for high-pressure steam sterilization with a sterilization pressure of 105kPa and a temperature of 120°C for 20 minutes;
[0070] d. Mix the soil polluted by heavy metal waste slag with the culture ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com