Rice processing technology
A rice processing and technology technology, applied in the field of invention, can solve the problems of low rice cleanliness, low rice processing quality, incomplete filtering of impurities, etc., so as to reduce the broken rice rate, increase the quality, and increase the service life. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
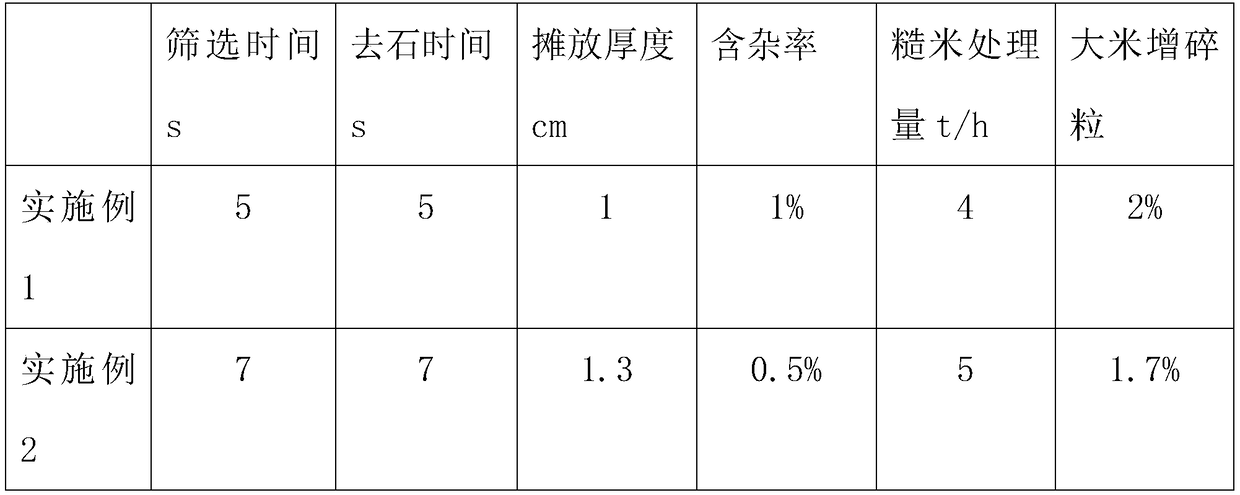
[0030] (1) Screening, put the harvested rice into the drum primary cleaning sieve to remove impurities such as straw, and the time is 5 seconds;
[0031] (2) remove the stone, put the rice screened in the step (1) into the stone remover to remove foreign matter such as soil, sandstone blocks mixed in the rice, the time is 5 seconds;
[0032] (3) magnetic separation, the paddy after stone removal in the step (2) is put into the magnetic separator to remove impurities such as iron filings, and the iron filings on the magnet of the magnetic separator should be removed before magnetic separation, with an impurity rate of 1%;
[0033] (4) dehumidification, the rice after the magnetic separation is spread in the drying room, and the thickness of the spread is 1cm, and the rice is repeatedly dried by hot air until the moisture content of the rice is 15%, and then the rice is cooled to room temperature;
[0034] (5) husking, put the dehumidified rice into the rice huller to remove the...
Embodiment 2
[0043] (1) Screening, put the harvested rice into the drum primary cleaning sieve to remove impurities such as straw, and the time is 7 seconds;
[0044] (2) remove the stone, put the rice screened in the step (1) into the stone remover to remove foreign objects such as soil, sand and stones mixed in the rice, and the time is 7 seconds;
[0045] (3) magnetic separation, the paddy after stone removal in step (2) is put into magnetic separator to remove impurities such as iron filings, before magnetic separation should remove the iron filings on the magnetic separator magnet, impurity rate 0.5%;
[0046] (4) dehumidification, the rice after the magnetic separation is spread in the drying room, the thickness of the spread is 1.3cm, and the hot air is used to dry the rice several times until the moisture content of the rice is 16%, and then the rice is cooled to room temperature;
[0047] (5) husking, put the dehumidified rice into the rice huller to remove the rice hulls, adjust ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] (1) Screening, put the harvested rice into the drum initial cleaning sieve to remove impurities such as straw, and the time is 10 seconds;
[0057] (2) Stone removal, put the rice screened in the step (1) into a stoner remover to remove foreign matter such as soil, sand and gravel blocks mixed in the rice, for 10 seconds;
[0058] (3) magnetic separation, the paddy after stone removal in the step (2) is put into magnetic separator to remove impurities such as iron filings, before magnetic separation should remove the iron filings on the magnetic separator magnet, impurity rate 0%;
[0059] (4) dehumidification, the rice after the magnetic separation is spread in the drying room, and the thickness of the spread is 1.5cm, and the rice is repeatedly dried by hot air until the moisture content of the rice is 17%, and then the rice is cooled to room temperature;
[0060] (5) husking, put the dehumidified rice into the rice huller to remove the rice hulls, adjust the gap betw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com