Method for analyzing microbial population function by using metagenome data
A metagenomic and microbial technology, applied in the field of microbial population function analysis using metagenomic data, can solve problems such as unreliability, increase the difficulty of integrated databases, and inability to splicing, and achieve improved utilization, excellent universality and information. comprehensive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] The construction of embodiment 1 microbial metagenomic reference database
[0064] In this embodiment, NCBI and KEGG are used as target biological information databases. Those skilled in the art can choose other biological information databases in the field to use the method of the present invention to carry out the construction of the microbial metagenomic reference database. scope of protection.
[0065] 1. Download the whole genome sequences of all microorganisms from different sources and different species in NCBI. The obtained data is a .fna file, which includes the NC number, base sequence, gi number and corresponding species information of the whole genome sequence.
[0066] 2. Download the .gbk annotation files of all microorganisms in NCBI, and extract the classification information of related species from the .gbk annotation files according to the NC number and species information obtained from the .fna file in the previous step, including phylum, class, ord...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Embodiment 2 Utilizes the method of metagenomic data to analyze microbial group function
[0074] 1. Sequence the metagenome of the microbial population to be tested, and perform quality control on the sequencing data: remove bases with a sequencing quality value less than 20, further remove sequences with reads less than 25bp in length, and remove reads derived from host DNA to reduce Errors that may occur during sample extraction and sequencing, so as to obtain high-quality whole-genome sequencing data.
[0075] 2. Calculation of species abundance: compare the microbial species data sets in the microbial metagenomic reference database constructed in Example 1 of the high-quality reads obtained in step 1, and perform species abundance calculations to obtain the Abundance values for all species. Based on the species abundance value, the difference analysis of various microbial compositions among different samples was carried out.
[0076] 3. Calculation of gene abun...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Example 3 Functional metagenomic analysis of microbial populations in intestinal contents of poultry with small sample size
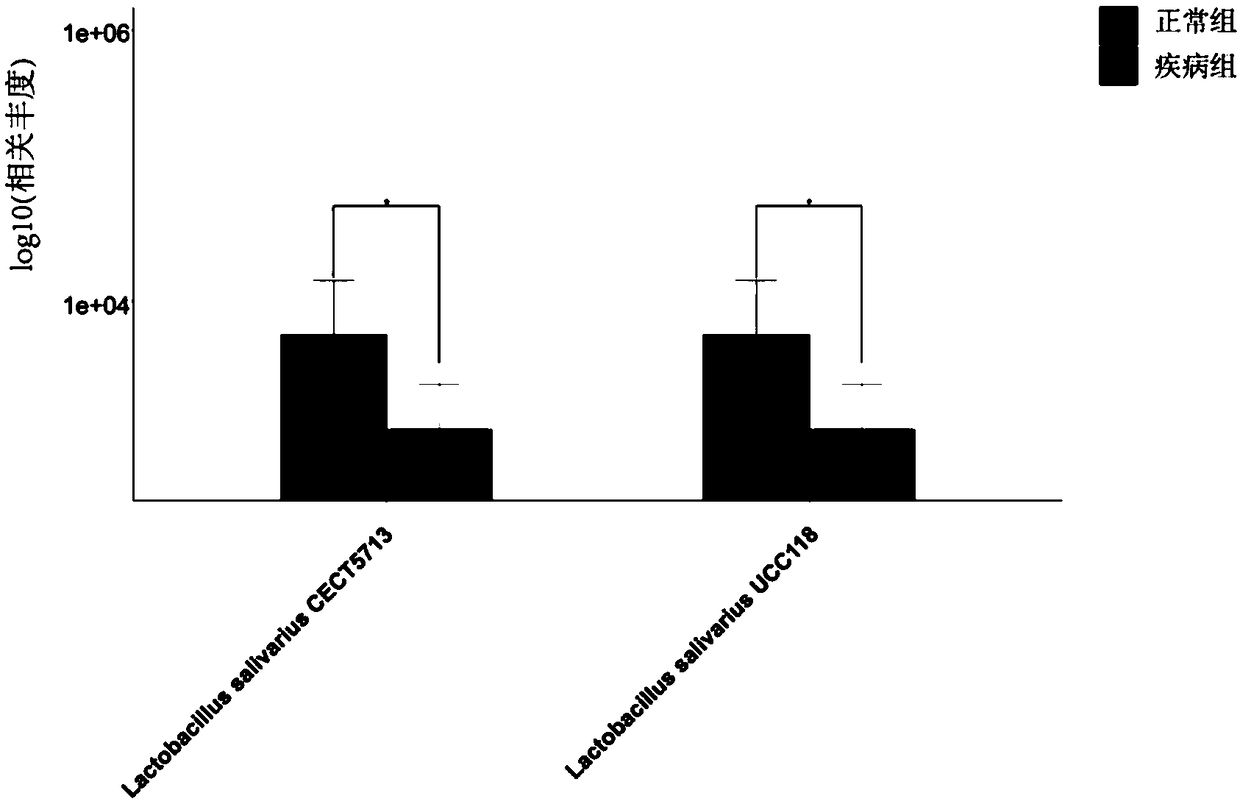
[0079] In this example, sequencing and data analysis were performed on the metagenomic data of intestinal contents of healthy and diseased poultry individuals with a small sample size. The experimental subjects used were 18 poultry individuals from the same industrial breeding factory, which were divided into two groups, with 9 samples in each group; the disease subject group was the disease individuals who had been diagnosed with poultry colibacillosis by veterinarians, and the control group The group is healthy individuals.
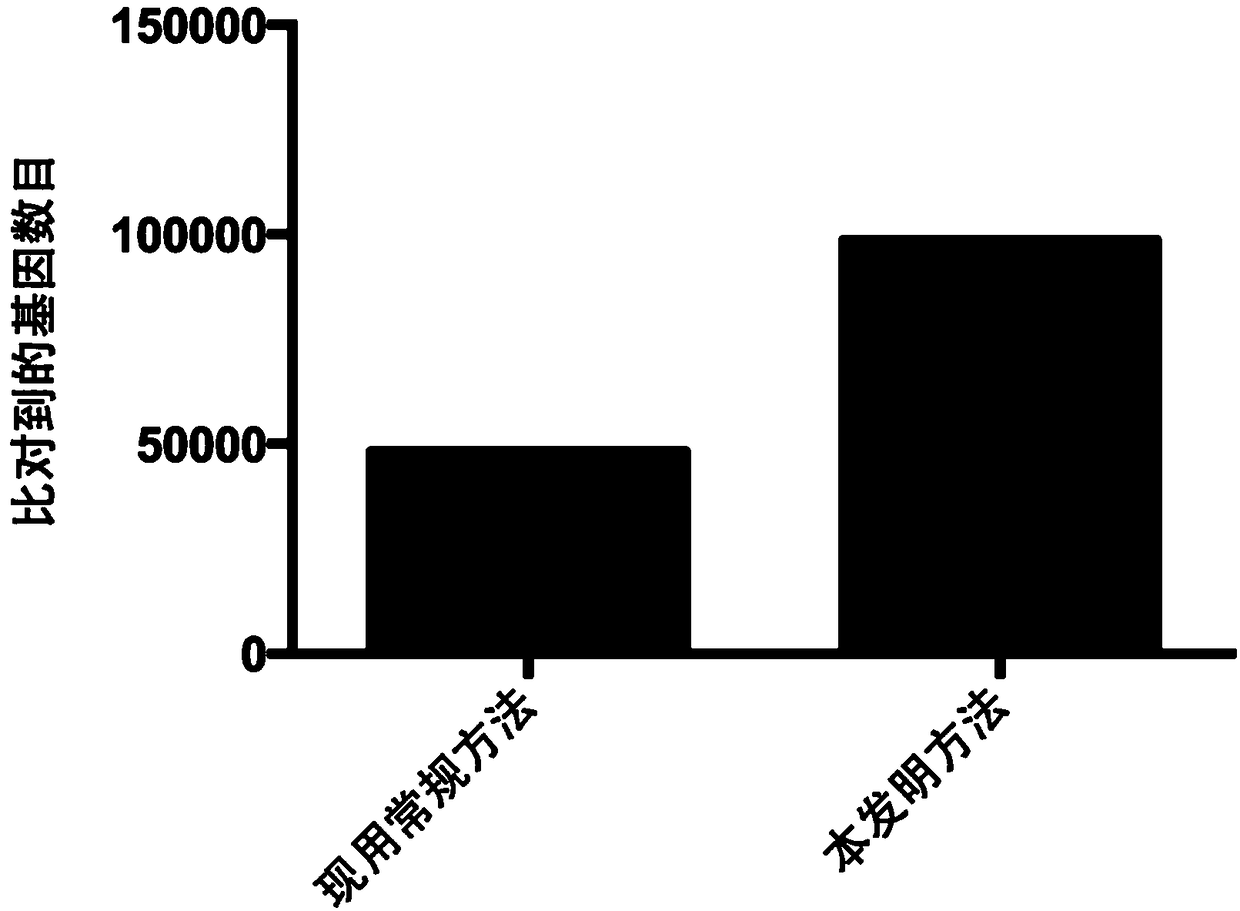
[0080] DNA extracted from the above 18 intestinal content samples was metagenomically sequenced by microbial whole-genome shotgun sequencing. Then use the method for analyzing the functions of microbial populations using metagenomic data established in Example 2 of the present invention and the existing conventional metho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com