Method for breeding high-temperature resistant strain of stropharia rugosoannulata
A technology of high-temperature resistant strains and Oleurotus giganta, applied in the methods of using microorganisms, methods based on microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of mycelium not resistant to high temperature, and the fruit bodies are easy to open umbrellas, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] The preparation and regeneration of protoplasts is the basis of protoplast breeding. The treatment conditions of lytic enzyme are the key to the preparation of protoplasts. If the concentration of lytic enzyme is too low, the release efficiency of protoplasts will be low; if the concentration of enzyme is too high, the bacteria will The silk cell wall is completely dissolved, and the cells are damaged and easily ruptured, which affects the regeneration ability of the protoplast. It has been found through many experiments that the optimal concentration of lysozyme for protoplast preparation is 1.5% (mass concentration).
[0039] The enzymatic hydrolysis temperature has a great influence on the yield of protoplasts, mainly in two aspects. On the one hand, with the increase of temperature, the reaction speed is accelerated, and the release of protoplasts is continuously increasing; on the other hand, the protein is gradually denatured as the temperature increases. The react...
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1: Breeding of Stropharia stropharia high temperature resistant strain
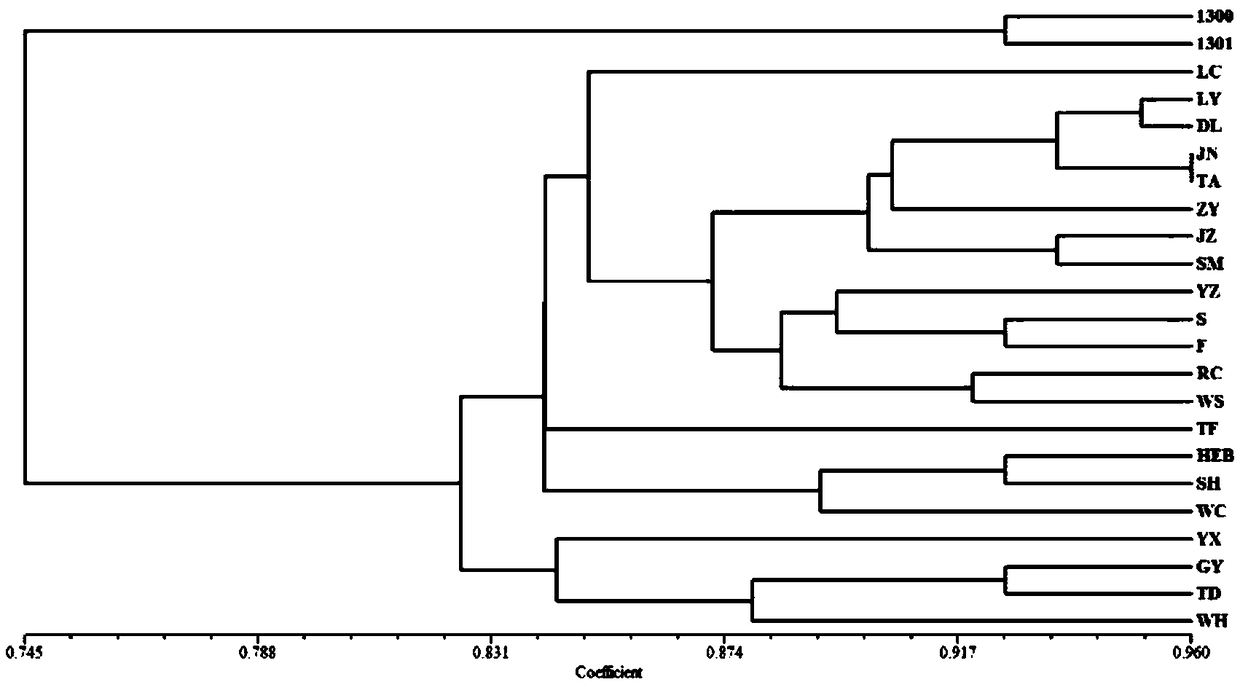
[0052] 1. Collect large stropharia from major cultivation areas of Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Taian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Sanming Fungi Research Institute, Sichuan Soil and Fertilizer Research Institute, Dalian in Liaoning, Suihua in Heilongjiang, Yuxi in Yunnan, and Jining in Shandong. A total of 23 Stropharia strains or fruiting bodies were obtained (Table 1). Among them, Mingda 128 (SM) and Stropharia 1 (TF) were the varieties certified by the state in 2008.
[0053] Table 1: Strain names and sources
[0054]
[0055] 2. Analysis of strain genetic diversity and kinship:
[0056] 2.1 Method:
[0057] 2.1.1 Strain activation, culture and DNA extraction
[0058] The collected strains and fruit bodies collected from the cultivation site were separated and purified by tissue culture, and then stored in a 4°C refr...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Embodiment 2: Breeding of Stropharia stropharia high temperature resistant strain
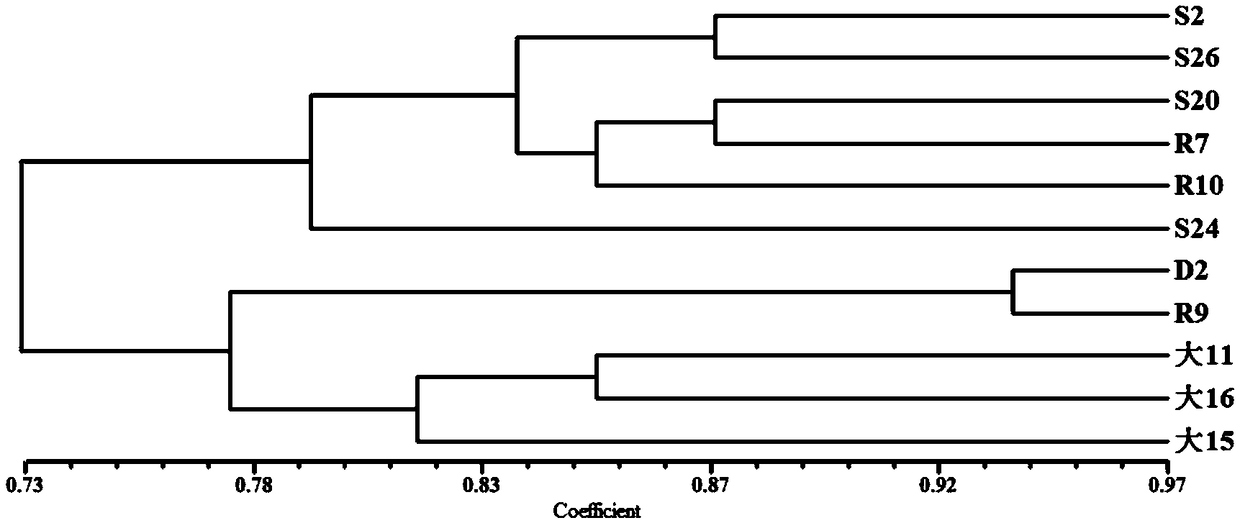
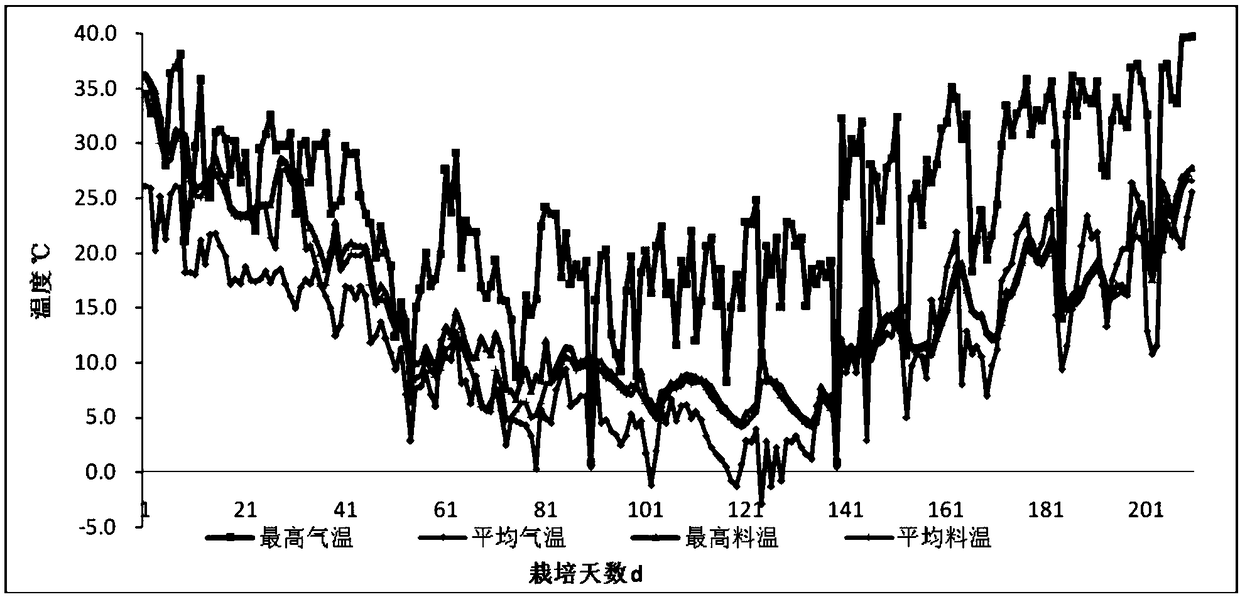
[0090] The difference with Example 1 is: after the protoplasts are prepared, the protoplasts are diluted to 10 5 cells / mL, gradient mutagenesis was carried out at a distance of 30cm with a stable 15W ultraviolet lamp, and the mutagenesis time was set to 30s. Then spread the protoplasts irradiated by ultraviolet rays on the regeneration medium, and recover at 26°C for 2 days, then adjust the temperature to 34°C to continue culturing. Eliminate the monokaryotic strains among them, and number the remaining strains according to 1st to 20th, and cultivate them at 26°C for 5 days, then adjust the temperature to 34°C, continue to cultivate for 5 days, and then adjust the temperature to 26°C to resume the culture for 5 days. The growth rate of each strain was recorded and compared, and 3 strains with fast mycelium growth, good growth and low heterogeneity after being cultured at 34°C were selec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com