Structure for improving thread bearing capacity by deformation compensation
A load-carrying capacity and deformation compensation technology, applied to transmission parts, belts/chains/gears, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as easy locking failure, improve load-carrying performance, avoid bad meshing state, and have high reliability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
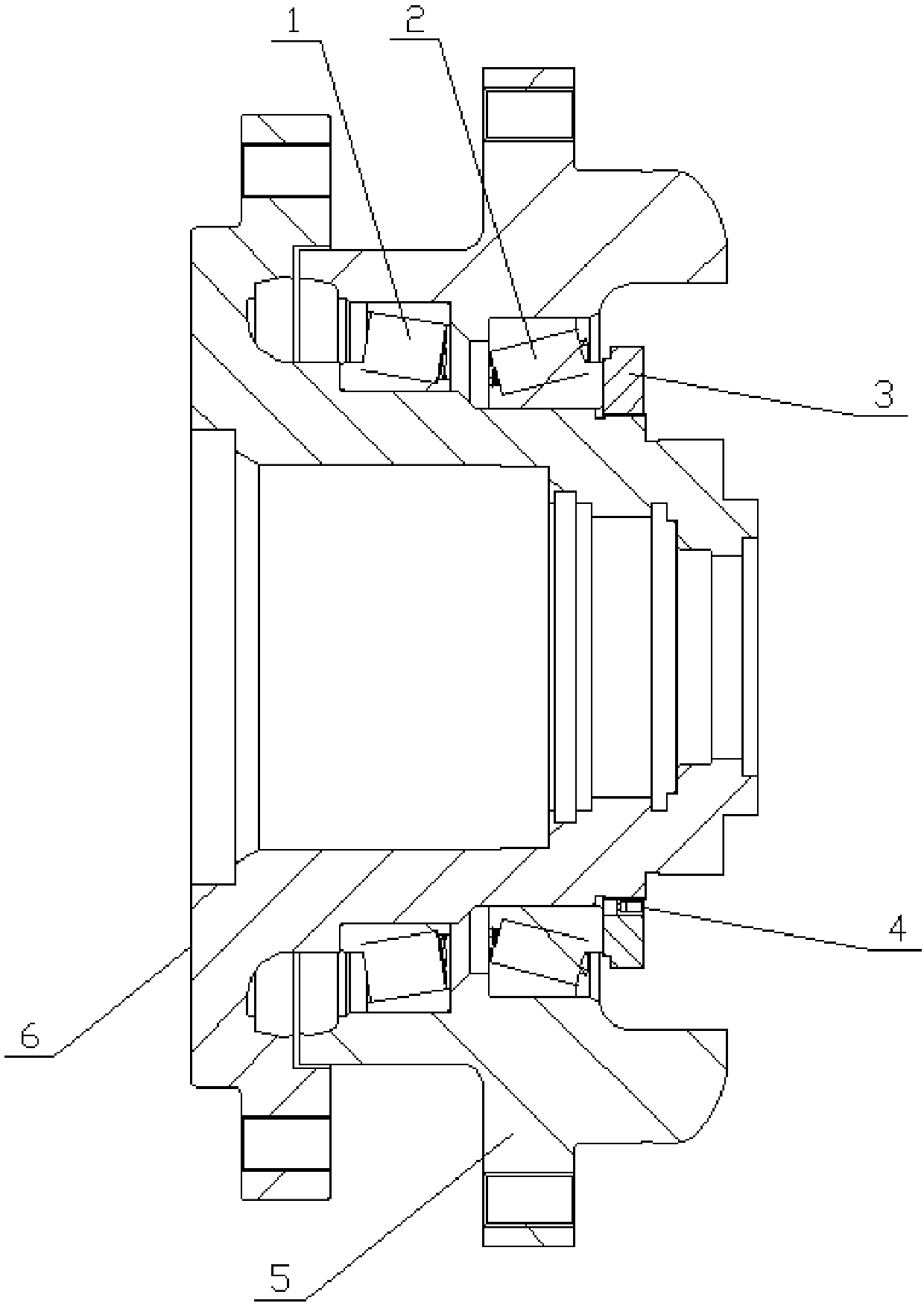
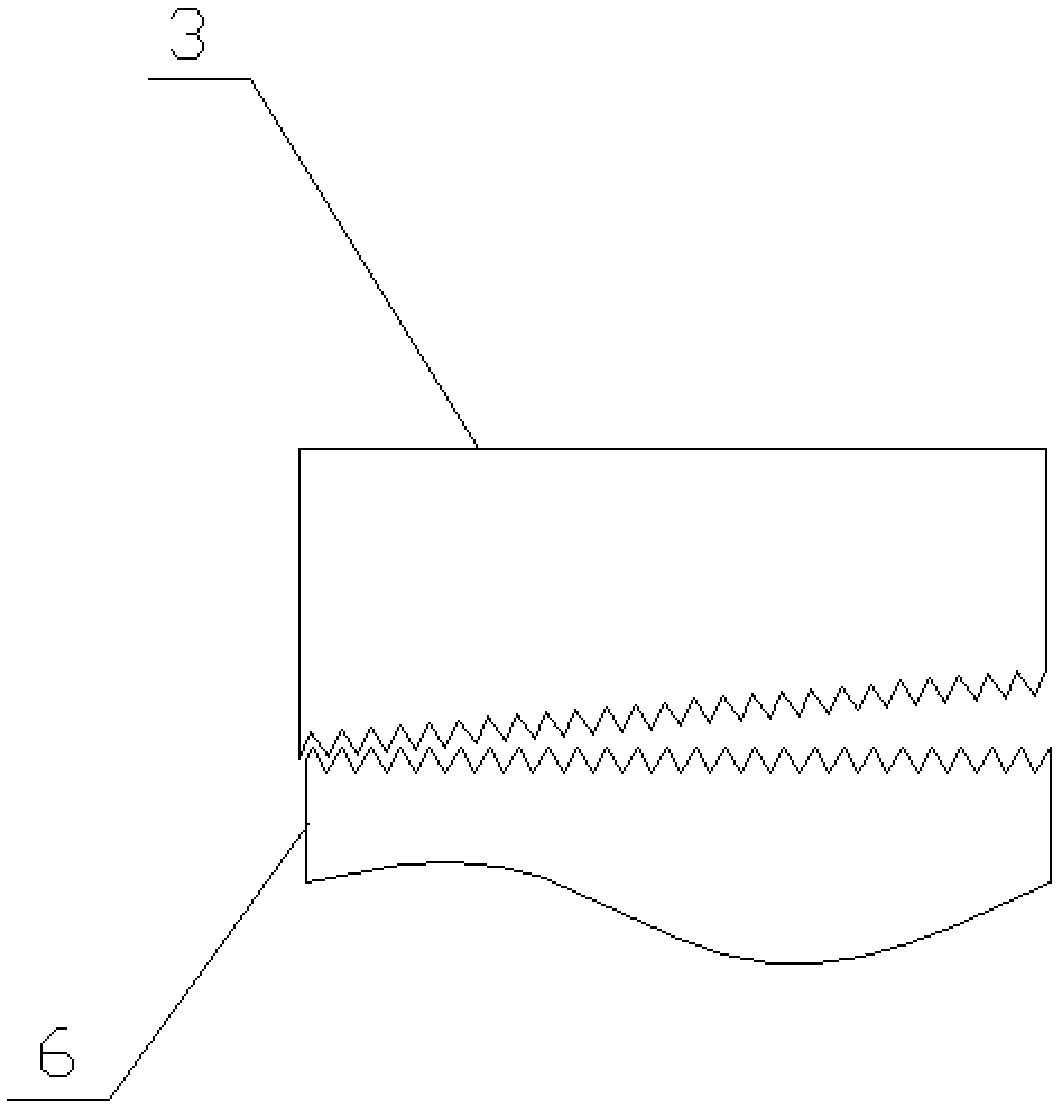
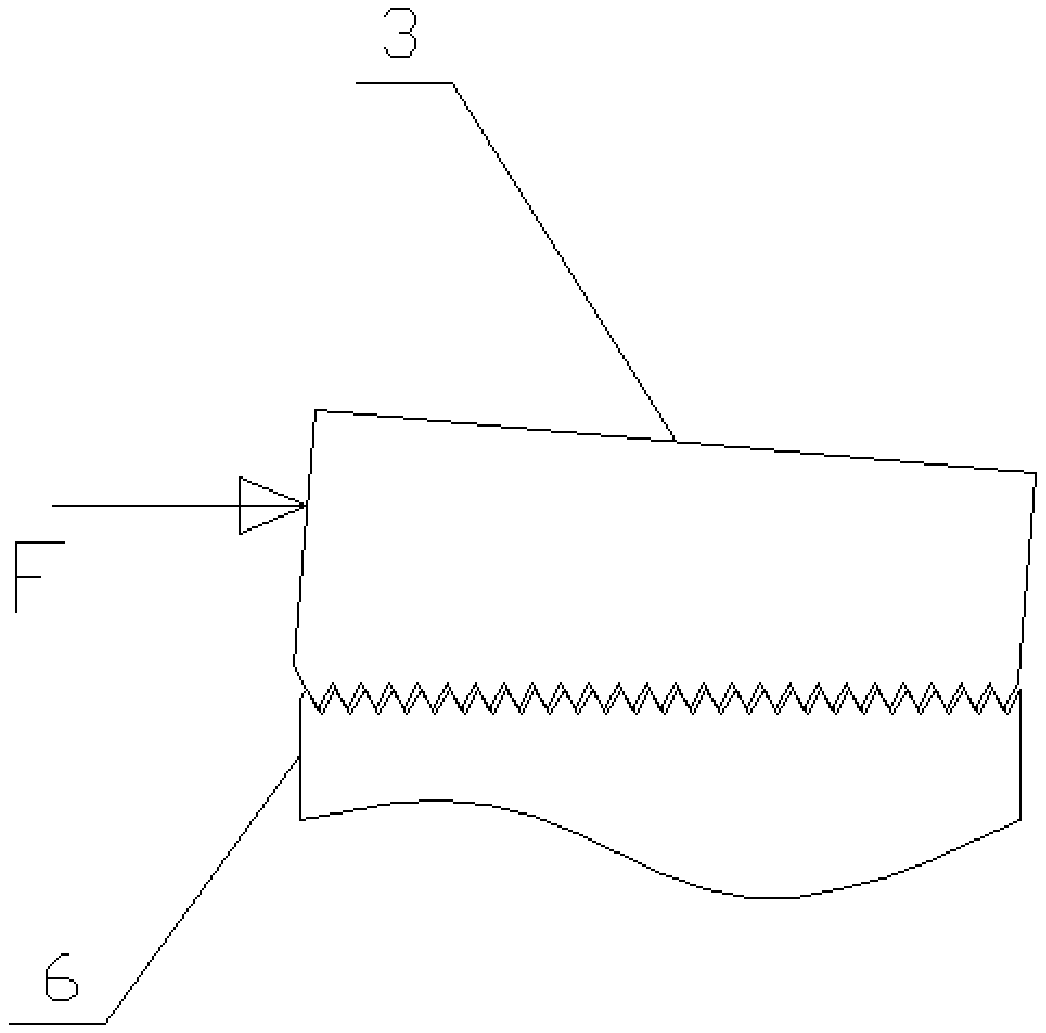
[0034] In the optional scheme of this embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment provides a structure for improving the thread bearing capacity through deformation compensation, including a fixed seat 6, a housing 5, a first bearing 1, a second bearing 2 and a lock nut 3; the first bearing 1 and the second bearing The two bearings 2 are all arranged between the fixed seat 6 and the housing 5; the lock nut 3 is threadedly connected to the end of the fixed seat 6; on the axial section of the lock nut 3, the extension direction of the internal thread of the lock nut 3 It forms an included angle with the extension direction of the external thread of the fixing seat 6 , and the opening direction of the included angle faces the outside of the locking nut 3 .
[0035] A lock nut 3 with an internal thread and a fixing seat 6 with an external thread form a thread pair, wherein the internal thread or / and the external thread are tapered threads with a certain taper.
...
Embodiment 2
[0053] In the optional solution of this embodiment, this embodiment provides a structure for improving the thread bearing capacity through deformation compensation, including a fixed seat 6, a housing 5, a first bearing 1, a second bearing 2 and a lock nut 3 ; The first bearing 1 and the second bearing 2 are both arranged between the fixed seat 6 and the housing 5; the lock nut 3 is threadedly connected to the end of the fixed seat 6; on the axial section of the lock nut 3, the lock nut The extending direction of the internal thread of 3 forms an included angle with the extending direction of the external thread of the fixing seat 6 , and the opening direction of the included angle faces the outside of the locking nut 3 .
[0054] In this embodiment, it can be understood that on the axial section of the locking nut 3 or on the axial section of the fixing seat 6, the extension direction of the inner thread of the locking nut 3 is in the same direction as the extension direction ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] In the optional solution of this embodiment, this embodiment provides a structure for improving the thread bearing capacity through deformation compensation, including a fixed seat 6, a housing 5, a first bearing 1, a second bearing 2 and a lock nut 3 ; The first bearing 1 and the second bearing 2 are both arranged between the fixed seat 6 and the housing 5; the lock nut 3 is threadedly connected to the end of the fixed seat 6; on the axial section of the lock nut 3, the lock nut The extending direction of the internal thread of 3 forms an included angle with the extending direction of the external thread of the fixing seat 6 , and the opening direction of the included angle faces the outside of the locking nut 3 .
[0069] In this embodiment, it can be understood that on the axial section of the locking nut 3 or on the axial section of the fixing seat 6, the extension direction of the inner thread of the locking nut 3 is in the same direction as the extension direction ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com