Method for using living seaweed to repair seawater nuclide strontium pollution
A seawater and living technology, applied in the field of remediation of nuclide pollution, can solve problems such as coastal water pollution, and achieve the effects of fast adsorption, low cost and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Detection and comparison of the ability of kelp and copper algae to enrich strontium under equilibrium state
[0025] Take kelp and copper algae seedlings with a length of about 10cm in a 1L beaker and place them at a temperature of 15°C and a light intensity of 40μmolphotons m -2 the s -1 , photoperiod 12h (L): 12h (D) in the incubator aerated culture; Fill in the beaker of the natural seawater that contains the strontium of different concentrations in the incubator, each group of experiments is set up 3 parallels, cultivate 7 days and take out appropriate amount of kelp and Copper algae sample, the content of strontium in the algal body under different conditions is detected through ICP-OES (see figure 1 );
[0026] Wherein, the final concentrations of strontium in seawater containing different concentrations of strontium are set to 7.4, 13.4 and 19.4mg / L, and the concentration of strontium in the natural seawater is 7.4mg / L.
[0027] See the test results figure 1...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2 Sea-tangle removes the water tank simulation experiment of strontium ion
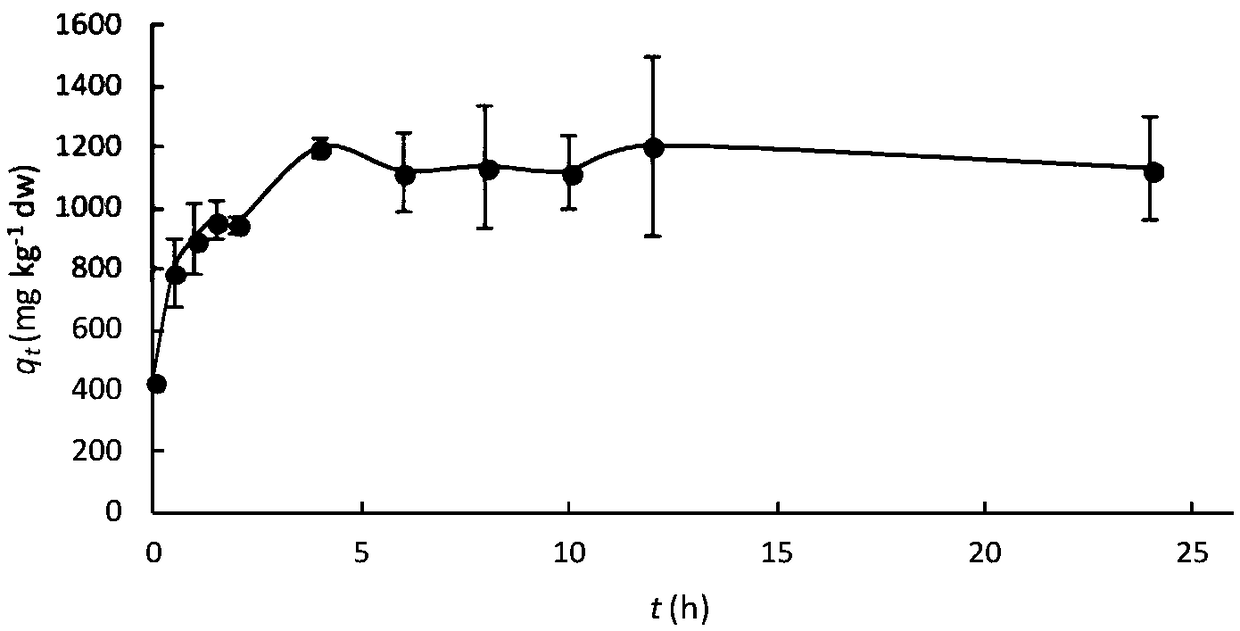
[0029] Add live kelp with a fresh weight of about 2.5kg in a 90L glass tank, and inflate it for cultivation. The final concentration of strontium in seawater is set to 24mg / L. Samples of algae and seawater are taken every 2h, and the content of strontium is detected respectively (see figure 2 with 3 ).
[0030] Depend on figure 2 with 3 The results showed that under artificial simulation conditions, the repair process of kelp to seawater nuclide strontium was basically completed in about 12 hours, after which the algae could be considered to be recycled, and fresh kelp could be added again until the strontium in seawater was completely removed.
[0031] At the same time, according to the above method, the content and enrichment factors (bioconcentration factors, BCFs) of strontium in other common and large biomass seaweeds in my country's coastal areas were compared, and it was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com