Online learning-based potential semantic cross-media hash retrieval method
A cross-media and cross-media technology, applied in the field of multimedia retrieval and pattern recognition, can solve the problems of speeding up the retrieval speed, the ability to distinguish the hash function, and the large training data set.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0062] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0063] The invention maps heterogeneous data to the same Hamming space, and only uses the new data to update the hash functions of different modalities when new data is generated; measures the data of different modalities in the learned shared Hamming subspace Similarity, to achieve the purpose of efficient cross-media retrieval.
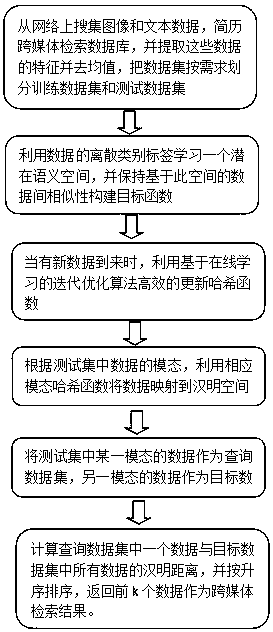
[0064] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the latent semantic cross-media hash retrieval method based on online learning in the present invention. A latent semantic cross-media hash retrieval method based on online learning proposed by the present invention includes the following steps.
[0065] Step 1: Collect image and text data from the Internet, build a database for cross-modal retrieval, extr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com