Fabric sensor for pressure distribution monitoring
A distributed monitoring and fabric sensor technology, applied in the field of fabric sensors, can solve problems such as increasing the manufacturing process, misalignment of upper and lower electrodes, and inability to conduct electrodes, etc., and achieve the effects of less manufacturing process, less damage, and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
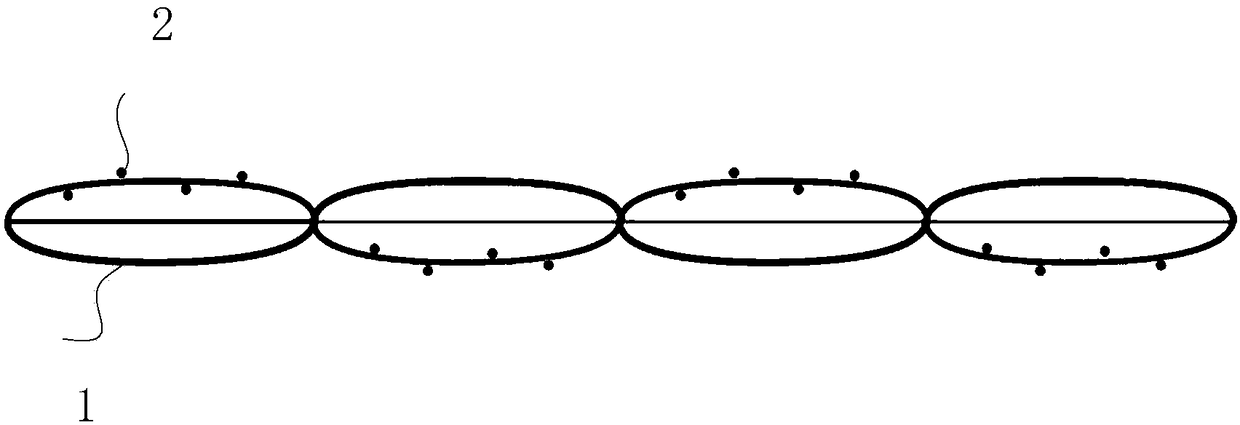
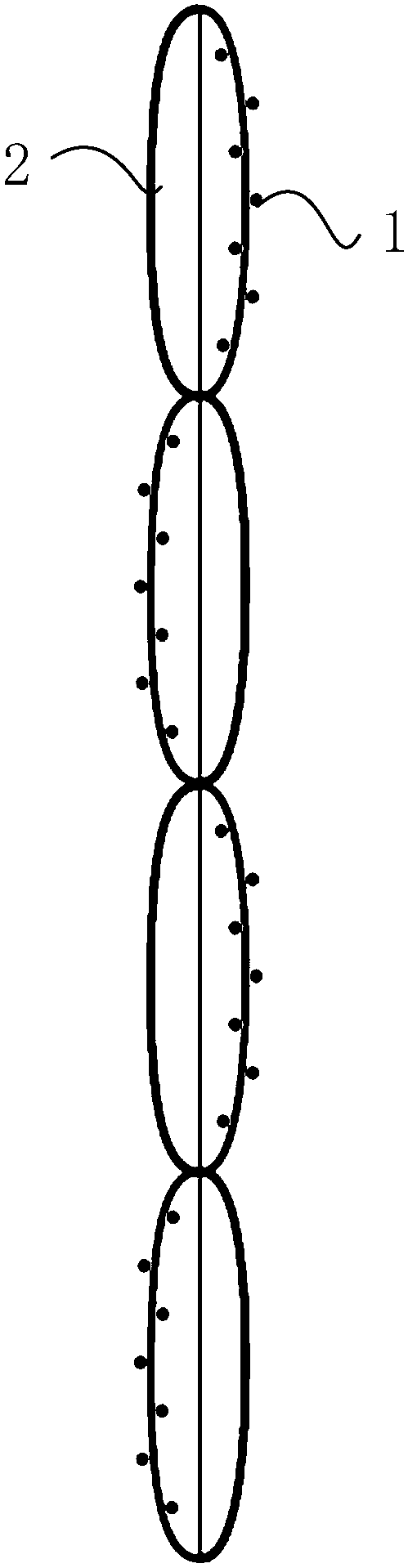
[0032] like figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 As shown, a fabric sensor for pressure distribution monitoring includes warp yarns 2 and weft yarns 1, the warp yarns 2 and weft yarns 1 are intersected and arranged, and the intersecting warp yarns 2 and weft yarns 1 constitute a sensing area 3 and a connecting area 4, The connection area 4 is positioned at the side of the induction area 3, and the head end of each row of warp yarns 2 in the connection area 4 is connected to the power supply end, and the head end of each row of weft yarns 1 in the connection area 4 is connected to the collection end. Area 3 is composed of staggered sensing units, and each sensing unit is arranged in a sandwich structure, wherein the upper layer and the lower layer are the positive electrode layer and the base layer respectively, and the middle layer is a conductive layer, and the positive electrode layer and the negative electrode layer are composed of several conductive layers. yarn and non-con...
Embodiment 1
[0035] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, as Figure 4 As shown, make it into 16*16 (row*column) samples for corresponding point pressure test. In the present invention, 70D silver-plated conductive yarn is used as the conductive weft yarn and conductive warp yarn in the upper and lower layers, and the twisted resistance yarn synthesized by 150D bright polyester yarn core and 20D nylon carbon black conductive yarn (winding yarn) is used as the middle layer resistance yarn , 70D polyester filament is used as the non-conductive warp yarn in each layer, and 150D polyester filament is used as the non-conductive weft yarn in each layer.
[0036] like Figure 5 Shown, adopt embodiment to combine the structure of embodiment again, to Figure 4 The point A on the sample surface in is subjected to press sampling, as shown in Table 1:
[0037] Table 1:
[0038]
[0039]
[0040] like Image 6 shown, yes Figure 4 Point B of the sample surface in the sample is s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com