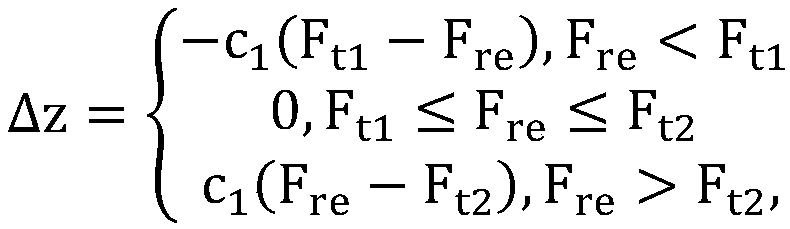Method for adjusting position and pose of capsule robot based on force feedback
A technology of capsule robot and posture adjustment, applied in medical science, endoscopy, diagnosis, etc., can solve problems such as loss of capsule control, damage to gastrointestinal tract, loss of magnetic connection, etc., to achieve smooth diagnosis process, relieve pain, The effect of avoiding damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A method for adjusting the pose of a capsule robot based on force feedback, the specific process is:
[0039] Step 1. Embedding a force sensing device in the capsule robot;
[0040] Step 2. Use the force sensing device embedded in the capsule robot to sense the normal force at the force sensing point along the cylindrical surface of the capsule robot when the robot contacts the gastrointestinal wall;
[0041] Step 3: Adjust the pose of the capsule robot according to the normal force and the set force threshold range, so that the normal force of the capsule robot is always kept within the force threshold range, and the force threshold range is [F t1 , F t2 ], where F t1 When the relative distance between the capsule robot and the guiding magnet is relatively large, the force threshold to ensure that the magnetic interaction will not be disconnected; F t2 When the relative distance between the capsule robot and the guiding magnet is small, the force threshold value tha...
Embodiment 2
[0044] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the method for adjusting the pose of the capsule robot is:
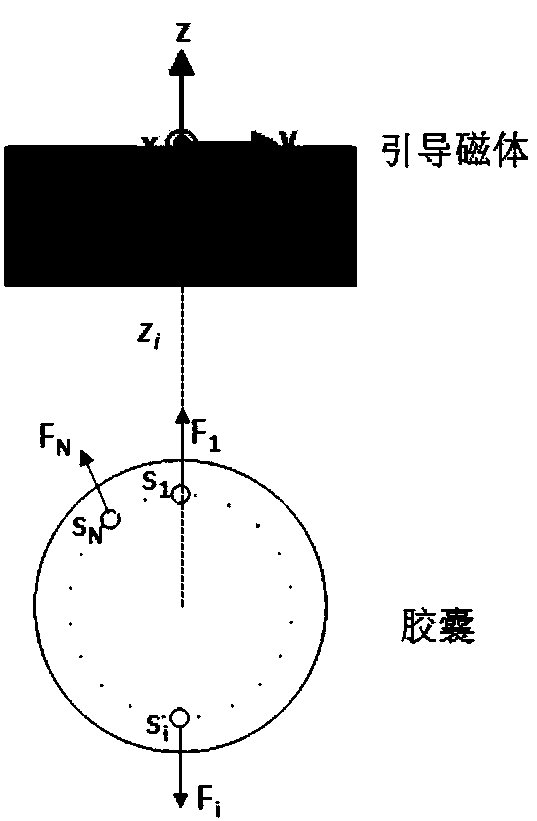
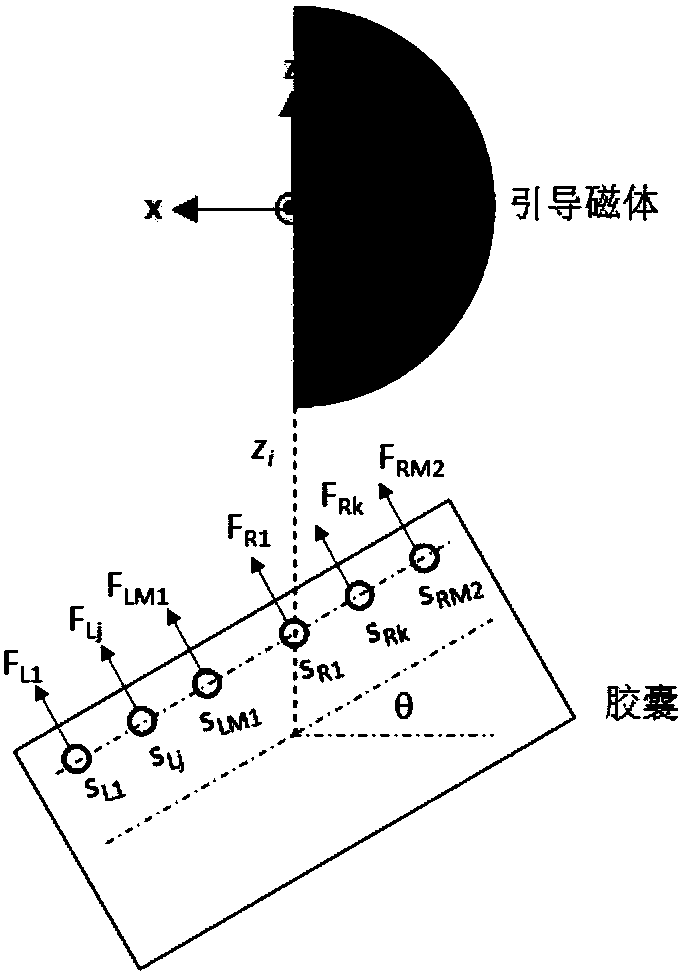
[0045] If no two force-sensing points are distributed along a straight line parallel to the axis of the capsule, the force-sensing points are considered to be distributed along the circumference, such as figure 1 As shown, the adjustment method based on the output information of the force sensing point distributed in the circumferential direction: If the maximum value of the normal force of the sensing point F re less than F t1 , then adjust the relative distance between the guiding magnet and the capsule robot to reduce it to ensure the magnetic interaction; if F re greater than F t2 , then adjust the relative distance between the guiding magnet and the capsule robot to increase it to ensure that the capsule robot will not squeeze and damage the gastrointestinal tissue; if F re in F t1 and F t2 , the relative distance between the guiding magnet and the capsule robot is not a...
Embodiment 3
[0050] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the method for adjusting the pose of the capsule robot is:
[0051] If there are no two force-sensing points distributed along a straight line parallel to the axial direction of the capsule, use the adjustment method based on the output information of the force-sensing points distributed in the circumferential direction, such as figure 1 As shown, there are N force-sensing points s distributed along the circumference of the capsule i {i=1, 2, ..., N}, where the reaction force F of the gastrointestinal wall that the capsule robot receives at this point can be sensed i {i=1, 2, ..., N}, F re is the maximum value of the force sensing output, that is, F re =max{F i , i=1, 2, . . . , N}. z i is the distance between the current guiding magnet and the capsule, according to F re , which controls the distance z′ between the magnet and the capsule in the next step of the original path planning of the capsule i+1 Based on the change Δz of , a n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com