A method for cell surface modification based on oxidative self-polymerization of plant polyphenol tannic acid
A polyphenol tannic acid, cell surface technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of irreversible experimental results, long experimental period of physical and chemical methods, low experimental safety factor, etc., and achieve the effects of mild experimental conditions, simple operation and avoiding pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In this embodiment, the method of modifying the cell surface based on the oxidative self-polymerization of plant polyphenol tannic acid prepared is as follows:
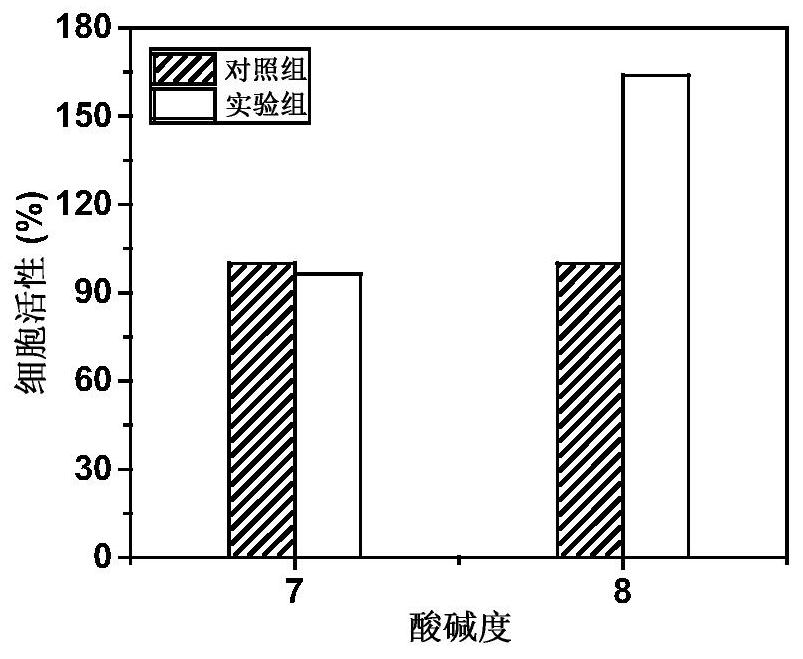
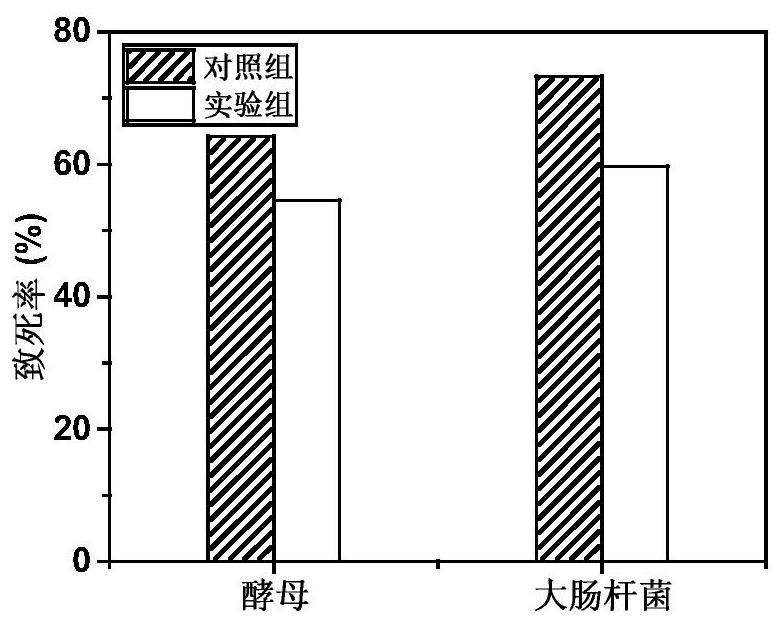
[0028] Select yeast as an illustration example, collect the Yarrowia lipolytica cells cultivated to the logarithmic phase with sterile centrifugal acid centrifugation, divide into different concentrations of tannic acid solutions prepared with different pH PBS solutions, shake on the shaker The reaction causes tannic acid to oxidize and self-polymerize on the cell surface to form a tight protective shell.
[0029] Specific steps include:
[0030] 1. Prepare PBS solution with pH=6.0~8.0. Liquid A: 0.05mol / LNa 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O solution, weigh 17.907 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, and fully dissolve it with 1000 ml of distilled water. Liquid B: 0.05mol / LKH 2 PO 4 Solution, weigh potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 6.8045g, fully dissolve with 1000ml distilled water. A and B liquids are mixed in...
Embodiment 2
[0037] In this embodiment, the method of modifying the cell surface based on the oxidative self-polymerization of plant polyphenol tannic acid prepared is as follows:
[0038] Centrifuge the Yarrowia lipolytica cultured to the logarithmic phase and collect it with a sterile centrifuge tube, divide it into the tannic acid solution prepared with PBS buffer, and shake it on the shaker to make the tannic acid on the cell surface Oxidative self-polymerization occurs to form a tight protective shell.
[0039] Specifically include the following steps:
[0040] 1. Transfer Yarrowia lipolytica ATCC201249 from the storage tube to the YPD solid medium, activate by streaking, pick a single colony and insert it into the YPD test tube for activation for 6-24 hours, then transfer to the YPD shake flask, at 30° C. Cultivate at 225rpm to OD=0.8~1.0, and collect bacteria by centrifugation at 3000rpm.
[0041] 2. Configure 95% 0.05mol / L Na in PBS solution with pH=8.04 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O and 5...
Embodiment 3
[0047] In this embodiment, the method of modifying the cell surface based on the oxidative self-polymerization of plant polyphenol tannic acid prepared is as follows:
[0048] The Escherichia coli cultured to the logarithmic phase was collected by centrifugation in a sterile centrifuge tube, divided into tannic acid solution prepared with PBS solution, and reacted in a shaking table to make tannic acid oxidize and self-polymerize on the cell surface to form A tight protective shell.
[0049] Specifically include the following steps:
[0050] 1. Transfer Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 from the storage tube to the LB solid medium, activate by streaking, pick a single colony and insert it into the LB test tube for activation for 6-12 hours, then transfer to the LB shaker flask, at 37°C, Cultivate at 225rpm to OD=0.8~1.0, and collect the bacteria by centrifugation at 2500rpm.
[0051] 2. Configure 95% 0.05mol / L Na in PBS solution with pH=8.04 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O and 5% of 0.05mol / L ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com