An empirical generalization method for multi-parameter equivalent roughness of flow resistance around piers
A bypass resistance, multi-parameter technology, applied in the field of generalization, can solve the problems of different submerged water depths, difficult to calculate the total bypass resistance coefficient of bridge piers, and differences in water flow velocity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
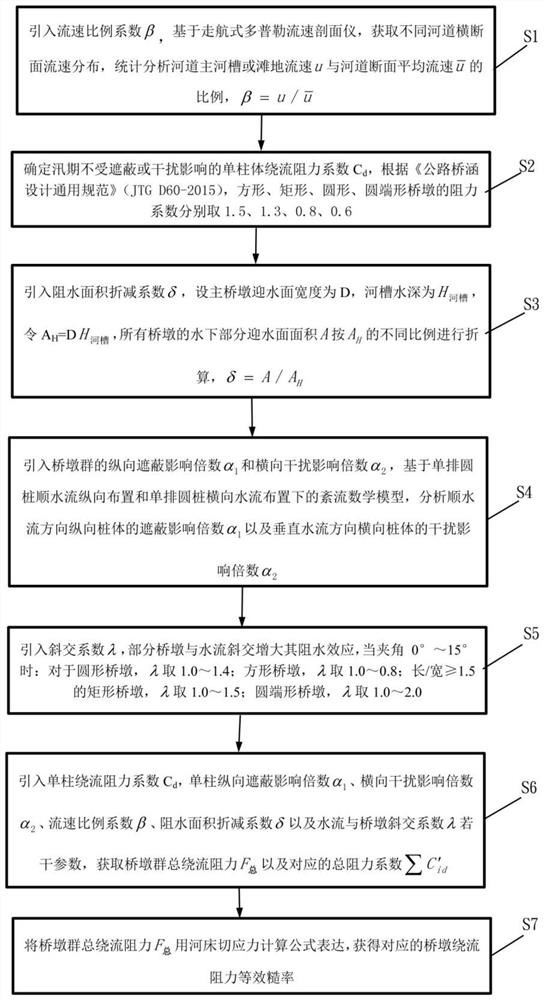
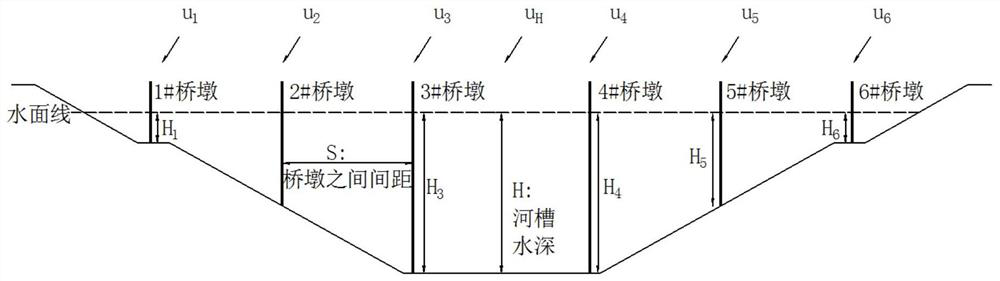
[0037] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the multi-parameter bridge pier flow resistance equivalent roughness empirical generalization method, the equivalent roughness generalization method includes:
[0038] S1: Introduce the flow velocity proportional coefficient β, based on the traveling Doppler velocity profiler, obtain the flow velocity distribution in different river cross-sections, and statistically analyze the flow velocity u of the main channel or beach of the river and the average flow velocity of the river section proportion,
[0039] S2: Determine the resistance coefficient C of the flow around a single cylinder that is not affected by shading or interference during the flood season d , according to the "General Code for Design of Highway Bridges and Culverts" (JTG D60-2015), the resistance coefficients of squa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com