A zero voltage switch boost circuit and its control method
A zero-voltage switching, current detection circuit technology, applied in control/regulation systems, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as large switching loss and reverse recovery, and achieve high light-load efficiency, simple application, Achieve the effect of light-load frequency reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
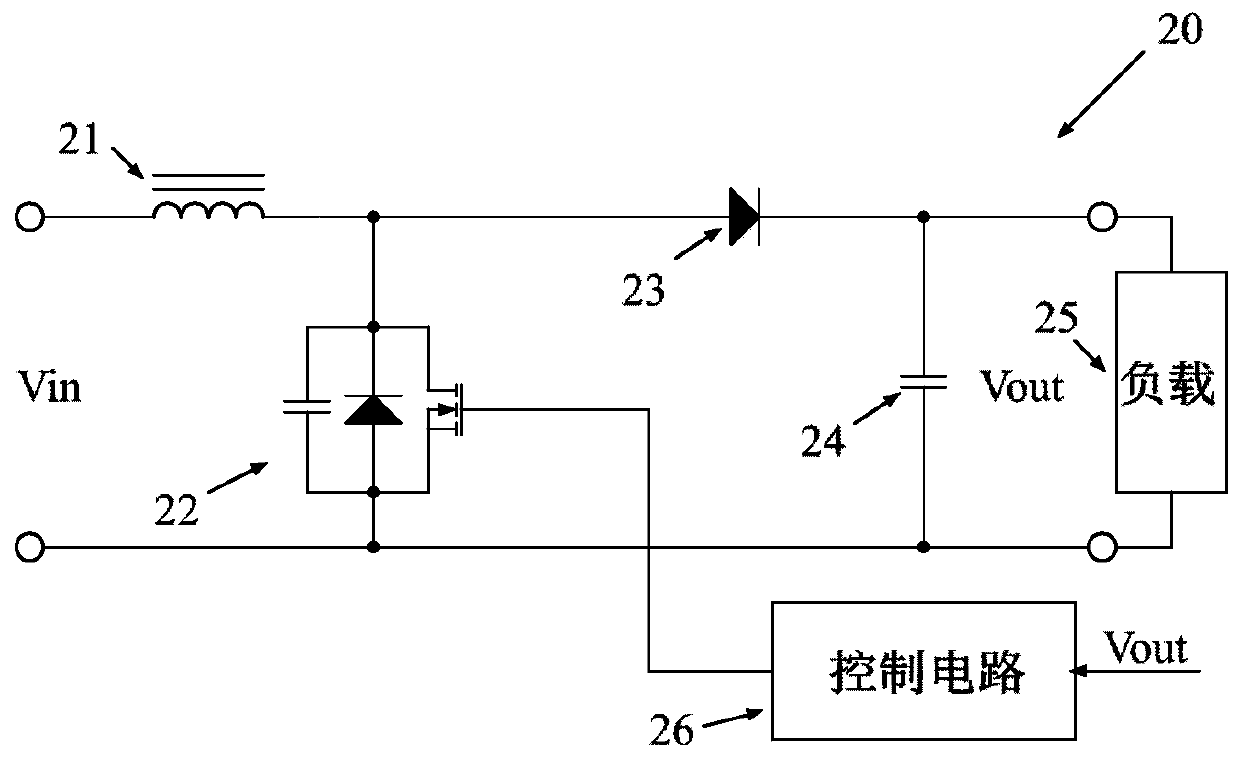
[0044] image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram 30 of the first embodiment of the zero voltage switch Boost circuit according to the present invention, similar to the traditional Boost circuit, the zero voltage switch Boost circuit 30 includes a boost inductor 31, a main switch tube 32, a rectifier diode 33, an output filter The capacitor 34 and the control circuit 36 output the output voltage Vout at both ends of the filter capacitor 34 to supply power to the load 35; the control circuit 36 generates a feedback voltage signal according to the output voltage Vout and adjusts the duty cycle of the main switching tube 32 according to the feedback voltage signal; One end of the boost inductor 31 is connected to the input voltage +, the other end of the boost inductor 31 is connected to the drain of the main switching tube 32, the source of the main switching tube 32 is connected to the input voltage -, and the gate of the main switching tube 32 is connected to the control circuit...
no. 2 example
[0064] Figure 8-1 The schematic diagram and control block diagram of the second embodiment of the present invention are shown. The difference from the first embodiment is that a CS current detection circuit is added between the source of the main switch 32 and the control circuit.
[0065] This embodiment is mainly embodied in the light load control, sampling the output voltage Vout to control the stability of the output voltage, and sampling the peak current of the main switching tube to realize the light load control. When the load decreases, the peak current of the main switching tube decreases, and when the load decreases to a certain extent, the circuit enters the DCM mode to work. When the peak current decreases to a certain level, keep the minimum peak current from the control and no longer decrease, that is, the minimum peak current control, that is to say, when the load continues to decrease, the output of the converter is stabilized by reducing the operating frequen...
no. 3 example
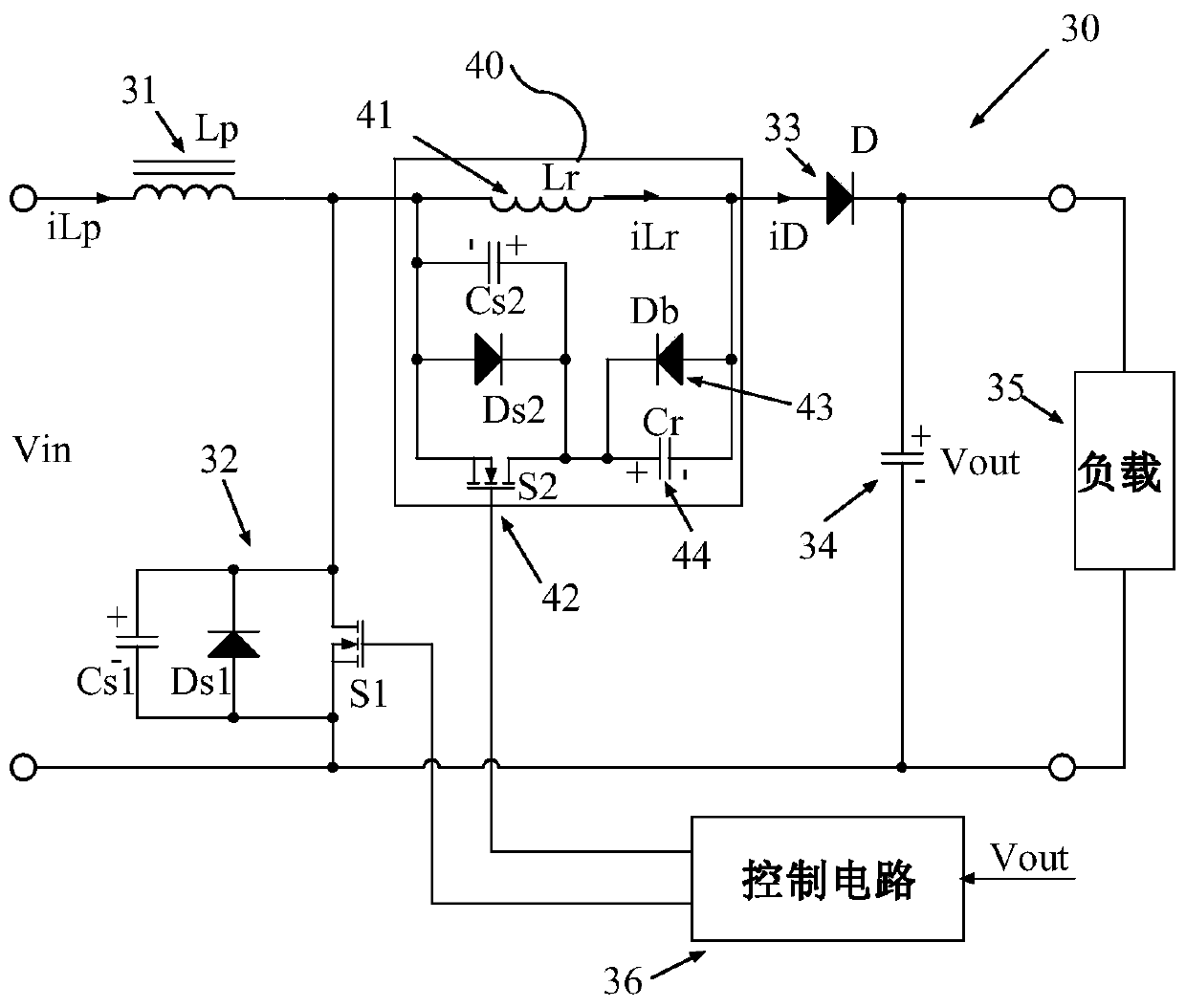
[0067] Figure 9It shows the principle diagram according to the third embodiment of the present invention, that is to say, the zero-voltage switching circuit 40 of the present invention is also applicable to the Boost circuit of synchronous rectification, and the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the rectifier diode 33 is replaced by synchronous rectification Switch tube 81, the input terminal of the zero voltage switching circuit 40 is connected to the drain of the main switch tube 32, the output terminal is connected to the source of the synchronous rectification switch tube 81, and the drain of the synchronous rectification switch tube 81 is connected to the output filter capacitor 34 positive. In addition, this embodiment also includes a control circuit 86. The control circuit 86 outputs three-way driving signals to control the switching of the main switching tube 32, the auxiliary switching tube 42, and the synchronous rectification switching tube 81, wherein the main ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com