Device and method for automatic balancing for unbalance faults of large rigid rotor
A rigid rotor, balance failure technology, applied in measurement devices, static/dynamic balance tests, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective real-time rotor, balance, etc., achieve precise position control, avoid the falling of the car, and achieve position control Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] combine Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 , a large-scale rigid rotor unbalance fault automatic balancing device in this embodiment includes a rotor 1 installed between two bearing brackets 2, and track mechanisms 4 respectively arranged on the vertical surfaces at both ends of the rotor 1.
[0044] The two bearing brackets 2 are symmetrically arranged to carry the rotor 1. The rotor 1 can be driven by a structure such as a motor. The specific driving form is selected according to the actual use, and this embodiment does not make specific requirements.
[0045]This embodiment is to dynamically balance the rotor 1 on both sides, including the track mechanism 4 arranged on the vertical surfaces at both ends of the rotor 1. The track mechanism 4 is arranged in a circular shape and must be coaxial with the rotor 1 to ensure that it can be used in the later stage. Provide an exact location.
[0046] The track mechanism 4 is vertically arranged to ensure that the counterweight trolley th...
Embodiment 2
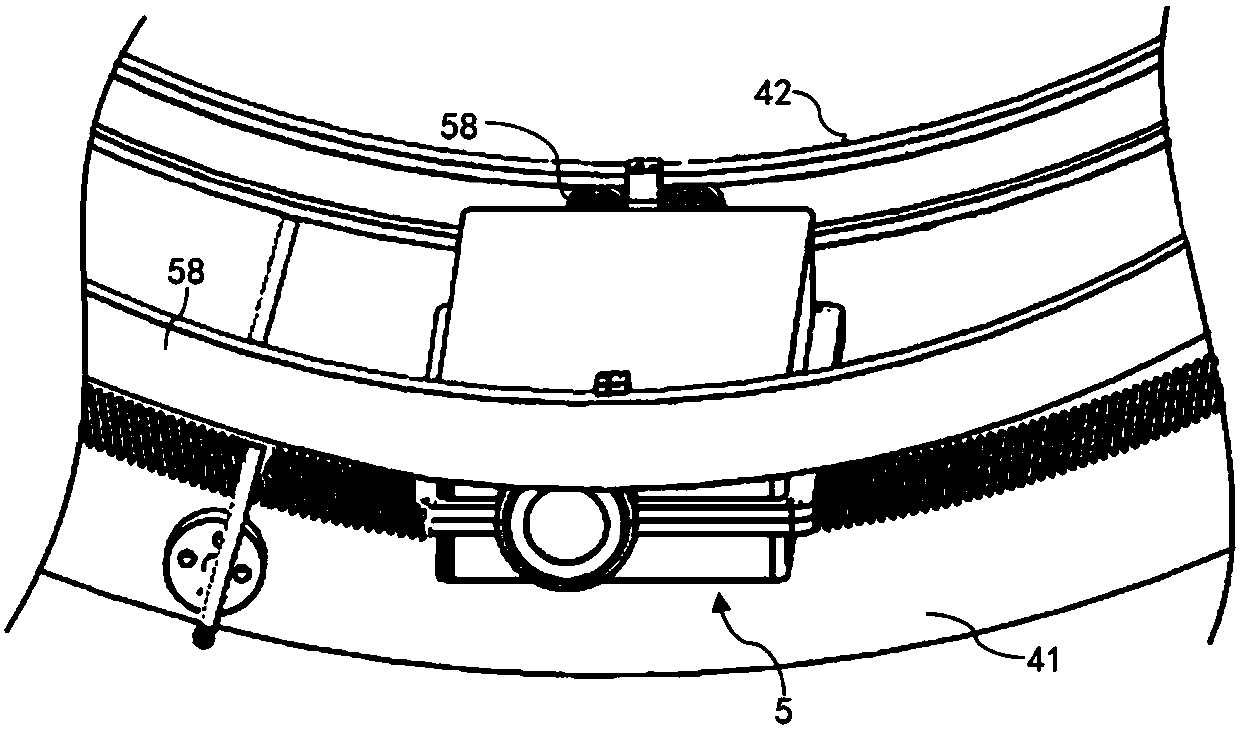
[0056] combine figure 2 , a large-scale rigid rotor unbalance fault automatic balancing device of the present embodiment, as a structural form of the counterweight trolley 5, it includes a driving power supply, a trolley housing 51, a travel gear 55 and a motor 52, and the travel gear 55 passes through the rotating shaft 57 is connected with the bearing at two ends of the trolley housing 51, and can rotate freely. The driving power supplies power to the motor 52 to drive the travel gear 55 to rotate. Since the travel gear 55 cooperates with the internal teeth of the track ring gear 41, the motion accuracy can be guaranteed.
[0057] Motor 52 is a stepper motor, in order to drive counterweight trolley 5 motions, it has multiple driving modes. For example, a pulley is connected to the rotating shaft of the motor 52, and the corresponding pulley is configured on the rotating shaft 57. The two pulleys are connected by a transmission belt, so that the driving force of the motor c...
Embodiment 3
[0061] In this embodiment, a structure in which the counterweight trolley 5 is driven is preferred. In this embodiment, a transmission gear 56 is connected to the rotating shaft of the motor 52 , and the transmission gear 56 meshes with the travel gear 55 .
[0062] A pair of bearing housings 54 are fixed on the trolley housing 51 , and the central axis of the transmission gear 56 is mounted on the bearing housings 54 . In this embodiment, a shaft coupling 53 is provided on the rotating shaft of the motor 52 , and the other end of the shaft coupling 53 is connected to the central shaft of the transmission gear 56 .
[0063] Because the traveling gear 55 meshes with the track ring gear 41 and the transmission gear 56 at the same time, when the stepper motor drives the transmission gear 56 to rotate, the travel gear 55 rotates, and then the counterweight trolley 5 can move in the track ring gear 41 .
[0064] Through gear transmission, compared with chain wheel and pulley transm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com